Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
126 results about "Cancer biomarkers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A cancer biomarker refers to a substance or process that is indicative of the presence of cancer in the body. A biomarker may be a molecule secreted by a tumor or a specific response of the body to the presence of cancer. Genetic, epigenetic, proteomic, glycomic, and imaging biomarkers can be used for cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and epidemiology. Ideally, such biomarkers can be assayed in non-invasively collected biofluids like blood or serum.
Reagents and Methods for miRNA Expression Analysis and Identification of Cancer Biomarkers
InactiveUS20090099034A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningTumor BiomarkersTumor Sample
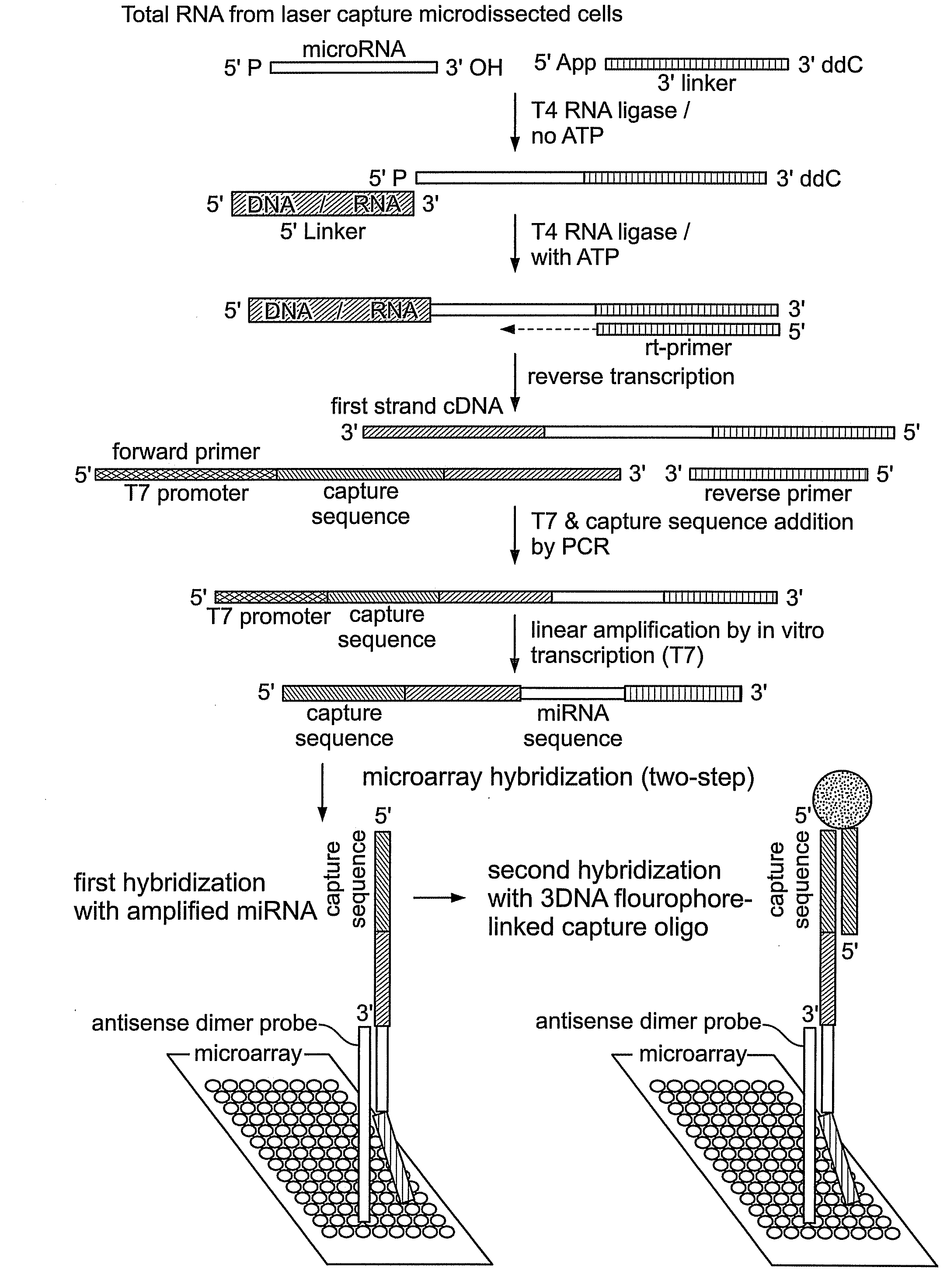
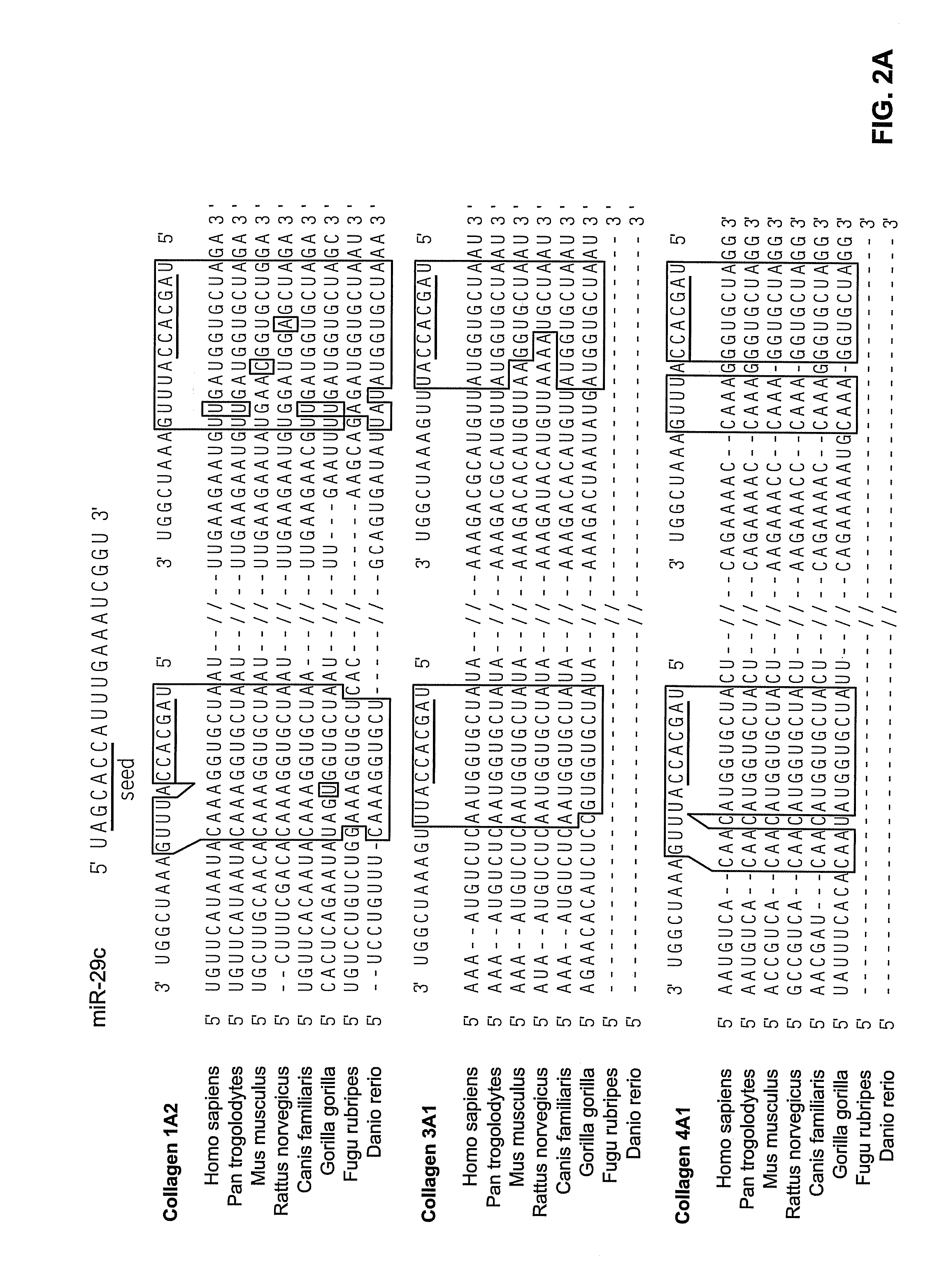
This invention provides methods for amplifying, detecting, measuring, and identifying miRNAs from biological samples, particularly limited amounts of a biological sample. miRNAs that are differentially expressed in tumor samples and normal tissues are useful as cancer biomarkers for cancer diagnostics.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
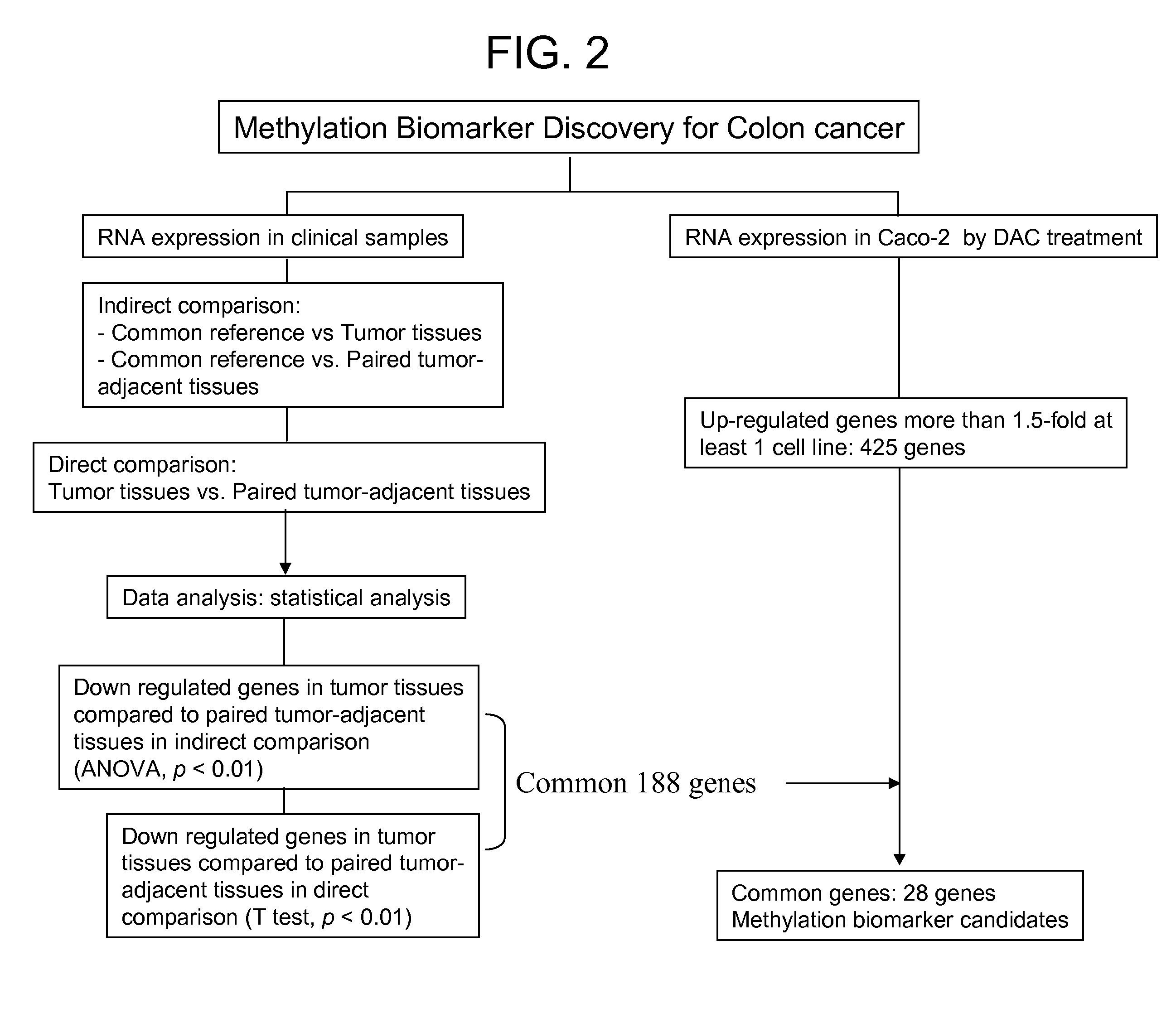
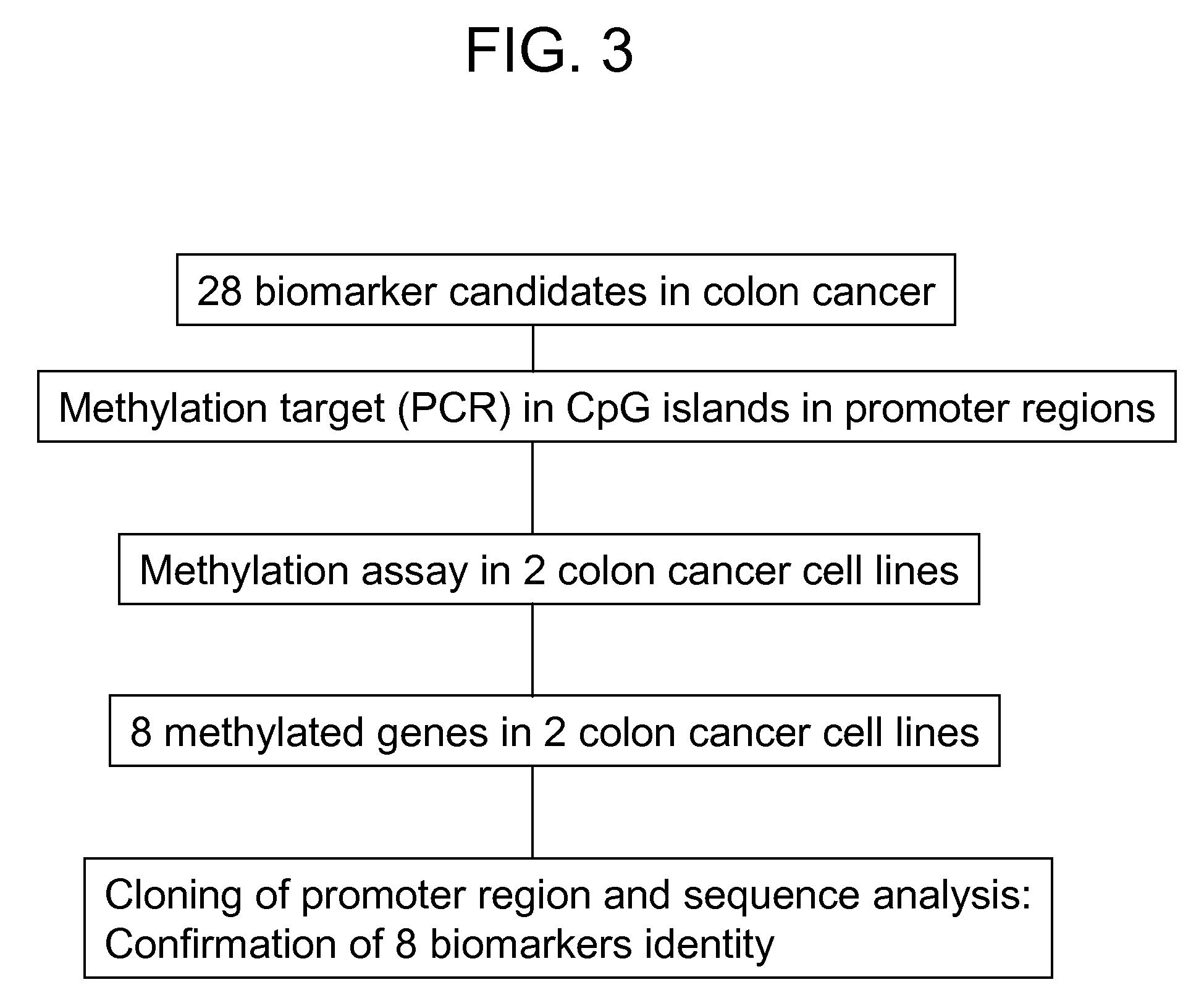
Colon cancer biomarker discovery
InactiveUS20060234254A1Early detectionAccurate diagnostic systemSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementTumor BiomarkersOncology
Owner:GENOMICTREE
Detection And Quantification Of Biomarkers Via A Piezoelectric Cantilever Sensor
