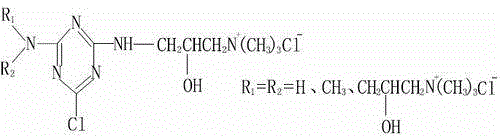Modified cellulose fibers obtained through modification with modifiers
A technology of cellulose fibers and modifiers, applied in the field of textile dyeing, can solve the problems of inapplicability to large-scale production, high chroma of dyeing raffinate, difficult treatment of wastewater, etc., achieve high success rate, good cationization effect, dye The effect of dosage reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
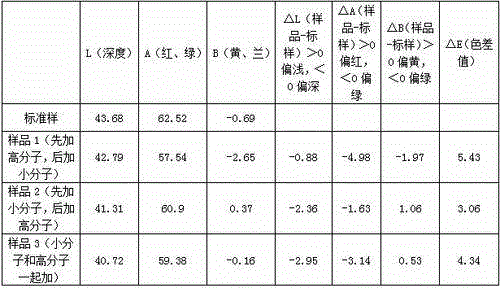
[0060] Modified cellulose fibers:
[0061] The modified cellulose fiber is modified by the cellulose fiber through the small molecule quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifier and the high molecular quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifier as the cationic modifier, and the obtained pH value is 6.5 When -8.5, the Zeta electrode potential value is the modified cellulose fiber of 0-15mV; The described small molecular quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifier is a chlorotriazine type quaternary ammonium salt compound, and the described polymer quaternary ammonium salt The cationic modifier is polyepichlorohydrin dimethylamine.
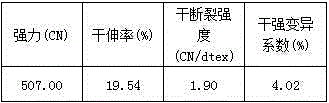
[0062] The above is the modified cellulose fiber of the present invention. Due to the small molecular weight of the small molecular quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifier, it can not only be adsorbed on the surface of the fiber but also diffuse into the fiber, while the high molecular weight quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifier has a large m...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Modified cellulose fibers:
[0065] The modified cellulose fiber is modified by the cellulose fiber through the small molecule quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifier and the high molecular quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifier as the cationic modifier, and the obtained pH value is 6.5 , the modified cellulose fiber whose Zeta electrode potential value is 15mV; the small molecule quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifier is a chlorotriazine type quaternary ammonium salt compound, and the high molecular quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifier Polyepichlorohydrin dimethylamine.
Embodiment 3
[0067] Modified cellulose fibers:
[0068] The modified cellulose fiber is modified by the cellulose fiber through the small molecule quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifier and the high molecular quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifier as the cationic modifier, and the obtained pH value is 8.5 When, the modified cellulose fiber whose Zeta electrode potential value is 0mV; the described small molecule quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifier is a chlorotriazine type quaternary ammonium salt compound, and the described polymer quaternary ammonium salt cationic modifier Polyepichlorohydrin dimethylamine.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Potential value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Potential value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Electric potential | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com