Colorectal cancer marker and application thereof
A marker, colorectal cancer technology, applied in the field of biomarkers, can solve the problem of lack of non-invasive early diagnosis methods for colorectal cancer, and achieve the effect of improving and restoring the intestinal microecological structure and preventing defects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
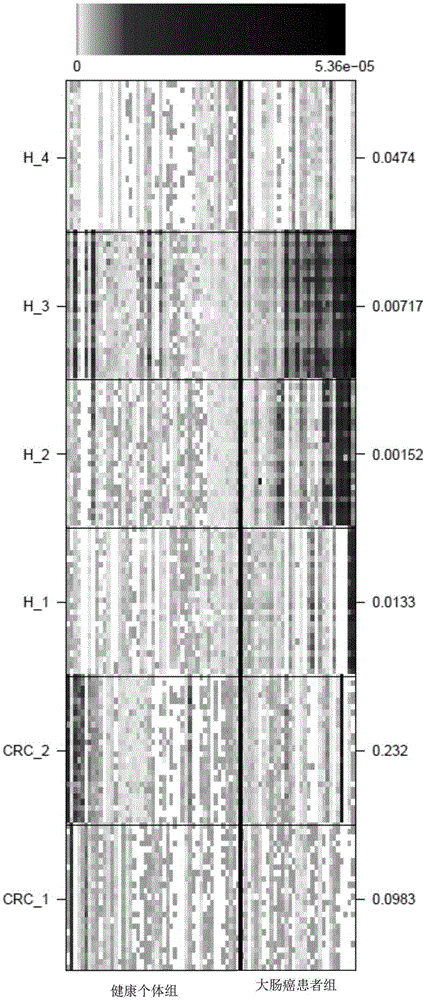
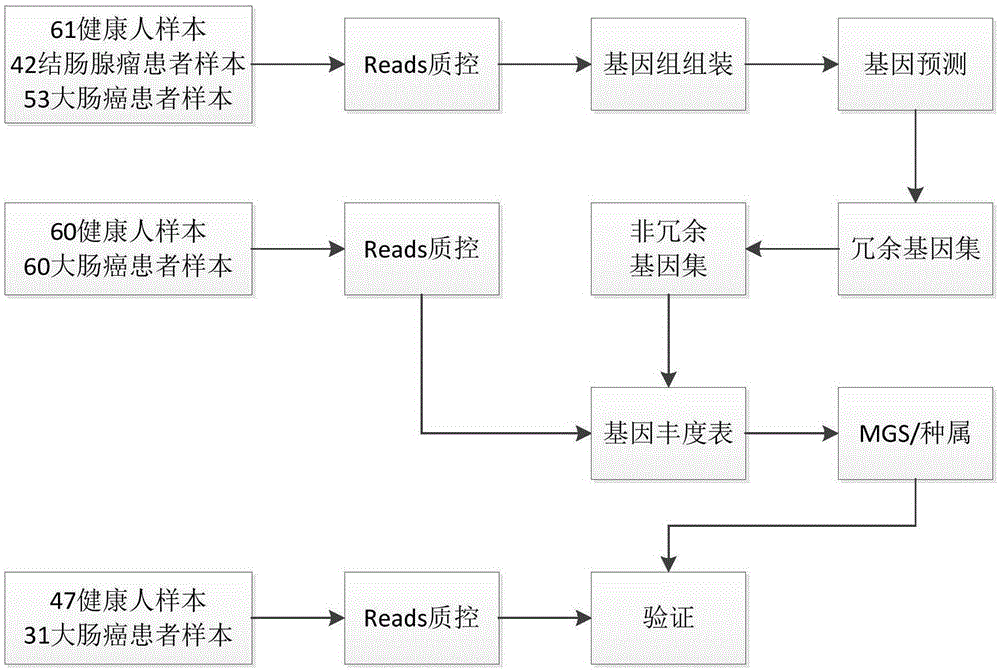
[0065] In this example, the inventors carried out correlation analysis of intestinal flora microorganisms to study the characteristics of fecal microbial communities and functional components from fecal samples of 53 patients with colorectal cancer, 42 patients with colonic adenoma, and 61 healthy individuals. In general, a total of about 1084.87Gb of sequencing data of each sample in the above-mentioned control group was downloaded, and a colorectal cancer reference gene set was constructed. Quantitative metagenomic analysis revealed that 14,993 genes were significantly different (fdr<0.05) in a large number of patients and healthy controls. Most of the genes can be classified into 6 gene clusters (MetagenomicSpecies, MGS) representing bacterial species, of which 2 MGS were enriched in the colorectal cancer patient group, and 4 MGS were enriched in the healthy group.