InactiveUS20090078023A1High sensitivityShort timeMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMicrobiological testing/measurementEscherichia coliMultiple sensor
Quantification of a target analyte is performed using a single sample to which amounts of the target analyte are added. Calibration is performed as part of quantification on the same sample. The target analyte is detectable and quantifiable using label free reagents and requiring no sample preparation. Target analytes include biomarkers such as cancer biomarkers, pathogenic Escherichia coli, single stranded DNA, and staphylococcal enterotoxin. The quantification process includes determining a sensor response of a sensor exposed to the sample and configured to detect the target analyte. Sensor responses are determined after sequential additions of the target analyte to the sample. The amount of target analyte detected by the sensor when first exposed to the sample is determined in accordance with the multiple sensor responses.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
Combination methods of diagnosing cancer in a patient
InactiveUS20120231479A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisTumor BiomarkersOncology
Owner:TRAXXSSON
Cancer biomarkers
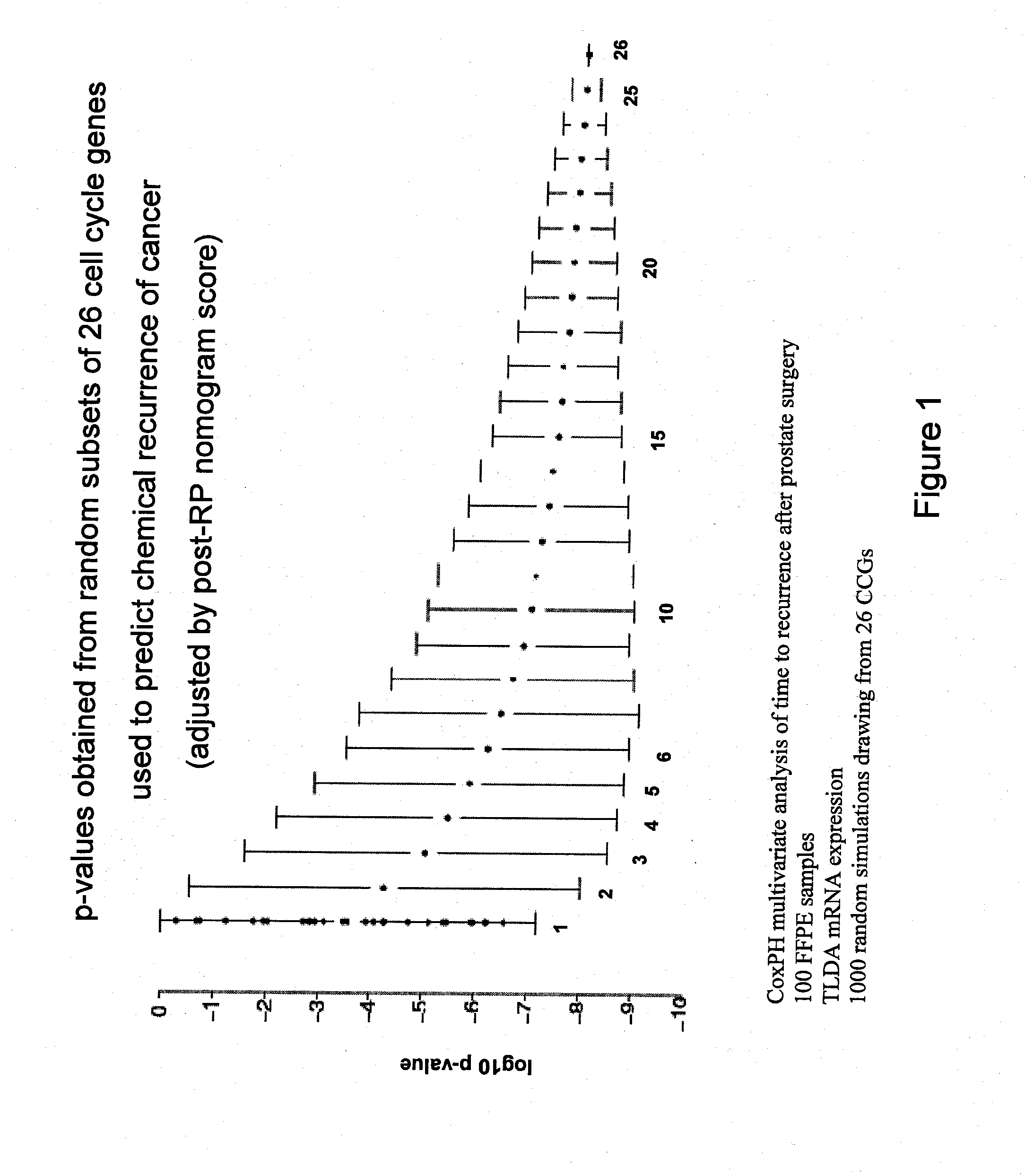
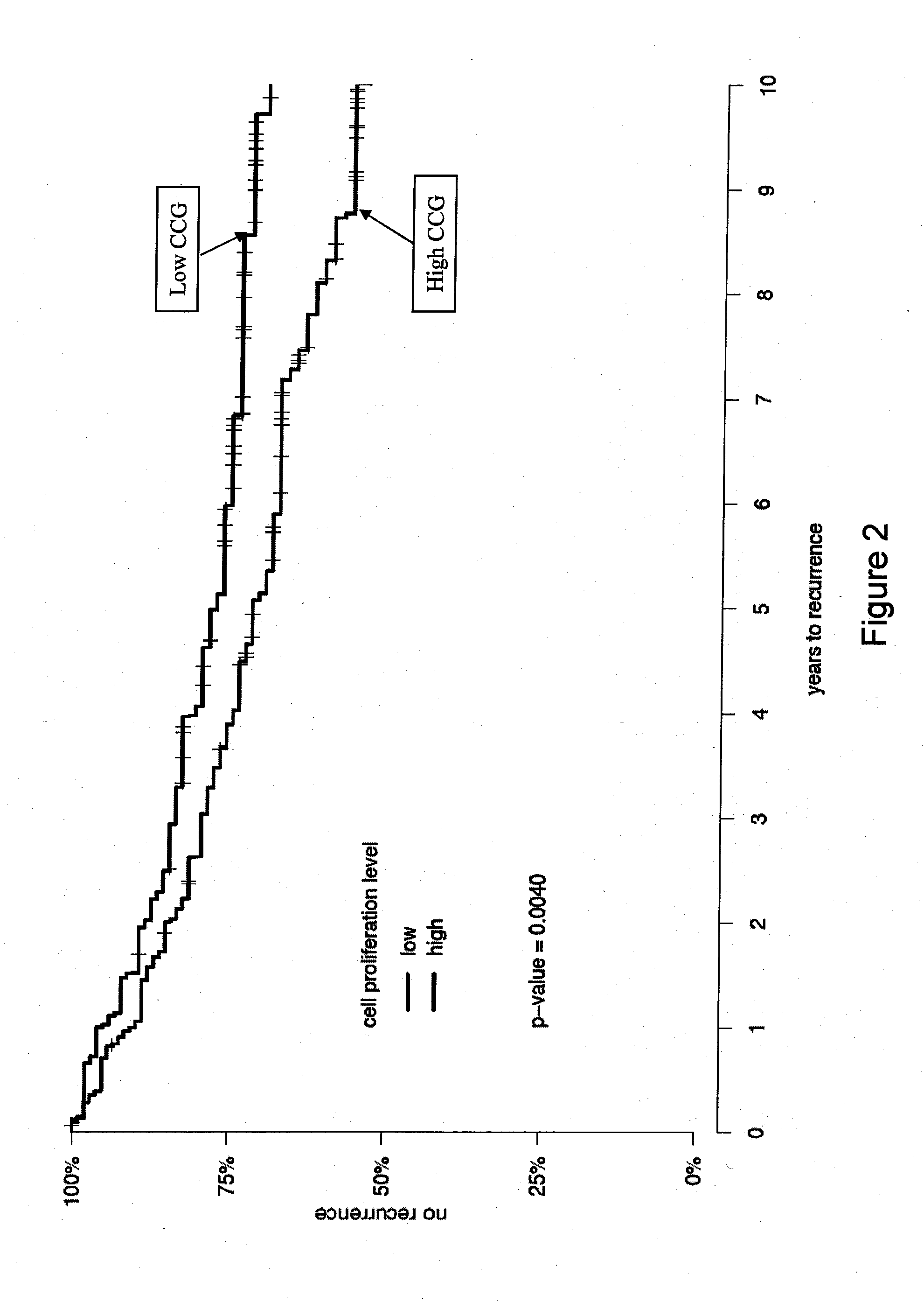
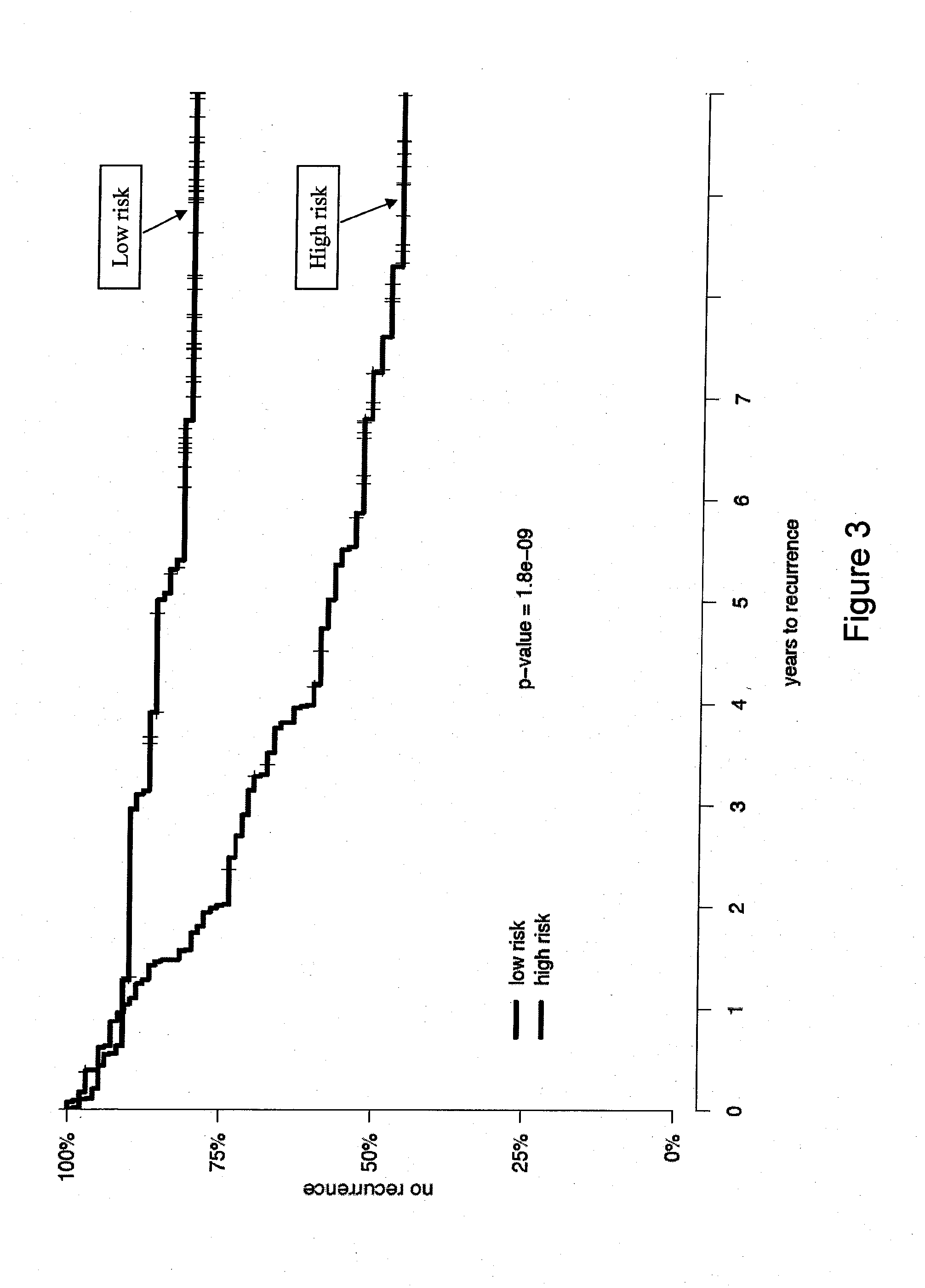
InactiveUS20120041274A1Improve predictive performanceIncreased likelihood of recurrenceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTumor BiomarkersBiologic marker
Biomarkers and methods using the biomarkers for the prediction of the recurrence risk of cancer in a patient are provided.
