Optical communication lens, optical communication module, and molding die
A technology for forming molds and optical communication, which is applied in the direction of condensers, household appliances, and other household appliances. It can solve the problems of high cost and expensive glass lenses, and achieve the effects of improved mold release, high optical performance, and uniform shrinkage.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
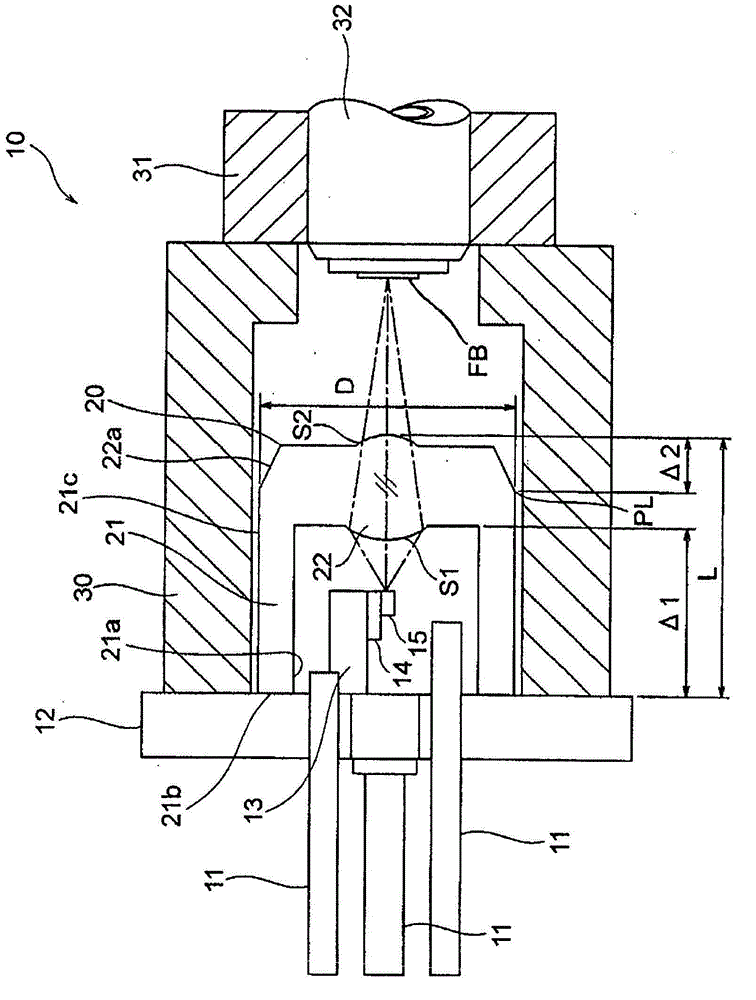
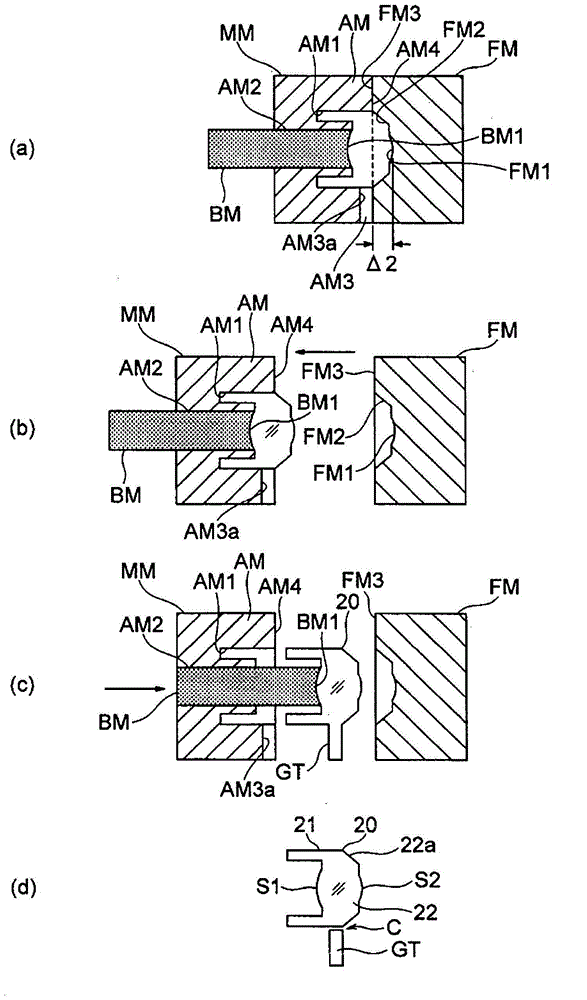
[0067] figure 2 It is a figure which shows the manufacturing process (a)-(d) of the lens suitable for the above-mentioned embodiment. The fixed mold FM has a transfer surface FM1 that transfers the optical surface S2, a transfer surface (taper surface slope) FM2 that transfers the tapered surface 22a, and a mating surface FM3. The mating surface FM3 of the fixed mold FM is located at a position away from the innermost (here, the center of the transfer surface FM1) of the fixed mold FM in the optical axis direction by Δ2=L / 10 to L / 2. The transfer surface FM2 is made a rough surface.
