An infrared laser beam detector
An infrared laser and detector technology, applied in instruments, alarms, anti-theft alarms, etc., can solve the problems of reduced debugging work efficiency, weak penetration ability, adjustment of up and down direction and adjustment of left and right direction interference, etc., to achieve debugging work efficiency Elevation, light path control is easy to control, and the effect of improving the shooting distance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
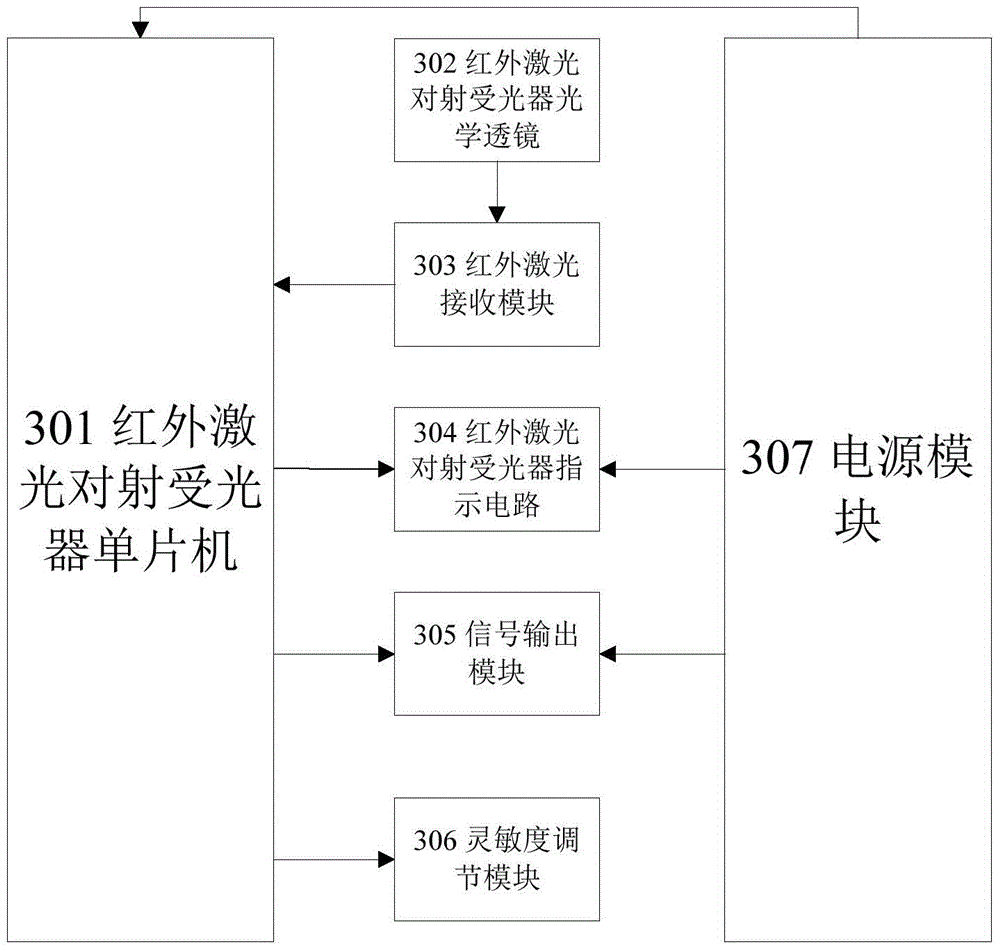
[0032] Such as figure 1 As shown, the infrared laser on-shooting detector of the present invention includes an infrared laser on-shooting light projector 101 and an infrared laser on-shooting light receiver 102; Laser beam with adjustable beam direction. The infrared laser beam receiving device 102 receives the laser beam emitted by the infrared laser beam projector 101, and the infrared laser beam receiver microcontroller counts the lost laser beam pulses.
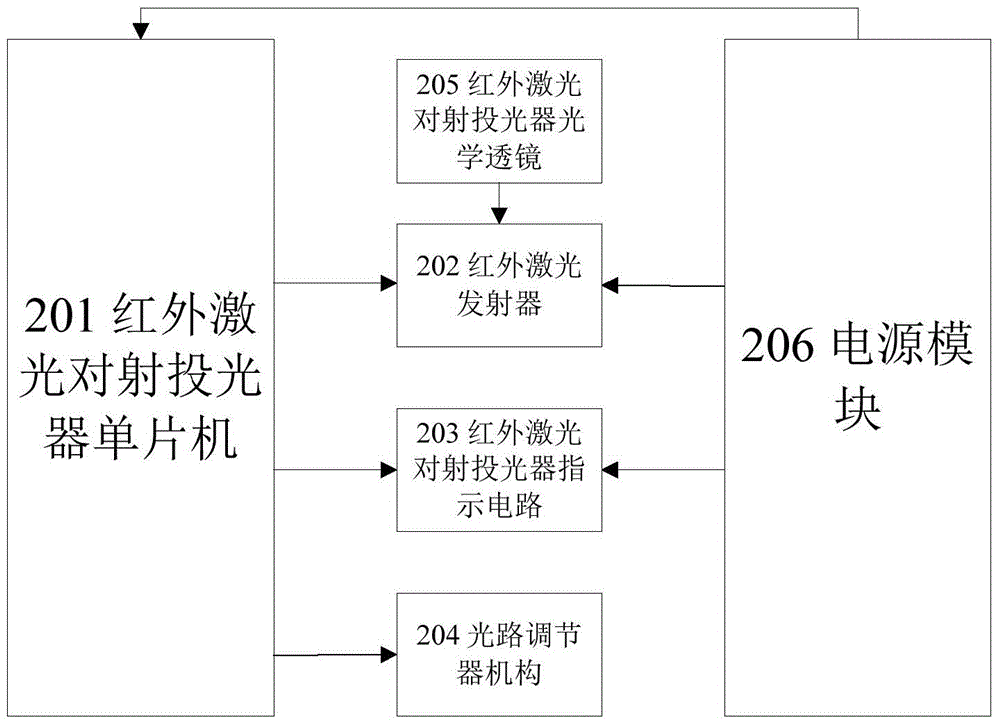
[0033] Such as figure 2 As shown, the infrared laser projector 101 is composed of an infrared laser projector microcontroller 201, an infrared laser transmitter 202, an infrared laser projector indicating circuit 203, an optical path adjustment mechanism 204, an infrared laser projector optical lens 205, and a power supply module 206. composition;
[0034] Static connection: the single-chip microcomputer 201 of the infrared laser projector, the indication circuit 203 of the infrared laser projector, and the power supp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com