Owner:MYRIAD GENETICS
Biomarkers and methods of treatment
InactiveUS20120089541A1Effective treatmentIncreased riskOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderTumor BiomarkersBiologic marker
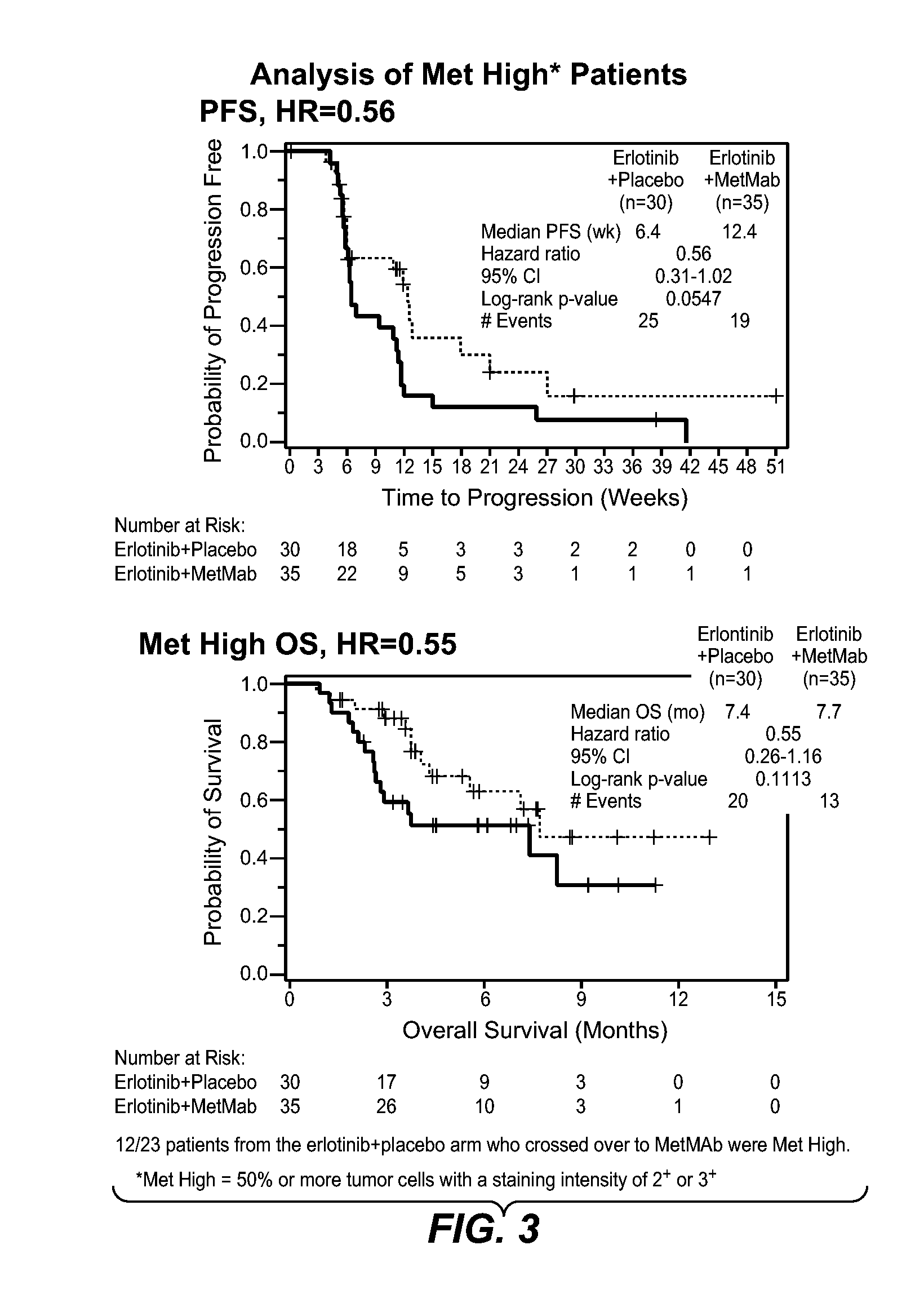
The present invention concerns cancer biomarkers. In particular, the invention concerns c-met as biomarkers for patient selection and patient prognosis in cancer, as well as methods of therapeutic treatment, articles of manufacture and methods for making them, diagnostic kits, methods of detection and methods of advertising related thereto.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Early detection and prognosis of colon cancers
InactiveCN101688239ASugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenes mutationTumor specific
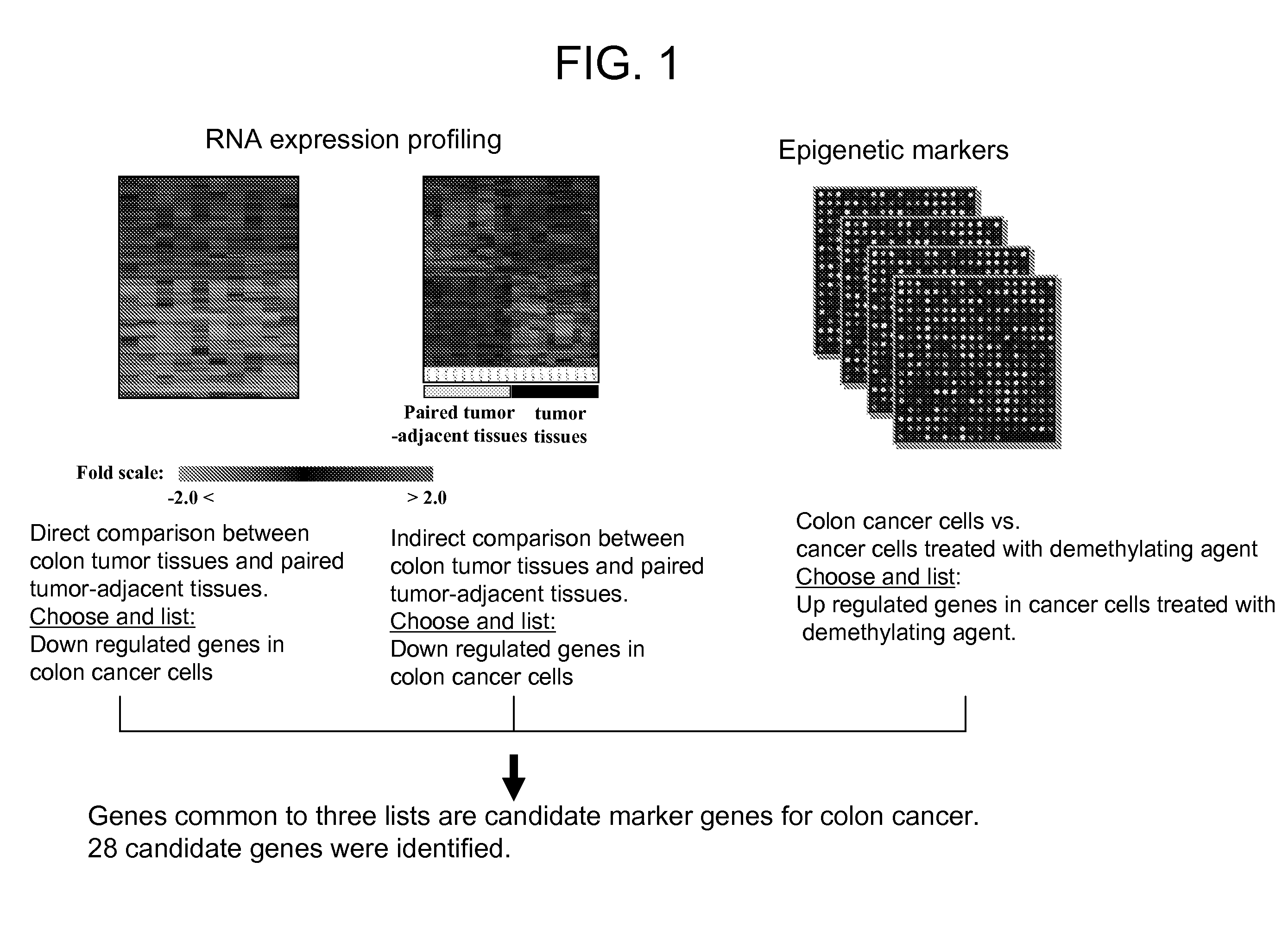
