Oxidation-chelation leaching combined remediation method for Cr-contaminated soil
A technology for chromium-contaminated soil and contaminated soil, applied in the field of remediation of heavy metal pollution in site soil, can solve the problems of low removal rate of total Cr in soil, interference of subsequent chelation leaching, and low removal rate of total Cr, so as to improve repair efficiency and facilitate Effect of rinsing removal and improvement of removal rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] (1) After the Cr-contaminated soil is air-dried, grind, pass through a 2mm sieve, and set aside;
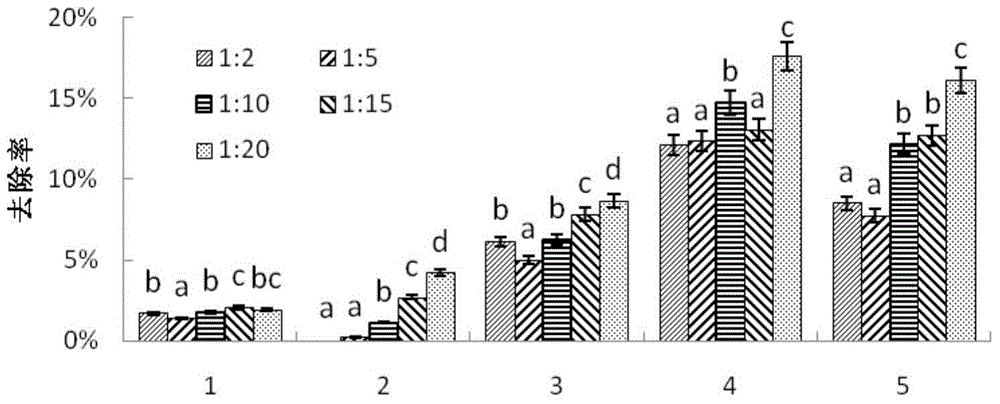
[0035] (2) According to the mass ratio of liquid to soil = 2.5:1, 10% H 2 o 2 Add to the Cr-contaminated soil pretreated in step (1), stir while adding, after mixing evenly, microwave at low level for 5 minutes; then add H 2 O to a mass ratio of liquid to soil of 6:1, vibrate or stir back and forth (180r / min) for 30 minutes, filter or centrifuge to remove the eluent.
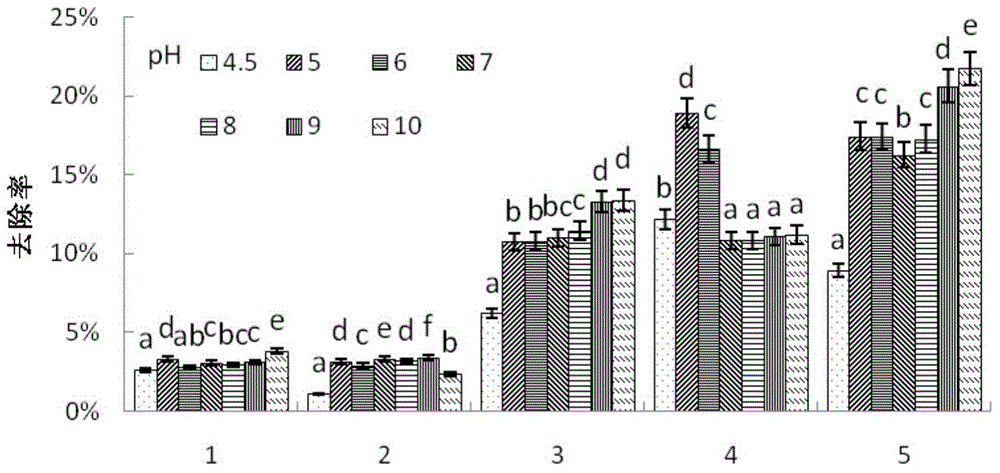
[0036] (3) Chelate rinsing: 0.15MEDTA is adjusted to pH=10 with HCl and NaOH, according to liquid-soil mass ratio=10:1, joins in the Cr-contaminated soil that step (2) handles, reciprocating vibration or stirring ( 180r / min) for 60 minutes, filter or centrifuge to remove the eluent, and rinse 3 times according to the pollution situation.
Embodiment 2
[0038] (1) The present invention tries to use microwave-hydrogen peroxide oxidation-microwave-EDTA leaching in the research process, but the inventors found that microwave treatment is also used in the rinsing process, resulting in a decrease in rinsing efficiency, which may be due to microwave Heating causes partial EDTA to be oxidized and decomposed, which reduces the rinsing efficiency. Considering the complexity and cost of the process, microwave treatment is not used in the rinsing step in the method adopted in the present invention.
[0039] (2) Choice of eluent:
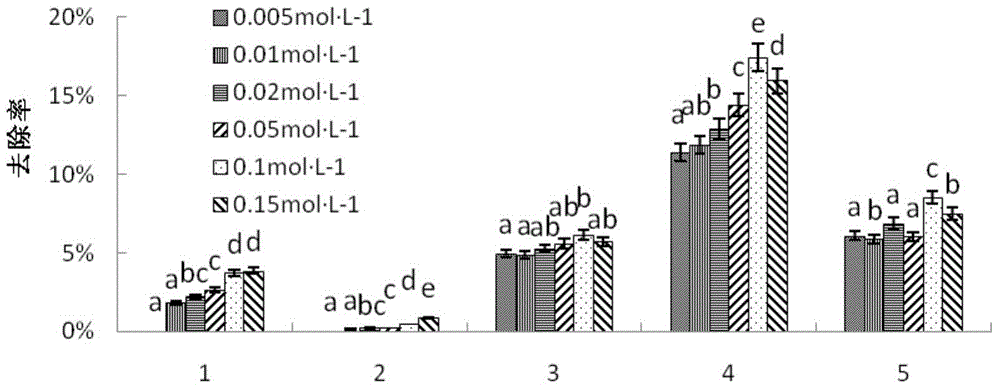
[0040] The present invention compares deionized water, DTPA, 0.1mol·L -1 HCl, 0.1mol L -1 Citric acid (CTA), 0.1mol·L -1 Disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), 0.1mol·L -1 h 3 PO 4 , 0.1mol·L -1 CaCl 2 , 0.1mol·L -1 The leaching effects of 8 kinds of leaching agents of NaOH hydrochloric acid, wherein the leaching agents all have the effect of leaching to remove Cr; among them, EDTA has the be...
Embodiment 3
[0042] (1) After air-drying the Cr-contaminated soil, grind it, pass through a 1mm sieve, and set aside;
[0043] (2) Microwave-H 2 o 2 Oxidation: According to the mass ratio of liquid to soil = 2:1, 10% H 2 o 2 Add to the Cr-contaminated soil pretreated in step (1), stir while adding, after mixing evenly, microwave at low-grade for 3 minutes; then add H 2 O to a mass ratio of liquid to soil of 5:1, vibrate or stir back and forth (180r / min) for 20 minutes, filter or centrifuge to remove the eluent.
[0044] (3) Chelate leaching: 0.1MEDTA is adjusted to pH=9 with HCl and NaOH, according to the mass ratio of liquid to soil=9:1, join in the Cr-contaminated soil processed in step (2), vibrate or stir back and forth ( 180r / min) for 30 minutes, filter or centrifuge to remove the eluent, and rinse once according to the pollution situation.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com