AAV vectors targeted to oligodendrocytes
A technology of oligodendrocytes and vectors, applied in the direction of vectors, cells modified by introducing foreign genetic materials, using vectors to introduce foreign genetic materials, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0252] Discovery and characterization of BNP61 AAV clone
[0253] The AAV capsid library shuffled with mutant DNA was injected intravenously into a rat model of Parkinson's disease, and cells were isolated from the caudate nucleus after 3 days. Using PCR rescue, a single clone (BNP61) appeared. Additional shuffling and selection resulted in identical clones. Such as figure 1 As shown, this clone is a chimera of several AAV serotypes.
[0254] The BNP61 clone was directly infused into the rat brain, resulting in an amazing pattern of cell transduction. So far, when gene expression is driven by a constitutive promoter, almost all different AAV serotypes and chimeras have shown greater neuronal effects. 95% tropism. The significant difference is that BNP61 showed> 95% tropism, without evidence of astrocyte or microglia transduction and very little neuronal transduction ( figure 2 A-2C ). figure 2A It shows GFP-positive oligodendrocytes in the rat caudate nucleus one week aft...
Embodiment 2
[0258] BNP61 crosses the affected blood-brain barrier
[0259] After the first round of selection, the BNP61 clone was packaged with GFP and a recombinant virus was produced. Then, 2 weeks after 6-OHDA treatment, press 8×10 11 The recombinant virus was administered intravenously at a dose of one vector genome / kg. One month later, the rats were sacrificed and the brains were sliced. In rats 2 weeks after these treatments, a large number of gene expressions were found in oligodendrocytes and some neurons in the striatum treated with 6-OHDA ( Figure 5 ), and no gene expression was found in the contralateral striatum, in the cortex or the syringe tract of the distal brain structure. Note: lack of colocalization of NeuN with many oligodendrocytes surrounding individual NeuN-positive neurons ( Figure 5 ). Therefore, it appears that after intravenous administration, this new AAV clone exhibits the ability to cross the 6-OHDA-damaged blood-brain barrier instead of the complete blo...
Embodiment 3
[0261] Generation of additional targeted clones of oligodendrocytes
[0262] Using the same AAV DNA capsid shuffling and in vivo directed evolution process described in Example 1, two additional oligodendrocyte targeting clones BNP62 and BNP63 were identified. Such as figure 1 As shown and similar to BNP61, these clones are chimeras of several AAV serotypes. See the amino acid sequence identity between these 3 clones Table 2 . All 3 clones are more than 95% identical to each other at the amino acid level.
[0263] Table 2: Sequence identity between clones
[0264] BNP61 BNP62 BNP63 BNP61 100% 96% 97% BNP62 96% 100% 96% BNP63 97% 96% 100%
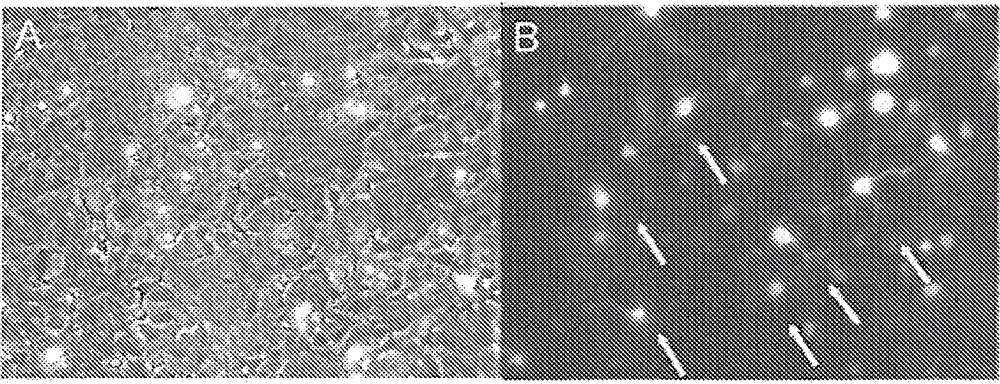
[0265] Image 6 The BNP63 clone was shown to transduce oligodendrocytes in the rat piriform cortex. BNP63 transduced cells (green) are not co-localized with the cell markers of astrocytes (GFAP, red). In addition, the transduced cells showed clear oligodendrocyte morphology.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com