We have developed a transcriptome-wide approach to identify genes affected by promoter CpG island hypermethylation and transcriptional silencing in colorectal cancer (CRC). By screening cell lines andvalidating tumor specific hypermethylation in a panel of primary human CRC samples, we estimate that nearly 5% of all known genes may be promoter methylated in an individual tumor. When directly compared to gene mutations, we find a much larger number of genes hypermethylated in individual tumors, and much higher frequency of hypermethylation within individual genes harboring either genetic or epigenetic changes. Thus, to enumerate the full spectrum of alterations in the human cancer genome, and facilitate the most efficacious grouping of tumors to identify cancer biomarkers and tailor therapeutic approaches, both genetic and epigenetic screens should be undertaken. The genes we identified can be used inter alia diagnostically to detect cancer, pre-cancer, and likelihood of developing cancer.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
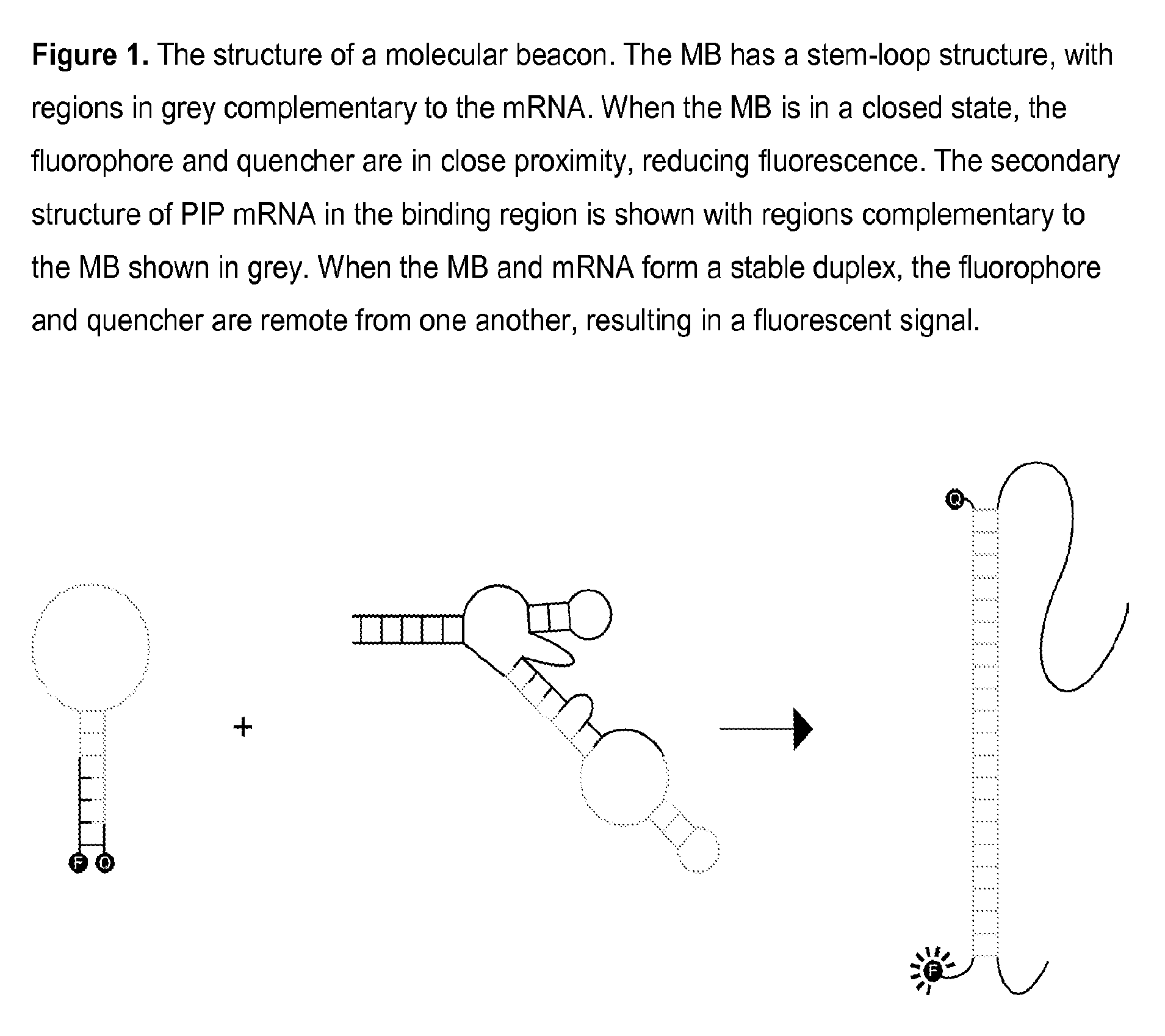
