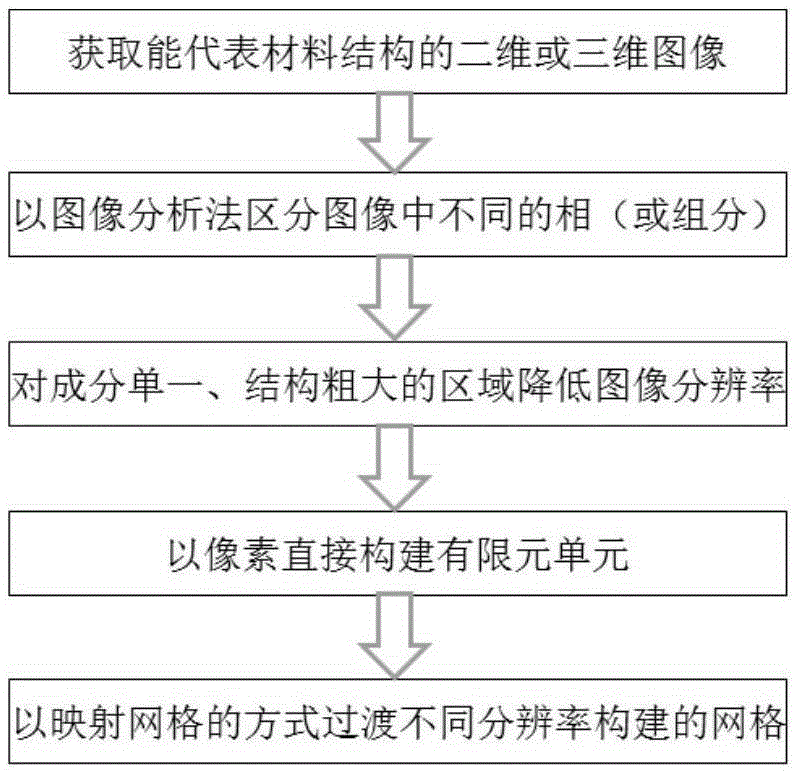
Image based adaptive finite element mesh division method
An adaptive grid, finite element technology, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve the problem of inappropriate image finite element modeling methods, avoid building solid models, and save system resources. , the effect of reducing the number of nodes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Example 1: Two-dimensional finite element modeling of cold-sprayed SiC-reinforced magnesium alloy composites.
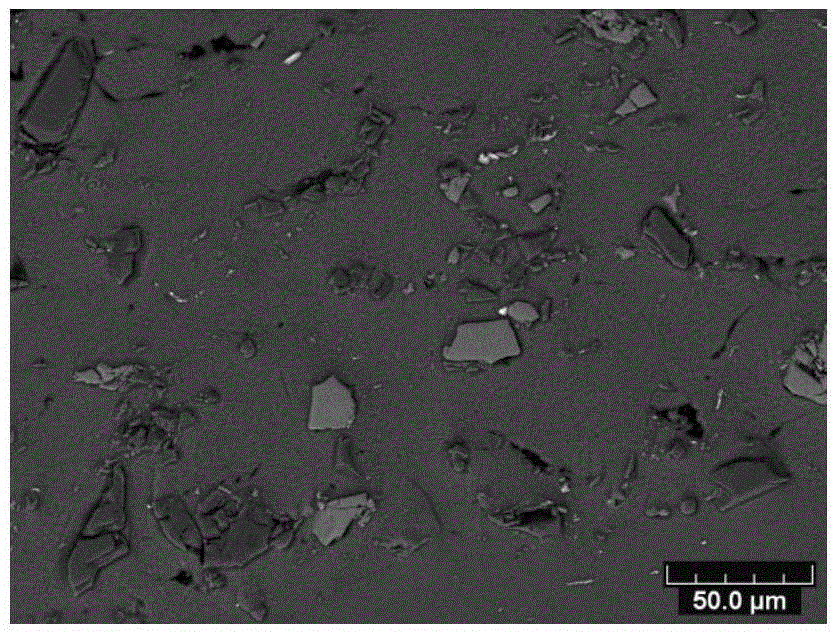
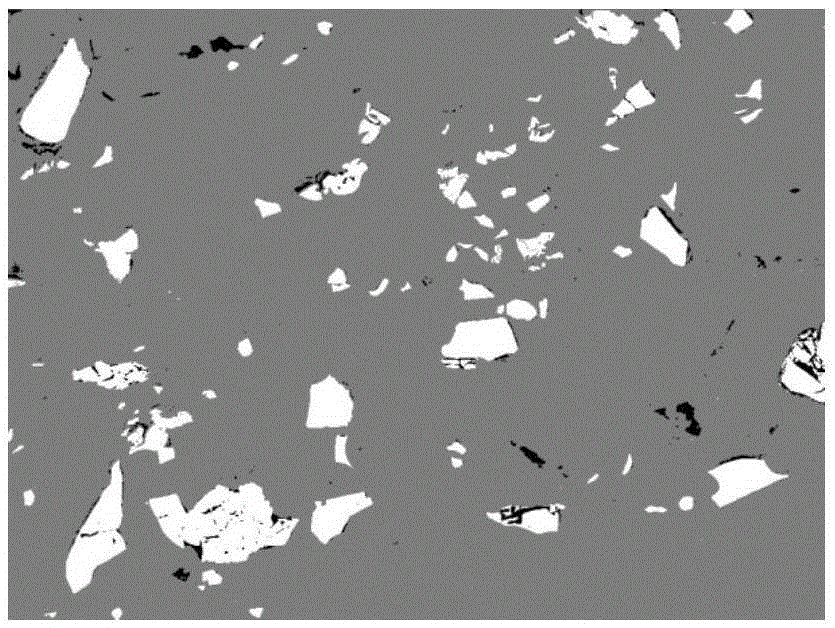
[0048] Composite materials usually contain more than two components. This example shows the modeling of composite materials with three components in the present invention. Multi-level scale triangular meshes and quadrilateral meshes are used in the model. For single-component, coarse Larger meshes are generated automatically for regions with complex components and finer structures, while finer meshes are generated for regions with complex composition and fine structure. This example can verify the two-dimensional grid division ability of the present invention for multi-component materials.
[0049] Adopting the present invention to carry out two-dimensional finite element modeling to the magnesium alloy composite material reinforced by cold spraying SiC, comprises the following steps:
[0050] (1) Obtain a two-dimensional polished cross-sectional image that c...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Example 2: Three-dimensional finite element modeling of plasma sprayed yttria stabilized zirconia (YSZ) coating.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com