A salt-free and low-alkali cycle dyeing process for cellulose fibers
A cellulose fiber and alkali recycling technology, applied in the field of textile dyeing, can solve the problems of not being suitable for large-scale production, high chroma of dyeing residue, difficult to treat wastewater, etc., achieving high success rate, good cationization effect, and dye consumption. reduced effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0079] Cellulose fiber dyeing process:
[0080] A salt-free and low-alkali cycle dyeing process for cellulose fibers, comprising the following process steps:
[0081] A. Cellulose fiber modification treatment
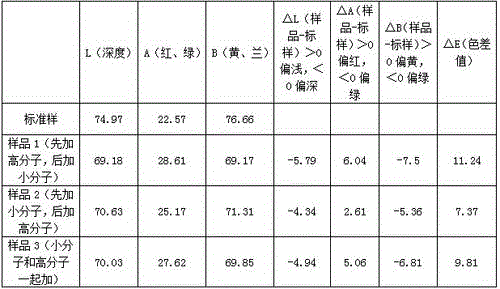
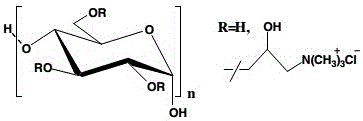
[0082] Put the cellulose fiber into the container, add water to the container, and then use two kinds of quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifiers, modifier A and modifier B, to modify the cellulose fiber, and obtain Modified cellulose fiber; the modifier A is a small molecule quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifier, and the modifier B is a high molecular weight quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifier;
[0083] B. Washing treatment
[0084] Washing the modified cellulose fibers obtained through the modification treatment in step A;
[0085] C. Cyclic dyeing
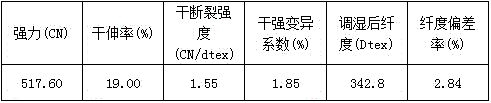
[0086]Put the modified cellulose fibers washed with water in step B into the first dyeing container, and carry out dyeing to obtain the dyed modified cellulose fibers and dyeing residue, and pump the dy...
Embodiment 2
[0089] Cellulose fiber dyeing process:
[0090] A salt-free and low-alkali cycle dyeing process for cellulose fibers, comprising the following process steps:
[0091] A. Cellulose fiber modification treatment
[0092] Put the cellulose fiber into the container, add water to the container, and then use two kinds of quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifiers, modifier A and modifier B, to modify the cellulose fiber, and obtain Modified cellulose fiber; the modifier A is a small molecule quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifier, and the modifier B is a high molecular weight quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifier;
[0093] B. Washing treatment
[0094] Washing the modified cellulose fibers obtained through the modification treatment in step A;
[0095] C. Cyclic dyeing
[0096] Put the modified cellulose fibers washed with water in step B into the first dyeing container, and carry out dyeing to obtain the dyed modified cellulose fibers and dyeing residue, and pump the d...
Embodiment 3
[0099] Cellulose fiber dyeing process:
[0100] A salt-free and low-alkali cycle dyeing process for cellulose fibers, comprising the following process steps:
[0101] A. Cellulose fiber modification treatment
[0102] Put the cellulose fiber into the container, add water to the container, and then use two kinds of quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifiers, modifier A and modifier B, to modify the cellulose fiber, and obtain Modified cellulose fiber; the modifier A is a small molecule quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifier, and the modifier B is a high molecular weight quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifier;
[0103] B. Washing treatment
[0104] Washing the modified cellulose fibers obtained through the modification treatment in step A;
[0105] C. Cyclic dyeing
[0106] Put the modified cellulose fibers washed with water in step B into the first dyeing container, and carry out dyeing to obtain the dyed modified cellulose fibers and dyeing residue, and pump the d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com