Molecular beacon based assay for the detection of biomarkers for breast cancer metastasis
InactiveUS9297047B2RobustnessShort analysis timeSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBreast cancer metastasisSerum ige
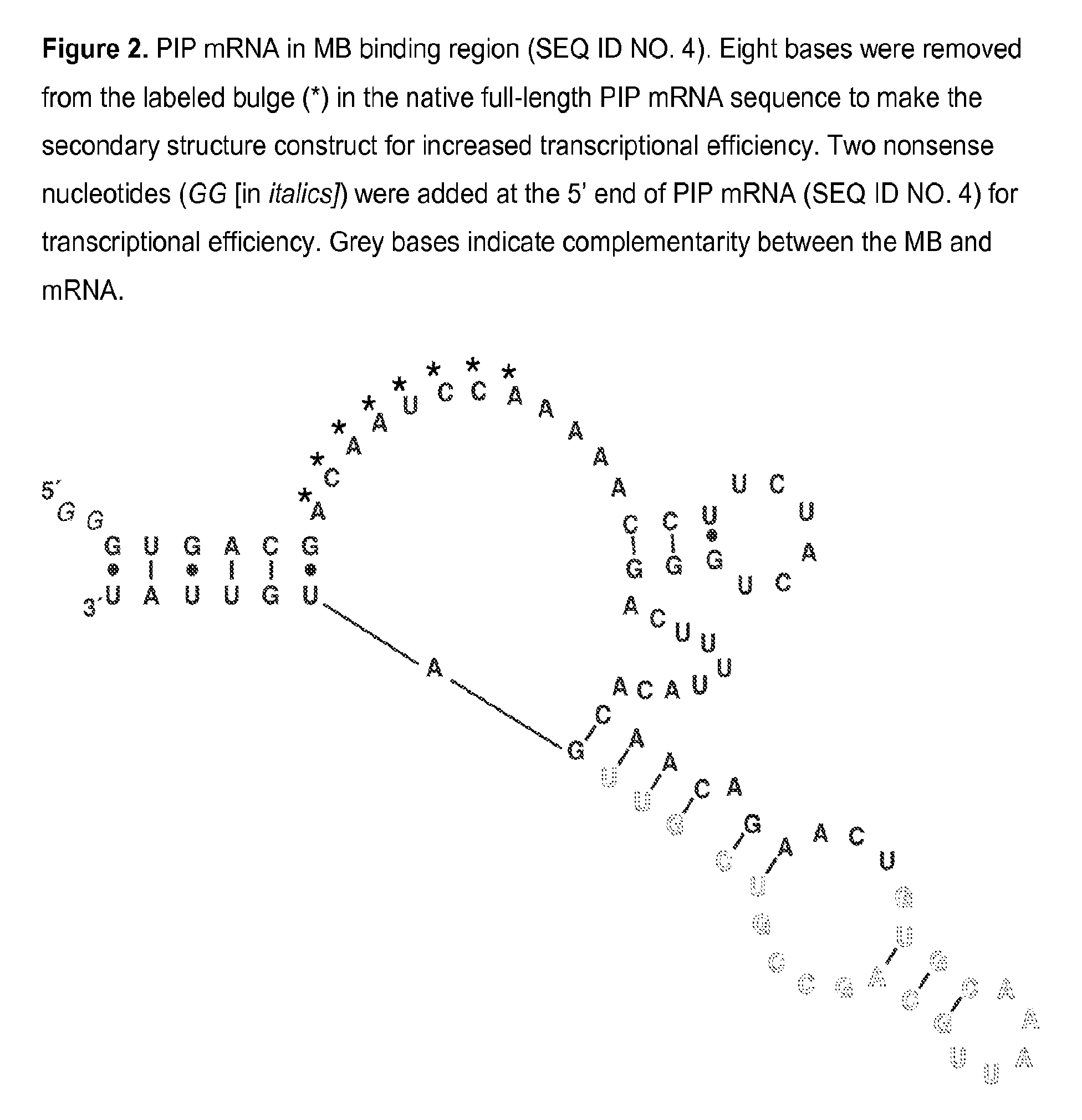
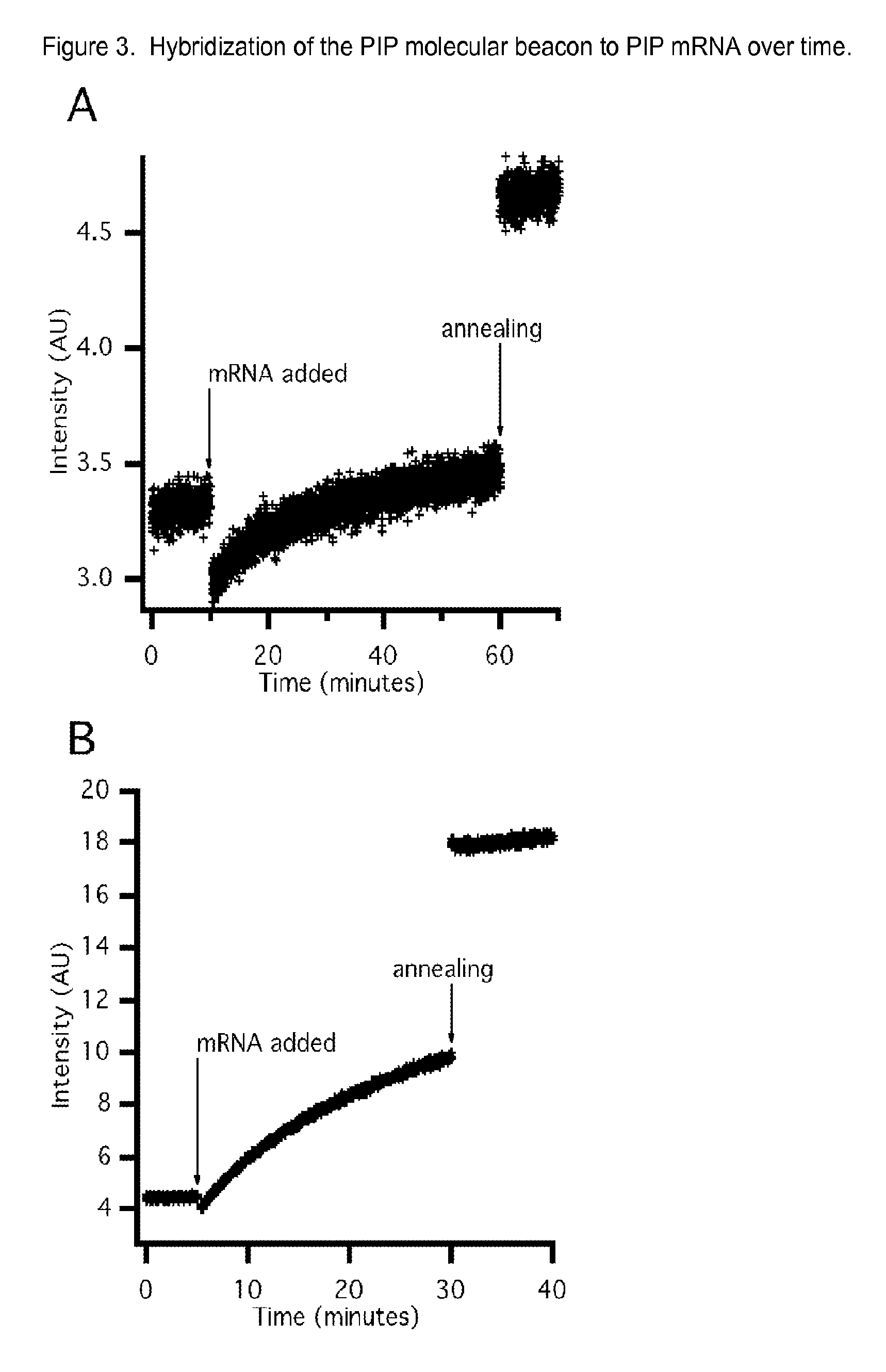
The invention encompasses molecular beacon (MB) probes for monitoring the presence of human breast cancer biomarkers and for the analysis of breast cancer metastasis. The molecular beacon is an oligonucleotide probe which sensitively and specifically identifies biomarker mRNA in samples, in the presence of serum, in minimal time using fluorescence detection. The molecular beacons may be comprised in kits for the detection / quantitation of cancer biomarkers in clinical samples. The invention provides improvements in simplicity, accuracy, and speed over current methods, which could allow for improved patient treatment and prognoses.
