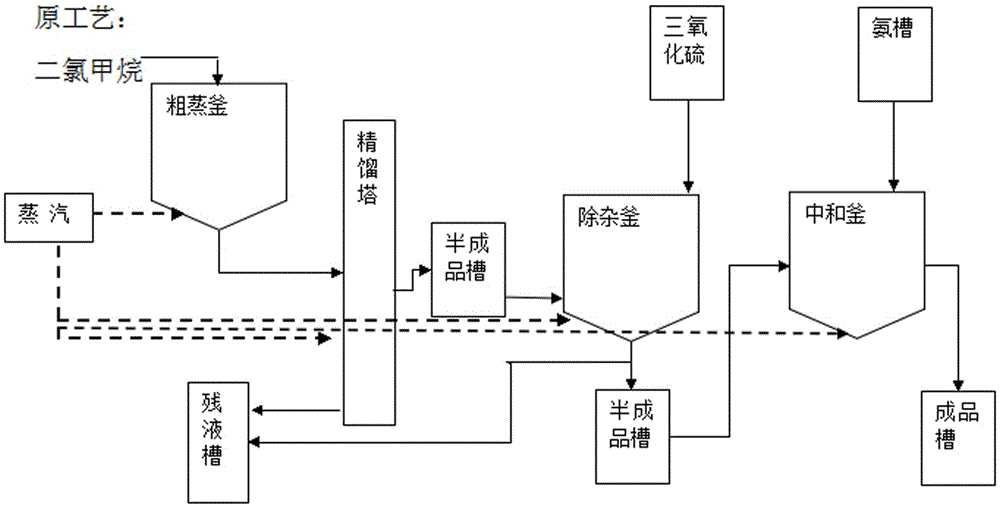
Method for recycling dichloromethane in acesulfame potassium synthesis process
A dichloromethane synthesis process technology, applied in the field of dichloromethane recovery, can solve the problems of long process reaction time, non-compliance with industrial policies, high production costs, etc., reduce impurities removal tanks and neutralization tanks, and improve production efficiency , The effect of improving the quality of materials and products
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
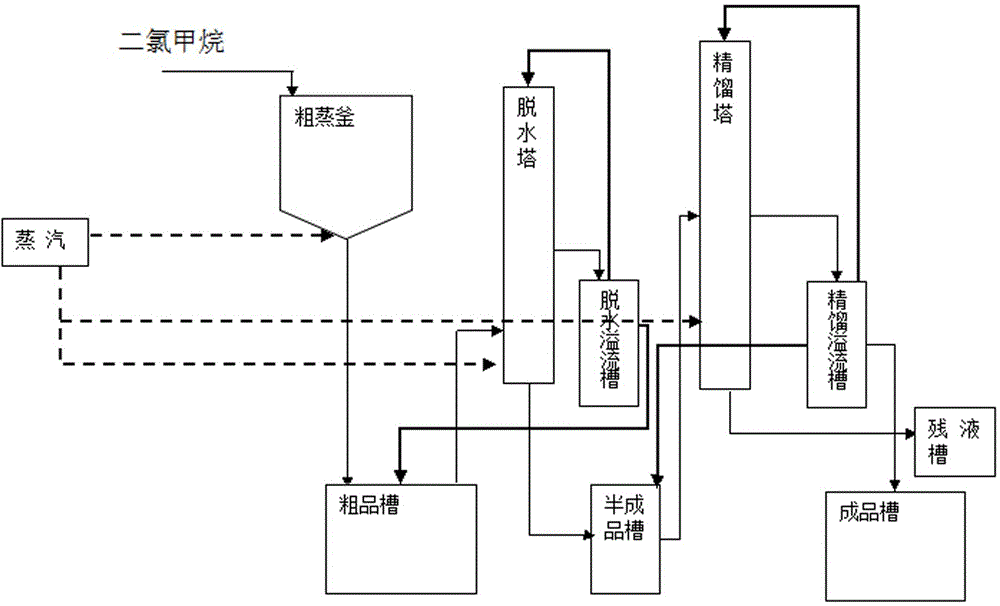
[0013] 1) if figure 2 As shown, the recovery method of dichloromethane in the synthesis process of acesulfame K includes the following steps: a. Add the dichloromethane after rough steaming into the dehydration tower, add steam to heat to 42°C, and dichloromethane and water mixed liquid The steam enters the dehydration overflow tank through condensation, and the dichloromethane with qualified bottom moisture enters the semi-finished product tank for use in the rectification tower; b. The dichloromethane with unqualified moisture at the bottom of the overflow tank enters the dehydration tower again through reflux, and the dichloromethane with high moisture at the top Dichloromethane enters the crude product tank, and the stratified water in the crude product tank is regularly discharged; c, the dichloromethane with qualified moisture in the semi-finished product tank enters the rectification tower, steams to 45 ° C, and the dichloromethane vapor enters the rectification overflo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com