A power-on surge current suppression circuit applied to switching power supply
A surge current, suppressing circuit technology, applied in electrical components, output power conversion devices, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the reliability of AC-DC converters, large power consumption of NTC resistors, and high cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
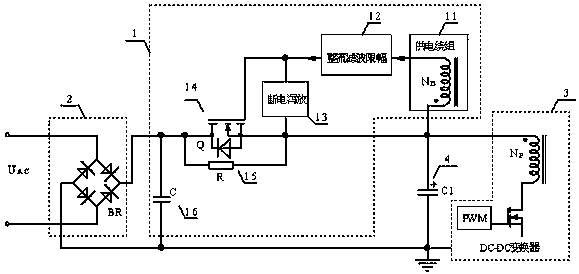
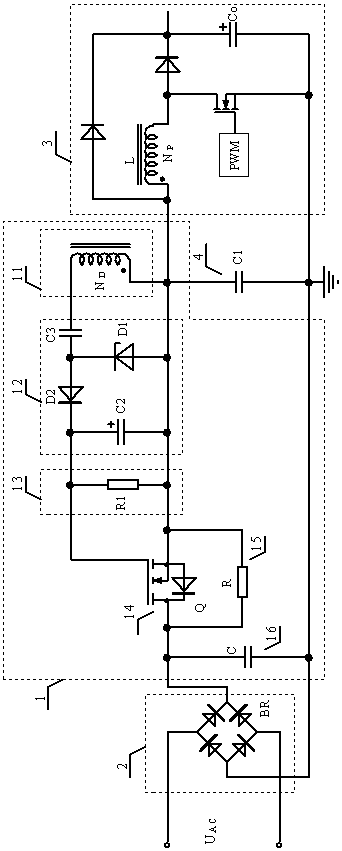
[0019] A power-on surge current suppression circuit 1 applied to switching power supplies, such as figure 2 As shown, the rectifying, filtering and limiting circuit 12 includes a coupling capacitor C3, a high frequency rectifying diode D2, a voltage stabilizing diode D1 and a filtering capacitor C2. Both ends of the filter capacitor C2 are respectively connected to the gate and source of the N-channel MOS transistor 14, the anode of the high-frequency rectifier diode D2 is connected to the cathode of the Zener diode D1, and the cathode of the high-frequency rectifier diode D2 is connected to the N-channel MOS transistor 14 connected to the gate, the anode of the Zener diode D1 is connected to the source of the N-channel MOS transistor 14; one end of the coupling capacitor C3 is connected between the high-frequency rectifier diode D2 and the Zener diode D1, and the other end is connected to the power supply winding 11 connected. Resistor R1 can be selected for the power-off b...
Embodiment 2
[0022] As a modification of Embodiment 1, such as image 3 As shown, in this embodiment, the power-on surge current suppression circuit 1 is connected to another position between the bridge rectifier 2 and the DC-DC converter 3, and the drain of the N-channel power MOS transistor 14 is connected to the DC-DC converter The common potential reference terminal of 3, that is, one end of the input filter capacitor C1, the source S is connected to the negative end of the bridge rectifier 2; and the main winding One end of the power supply winding 11 connected together with the ends of the same name is connected to the source of the N-channel MOS transistor 14, and the other end of the power supply winding 11 is connected to the input end of the rectification filter limiting circuit, and is connected to one end of the coupling capacitor C3.
Embodiment 3
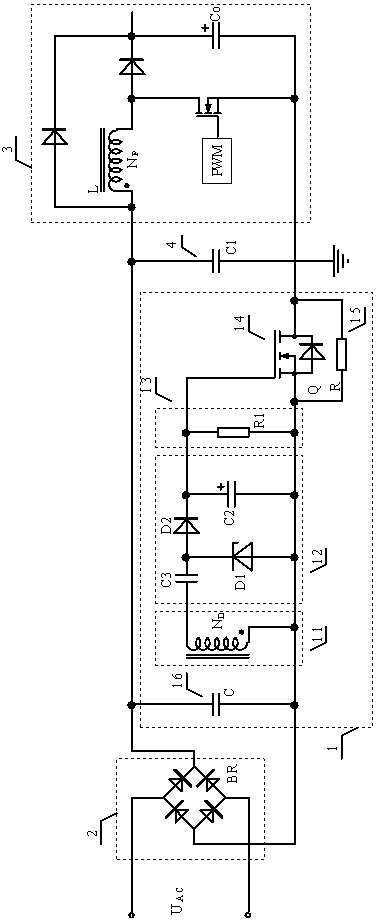
[0024] A power-on surge current suppression circuit 1 applied to switching power supplies, such as Figure 4 As shown, the rectifying, filtering and limiting circuit 12 includes a voltage dividing and current limiting resistor R2, a high frequency rectifying diode D2, a voltage stabilizing diode D1, and a filtering capacitor C2. The cathode of the Zener diode D1 is connected to the gate of the N-channel MOS transistor 14 , and the anode of the Zener diode D1 is connected to the source of the N-channel MOS transistor 14 . Both ends of the filter capacitor C2 are respectively connected to the gate and source of the N-channel MOS transistor 14; the cathode of the high-frequency rectifier diode D2 is connected to the gate of the N-channel MOS transistor 14, and the anode of the high-frequency rectifier diode D2 is connected to the voltage divider One end of the current limiting resistor R2, and the other end of the voltage dividing current limiting resistor R2 is connected to the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com