Grating subdivision device and method based on FPGA
A technology of grating and differential amplifying circuit, which is applied in the direction of using optical devices to transmit sensing components, etc., can solve the problems that the subdivision device cannot meet the requirements, the speed is not fast enough, and the subdivision multiple is high.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
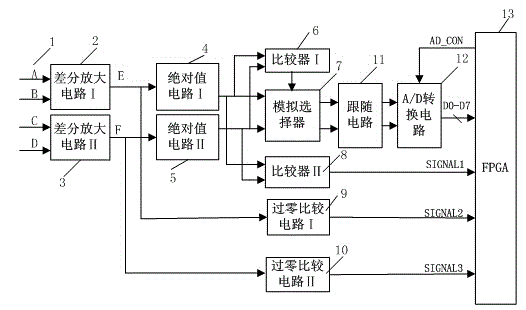
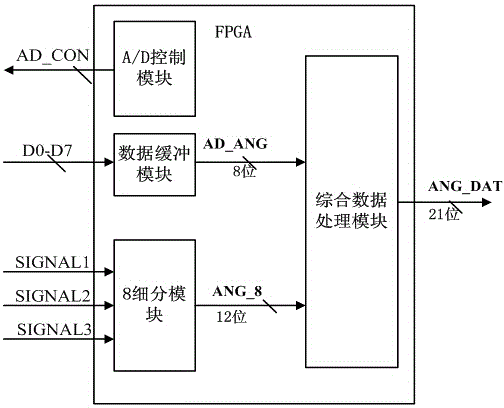
[0049] Embodiment 1: as Figure 1-7 As shown, a raster subdivision device based on FPGA includes input signal 1, differential amplifier circuit I2, differential amplifier circuit II3, absolute value circuit I4, absolute value circuit II5, comparator I6, analog selector 7, comparator II8 , Zero-crossing comparison circuit I9, zero-crossing comparison circuit II10, follower circuit 11, A / D conversion circuit 12, FPGA device 13;
[0050] Wherein, the FPGA device 13 outputs a signal to control the clock and the chip selection terminal of the A / D conversion circuit 12;
[0051] After the input signal 1 passes through the differential amplifier circuit I2 and the differential amplifier circuit II3: the zero-crossing comparison circuit I9 and the zero-crossing comparison circuit II10 generate a 2-bit level signal; at the same time, the absolute value signal is obtained through the absolute value circuit I4 and the absolute value circuit II5: The absolute value signal passes through ...
Embodiment 2
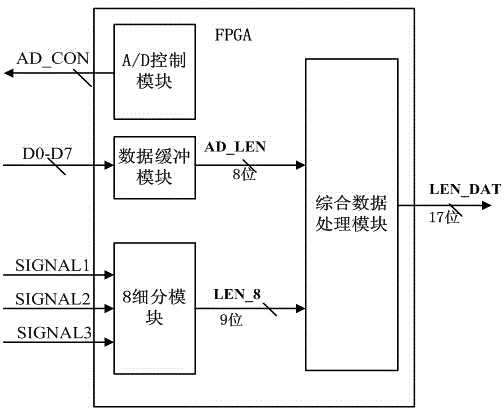
[0067] Embodiment 2: as Figure 1-7 As shown, a raster subdivision device based on FPGA includes input signal 1, differential amplifier circuit I2, differential amplifier circuit II3, absolute value circuit I4, absolute value circuit II5, comparator I6, analog selector 7, comparator II8 , Zero-crossing comparison circuit I9, zero-crossing comparison circuit II10, follower circuit 11, A / D conversion circuit 12, FPGA device 13;
[0068] Wherein, the FPGA device 13 outputs a signal to control the clock and the chip selection terminal of the A / D conversion circuit 12;
[0069] After the input signal 1 passes through the differential amplifier circuit I2 and the differential amplifier circuit II3: the zero-crossing comparison circuit I9 and the zero-crossing comparison circuit II10 generate a 2-bit level signal; at the same time, the absolute value signal is obtained through the absolute value circuit I4 and the absolute value circuit II5: The absolute value signal passes through ...
Embodiment 3
[0076] Embodiment 3: as Figure 1-7 As shown, a raster subdivision device based on FPGA includes input signal 1, differential amplifier circuit I2, differential amplifier circuit II3, absolute value circuit I4, absolute value circuit II5, comparator I6, analog selector 7, comparator II8 , Zero-crossing comparison circuit I9, zero-crossing comparison circuit II10, follower circuit 11, A / D conversion circuit 12, FPGA device 13;
[0077] Wherein, the FPGA device 13 outputs a signal to control the clock and the chip selection terminal of the A / D conversion circuit 12;
[0078] After the input signal 1 passes through the differential amplifier circuit I2 and the differential amplifier circuit II3: the zero-crossing comparison circuit I9 and the zero-crossing comparison circuit II10 generate a 2-bit level signal; at the same time, the absolute value signal is obtained through the absolute value circuit I4 and the absolute value circuit II5: The absolute value signal passes through ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com