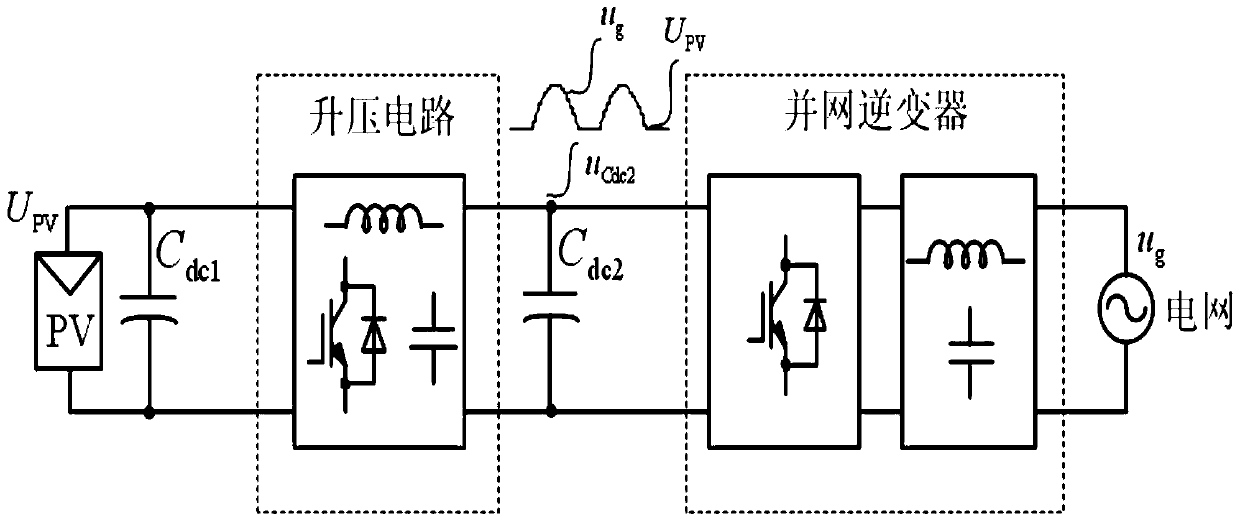
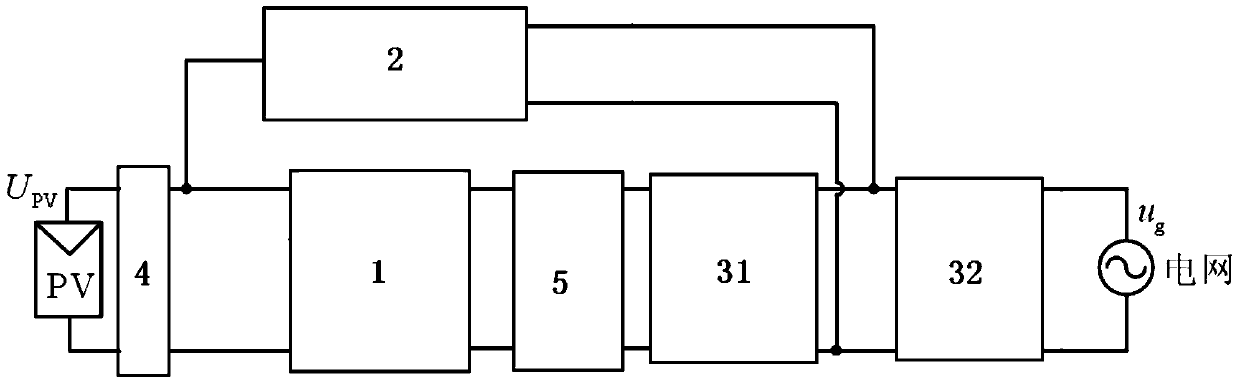
A photovoltaic grid-connected inverter and its control method
A technology of inverters and photovoltaics, applied in photovoltaic power generation, AC network circuits, single-network parallel feeding arrangements, etc., can solve the problems of large DC bus capacitor voltage fluctuations, limited DC bus capacitors, and booster circuits not working, etc. Achieve the effects of increasing power density, reducing filter inductance value, and reducing output voltage variation amplitude
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
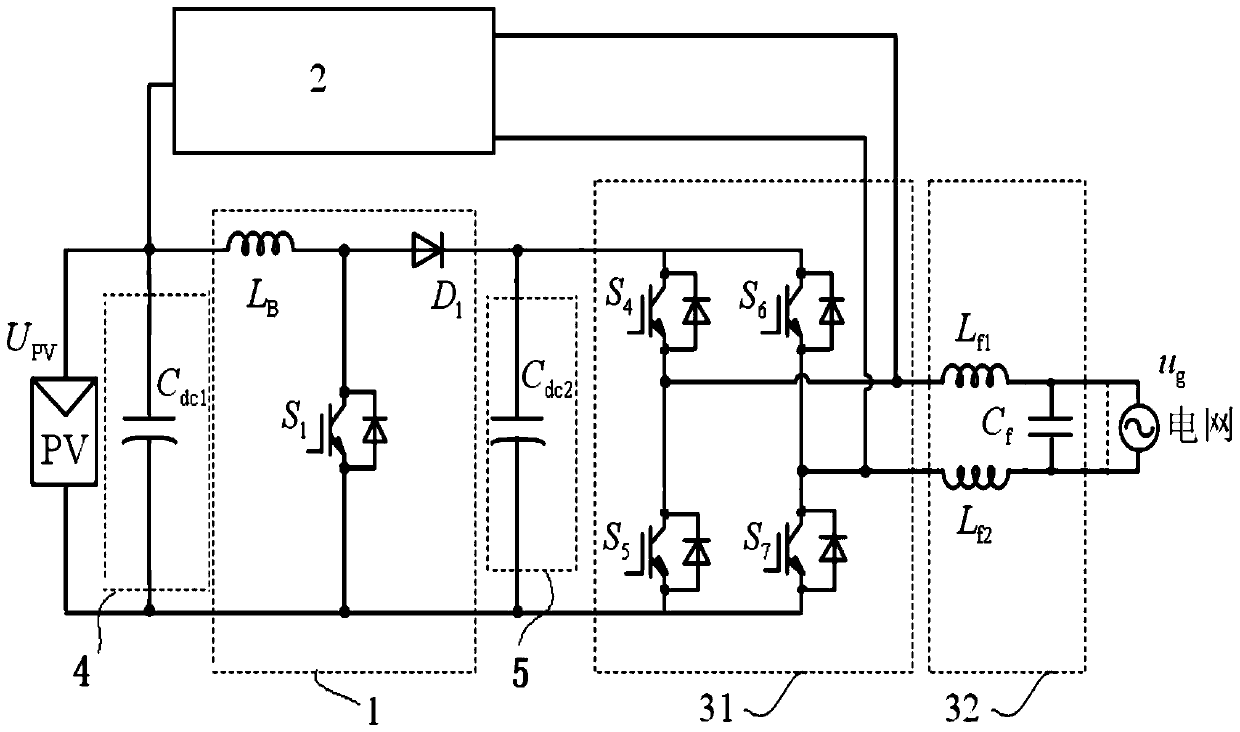
[0038] The photovoltaic grid-connected inverter described in Embodiment 1 adopts the DC bypass branch 2 of the first structure, which includes six working modes:
[0039] Mode 1: the fourth power switch tube S in the full-bridge inverter circuit 31 4 and the seventh power switch S 7 turn on, the other switches in the full-bridge inverter circuit 31 are turned off, and the grid current flows through the fourth power switch S in sequence 4 , the first filter inductance L f1 , grid u g , the second filter inductance L f2 , the seventh power switch tube S 7 ; The bridge arm voltage output by the full-bridge inverter circuit 31 is the second DC bus capacitor C dc2 Voltage;
[0040] Mode 2: the second power switch S in the DC bypass branch 2 2 turn on, the third power switch S 3 turn off, the seventh power switch tube S in the full-bridge inverter circuit 31 7 turn on, the other switch tubes in the full-bridge inverter circuit 31 are turned off, and the incoming current flo...
Embodiment 2
[0061] The photovoltaic grid-connected inverter described in Embodiment 2 adopts the DC bypass branch 2 of the first structure, which includes six working modes:
[0062] Mode 1: the fourth power switch tube S in the full-bridge inverter circuit 31 4 and the seventh power switch S 7 turn on, the other switches in the full-bridge inverter circuit 31 are turned off, and the grid current flows through the fourth power switch S in sequence 4 , the first filter inductance L f1 , grid u g , the second filter inductance L f2 , the seventh power switch tube S 7 ; The bridge arm voltage output by the full-bridge inverter circuit 31 is the second DC bus capacitor C dc2 Voltage;
[0063] Mode 2: the second power switch S in the DC bypass branch 2 2 turn on, the third power switch S 3 turn off, the fourth power switch tube S in the full-bridge inverter circuit 31 4 turn on, the other switches in the full-bridge inverter circuit 31 are turned off, and the grid current flows throug...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com