[0066] 1. Download the sequencing data of the control group
[0067] The DNA sequencing data of stool sampl...
Embodiment 2
[0098] In order to verify that the species markers determined in Example 1 can be used as colorectal cancer markers, the MGS abundances of the remaining 47 healthy people and 31 colorectal cancer patients were used for verification. Wherein, the extraction and sequencing of DNA and the analysis of gene abundance were carried out with reference to the instructions of commercially available DNA extraction kits, the library construction and sequencing instructions of the selected sequencing platform, and the above steps.
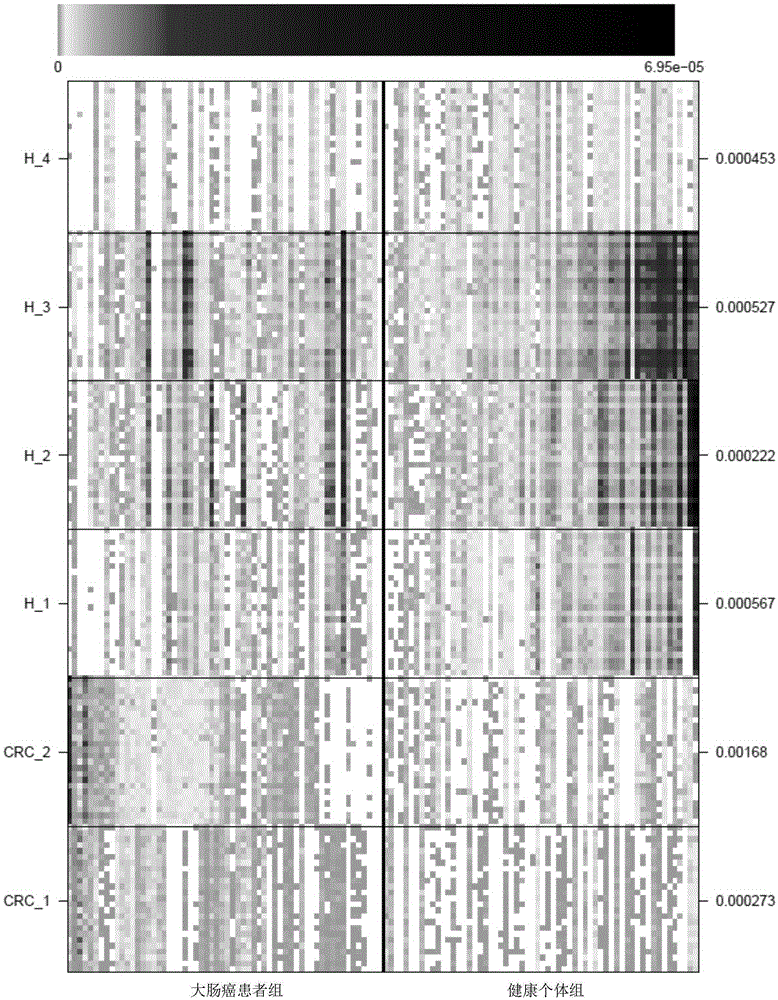
[0099] The verification result is as image 3 shown. Taking the significance level α=0.05, the 4 markers determined in Example 1 that are significantly enriched in the healthy population have a significant difference in the abundance of the healthy group and the disease group in the verification group (P<0.05), as shown in Table 3. Eubacterium halllii is Enterobacter hallii, and it has been reported that enterobacterium hallii in the termite gut has a decompo...
Embodiment 3
[0104] Thirty-five stool samples were used to test the individual status of the sample source.
[0105]Determine the abundance of MGSH_1 and MGSH_2 in each stool sample with reference to the method in Example 2, that is, determine the abundance of Eubacterium_hallii_DSM_3353 and Clostridium in the sample, and compare whether the abundance of Eubacterium_hallii_DSM_3353 and Clostridium in each sample falls into the one determined in Example 2 The 95% confidence interval of MGSH_1 and MGSH_2 of the disease group or the healthy group, it is determined that the individual whose abundance of the two species falls into the corresponding interval of the disease group corresponds to a colorectal cancer patient, and it is determined that the abundance of the two species is equal The status of the individual corresponding to the sample falling into the corresponding interval of the healthy group is non-colorectal cancer patient.
[0106] The individual status of 31 of the samples can be...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com