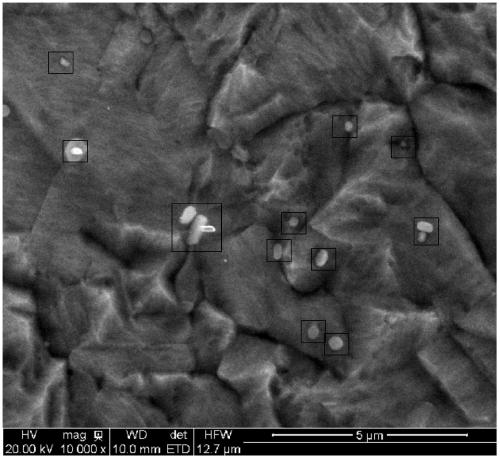
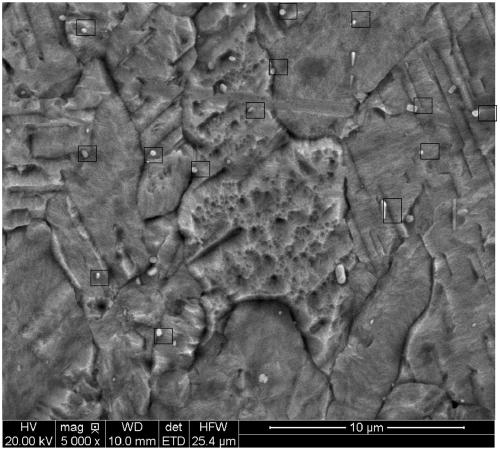
A kind of precipitation strengthened brass alloy and its preparation method
A brass alloy, precipitation strengthening technology, applied in the field of alloys, can solve problems such as limitations in application fields
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
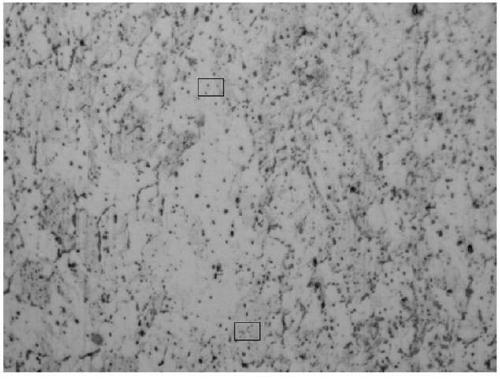
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-45
[0044] Wherein the alloy of embodiment 1 is national standard H70 (American standard C26000), the alloy of embodiment 2 is national standard HSn70-1 (American standard C44300), the alloy of embodiment 26 is H80 (American standard C24000), the alloy of embodiment 27 is QSn6.5-0.1 (American Standard C51900), the alloy of Example 35 is H85 (American Standard C23000), and the alloy of Example 44 is H90 (American Standard C22000).
Embodiment 3-17
[0045] Examples 3-17: each group is prepared according to the designed composition, wherein Mg and P are respectively added as Cu-Mg master alloy and Cu-P master alloy. Each group of ingredients is melted and cast ingots in a 10Kg intermediate frequency furnace, turned into Φ50 extrusion ingots, extruded into Φ15 billets, and the billets are water-cooled. The components of each embodiment are shown in Table 1 and Table 2. The components are post-furnace components, and samples are taken from the billets after extrusion. The extruded billets are processed in sequence as follows: 60% processing rate cold drawing→550°C aging heat treatment for 5h→30% processing rate cold drawing→450°C aging heat treatment for 4h→20% processing rate cold drawing→280°C aging heat treatment for 3h→cleaning. The finished product is processed into a Φ7 standard tensile sample, and the tensile test is performed on the sample on a 10-ton hydraulic drawing machine to test its tensile strength, yield stre...
Embodiment 46-55
[0051] For the production of rods, including Examples 46-55, the ingredients of each example are formulated according to the design components, and P is added in the form of CuP master alloy. The components of each embodiment are shown in Table 3, and the components are post-stove components, and samples are taken from the billets after extrusion.
[0052] Among them, Examples 46-50 were smelted in a power frequency furnace, the smelting temperature was 1080°C-1180°C, and vertical semi-continuous casting was used to cast Φ170mm ingots. Examples 51-55 were smelted in an intermediate frequency furnace at a melting temperature of 1150°C-1250°C. After alloying, the furnace was poured into an intermediate frequency holding furnace, and horizontal continuous casting was used to produce Φ170mm ingots.
[0053] Extrude Φ15 straight rods in a 1250T horizontal extrusion machine with double-flow water seals. Wherein the extrusion temperature of Examples 46-50 is 700°C-780°C, and the ext...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com