[0068] On the other hand, the movable mold MM that is movable with respect to the fixed mold FM has a main mold AM and an insert mold (sub-mold) BM. The main mold AM has a transfer surface AM1 of the transfer leg 21, a circular opening AM2 in the center, an inject part AM3 for injecting resin from the outside, and a mating surface AM4.
[0069] The cylindrical insert mold BM is fitted into the circu...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
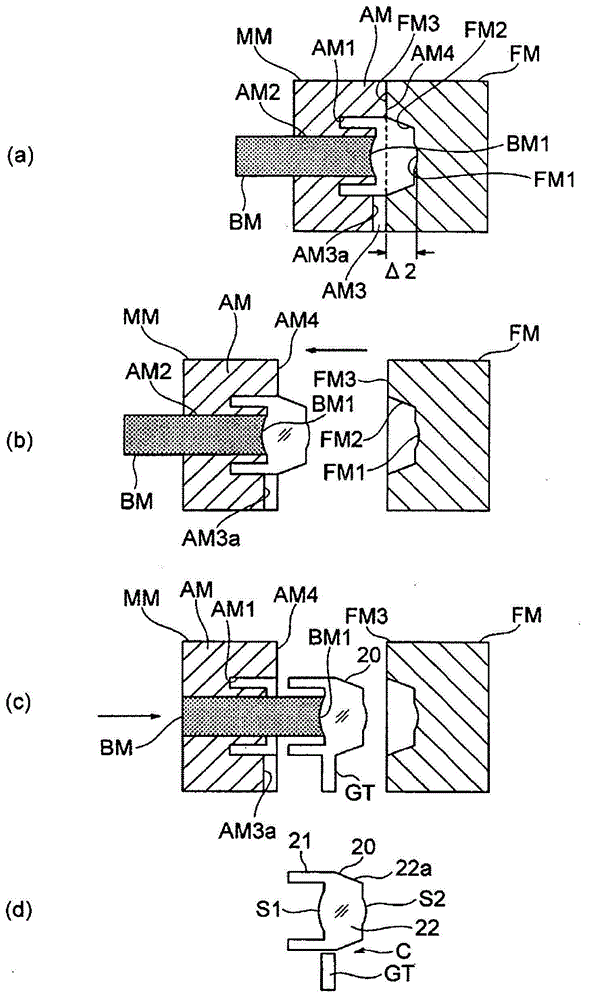
[0075] image 3 It is a figure which shows the manufacturing process (a)-(d) of the lens of 2nd Embodiment. In this embodiment, the distance Δ2 in the optical axis direction from the innermost surface of the fixed mold FM to the mating surface FM3 of the fixed mold FM is further increased compared to the first embodiment. Since the other configuration is the same as the above-mentioned embodiment, the description is omitted.
[0076] (3rd embodiment)
[0077] Figure 4 It is a figure which shows the manufacturing process (a)-(d) of the lens of 3rd Embodiment. This embodiment is different from the first embodiment in that a transfer surface (curved surface transfer surface) FM2' for transferring a curved surface is provided around the transfer surface FM1 of the fixed mold FM. Thus, as Figure 4 As shown in (d), around the optical surface S2 of the lens 20, a curved surface 22a' whose diameter decreases as it approaches the optical surface S2 is formed. The curved surface 22a' be...
no. 4 Embodiment approach
[0079] Figure 5 It is a figure (a)-(d) which shows the manufacturing process of the lens of 4th Embodiment. In the present embodiment, it is an example in which the diameter around the transfer surface FM1 of the fixed mold FM is reduced compared to the first embodiment. Thus, as Figure 5 As shown in (d), a stepped surface 22a" having a reduced diameter is formed around the optical surface S2 of the lens 20. Here, FM2 is a stepped transfer surface. It is preferable to use the stepped surface 22a" as the outer peripheral surface of the flange portion. (The outer peripheral surface) is made into a rough surface. Since the other configuration is the same as the above-mentioned embodiment, the description is omitted.
[0080] (Fifth embodiment)
[0081] Image 6 It is a figure (a)-(d) which shows the manufacturing process of the lens of 5th Embodiment. In this embodiment, with respect to the fourth embodiment, the diameter around the transfer surface FM1 of the fixed mold FM is ma...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com