Induction motor control device and induction motor control method
A technology of induction motor and control device, applied in motor control, AC motor control, control device and other directions, can solve the problem of inability to suppress the torsional vibration of the drive shaft
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
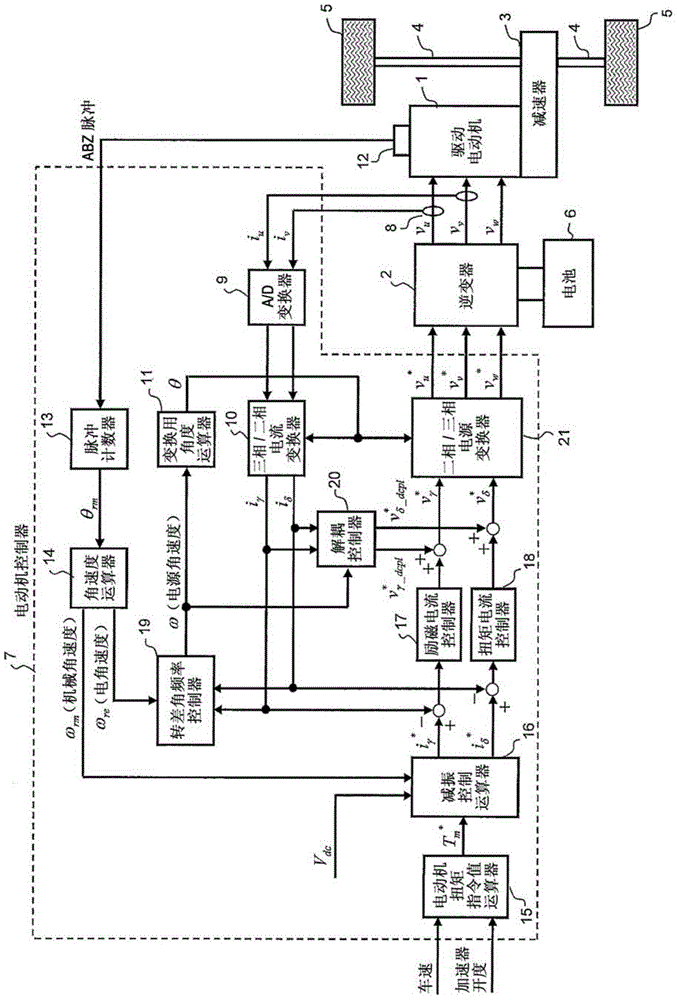
[0023] figure 1 It is a block diagram showing the configuration of the induction motor control device according to the first embodiment. This induction motor control device is applied to electric vehicles, for example. exist figure 1 shows a structural example applied to an electric vehicle. In addition, in addition to electric vehicles, for example, it can also be applied to hybrid vehicles and fuel cell vehicles.
[0024] The motor controller 7 inputs signals of various vehicle variables such as vehicle speed, accelerator opening degree, rotor position signal, and current flowing through the drive motor 1 as digital signals, and generates and controls the drive motor 1 according to various vehicle variables. A PWM signal corresponding to the PWM signal generates a drive signal for the inverter 2 through the drive circuit.
[0025] The inverter 2 has two pairs of switching elements (for example, power semiconductor elements such as IGBTs and MOS-FETs) for each phase, and ...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
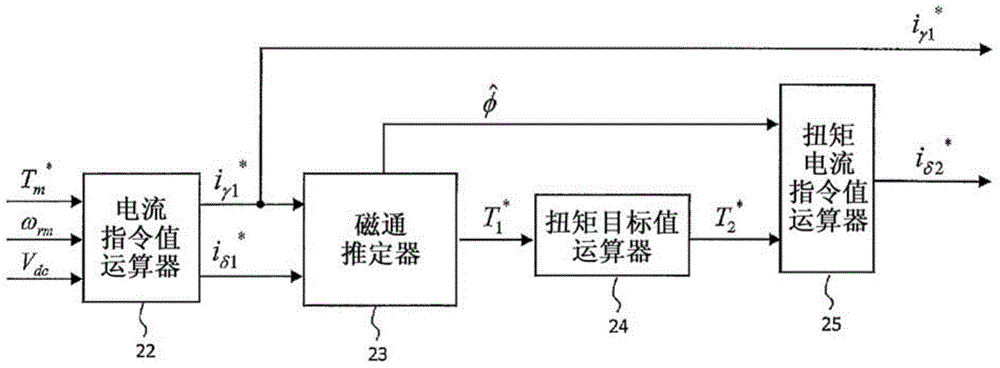
[0144] When the current response is sufficiently faster than the rotor magnetic flux response, the current response estimation calculation process by the magnetic flux estimator 23 can be omitted.
[0145] Figure 8 It is a block diagram showing the detailed configuration of the magnetic flux estimator 23 of the second embodiment. The magnetic flux estimator 23 of the second embodiment has a magnetic flux response calculator 61 and a multiplier 62, and calculates the first torque command value T by the following equations (28) and (29). 1 * and rotor flux estimated value Among them, K T is a coefficient determined by the parameters of the induction motor, is the time constant of the rotor flux response.
[0146] [Formula 28]
[0147] T 1 * = K T · φ ^ · i δ ...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
[0152] When the induction motor generates torque from a state where the rotor magnetic flux is zero, a response lag in torque generation occurs due to a lag in the response of the rotor magnetic flux. In the induction motor control device according to the third embodiment, a constant amount of rotor magnetic flux is generated in advance before the motor torque command value is input.
[0153] Figure 9 It is a block diagram showing the detailed configuration of the magnetic flux estimator 23 in the third embodiment. The magnetic flux estimator 23 in the third embodiment has a magnetic flux response calculator 71, a multiplier 72, a subtractor 73, and an adder 74, and calculates the first torque command value T by the following equations (30) and (31). 1 * and rotor flux estimated value Among them, K T is a coefficient determined by the parameters of the induction motor, is the time constant of the rotor flux response. In addition, iγ 1#offset is the pre-entered γ-axis ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com