Owner:FURCHAK JENNIFER +2
Device for capture, enumeration, and profiling of circulating tumor cells
InactiveUS20120100560A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSpatial mappingBiology
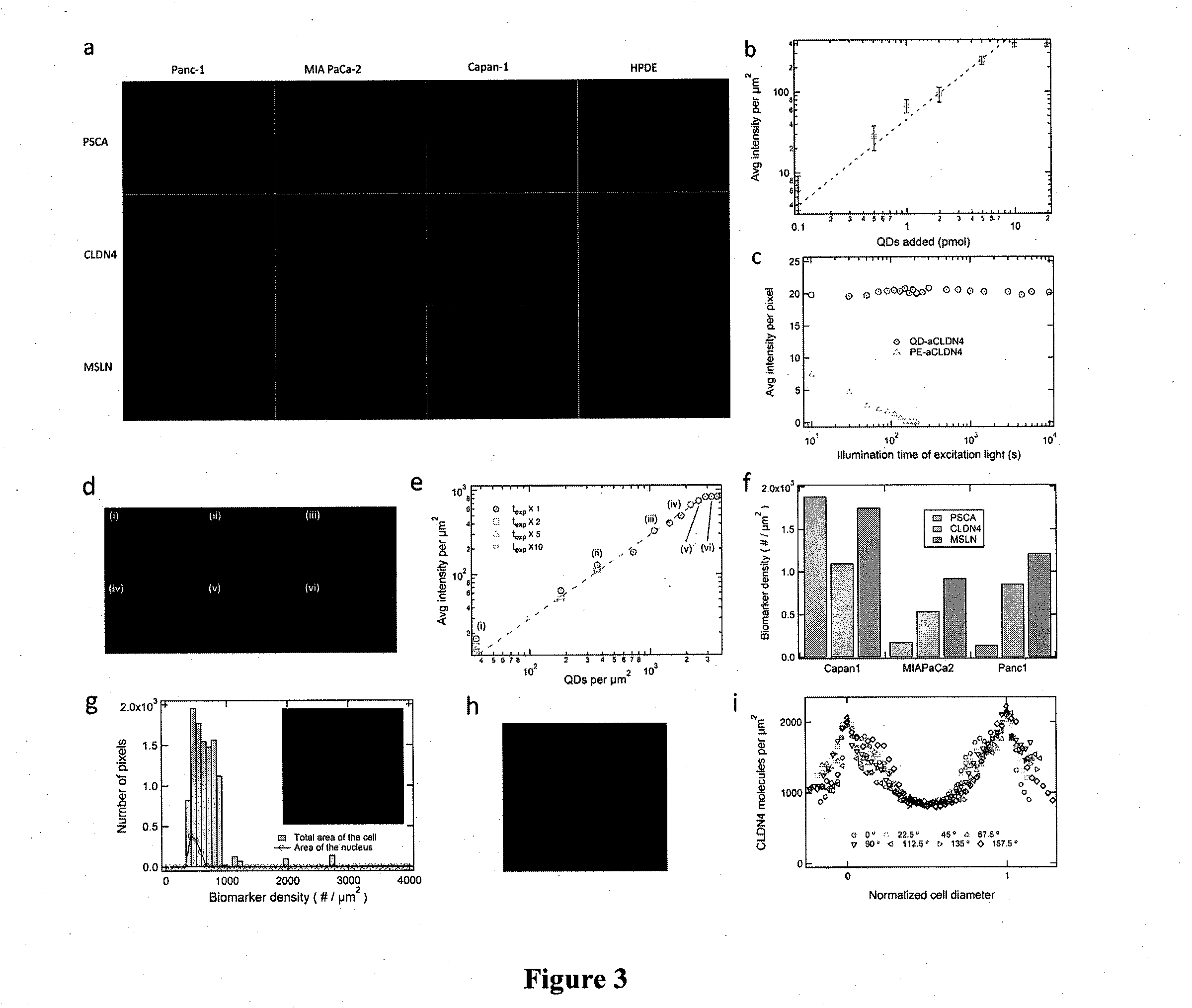
Applications in nanomedicine, such as diagnostics and targeted therapeutics, rely on the detection and targeting of membrane biomarkers. The present invention, in one embodiment, utilizes quantitative profiling, spatial mapping, and multiplexing of cancer biomarkers using functionalized quantum dots. This approach provides highly selective targeting molecular markers for pancreatic cancer with extremely low levels of non-specific binding and provides quantitative spatial information of biomarker distribution on a single cell, which is important since tumors cell populations are inherently heterogeneous. The quantitative measurements (number of molecules per square micron) is validated using flow cytometry and demonstrated using multiplexed quantitative profiling using color-coded quantum dots.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Biomarkers associated with brm inhibition
ActiveUS20160032402A1Simple designMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningTumor BiomarkersOncology
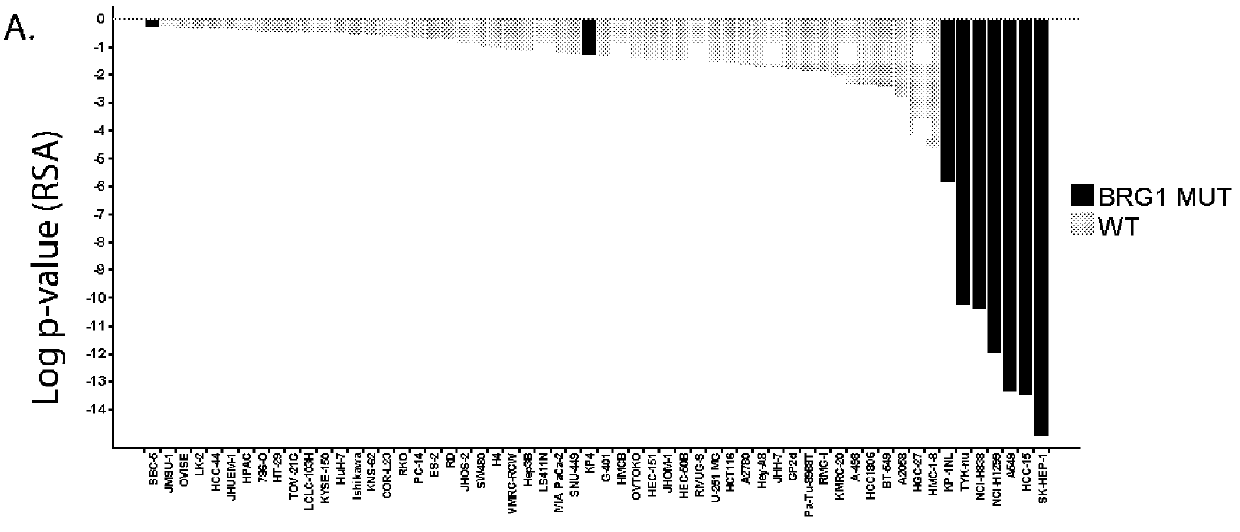
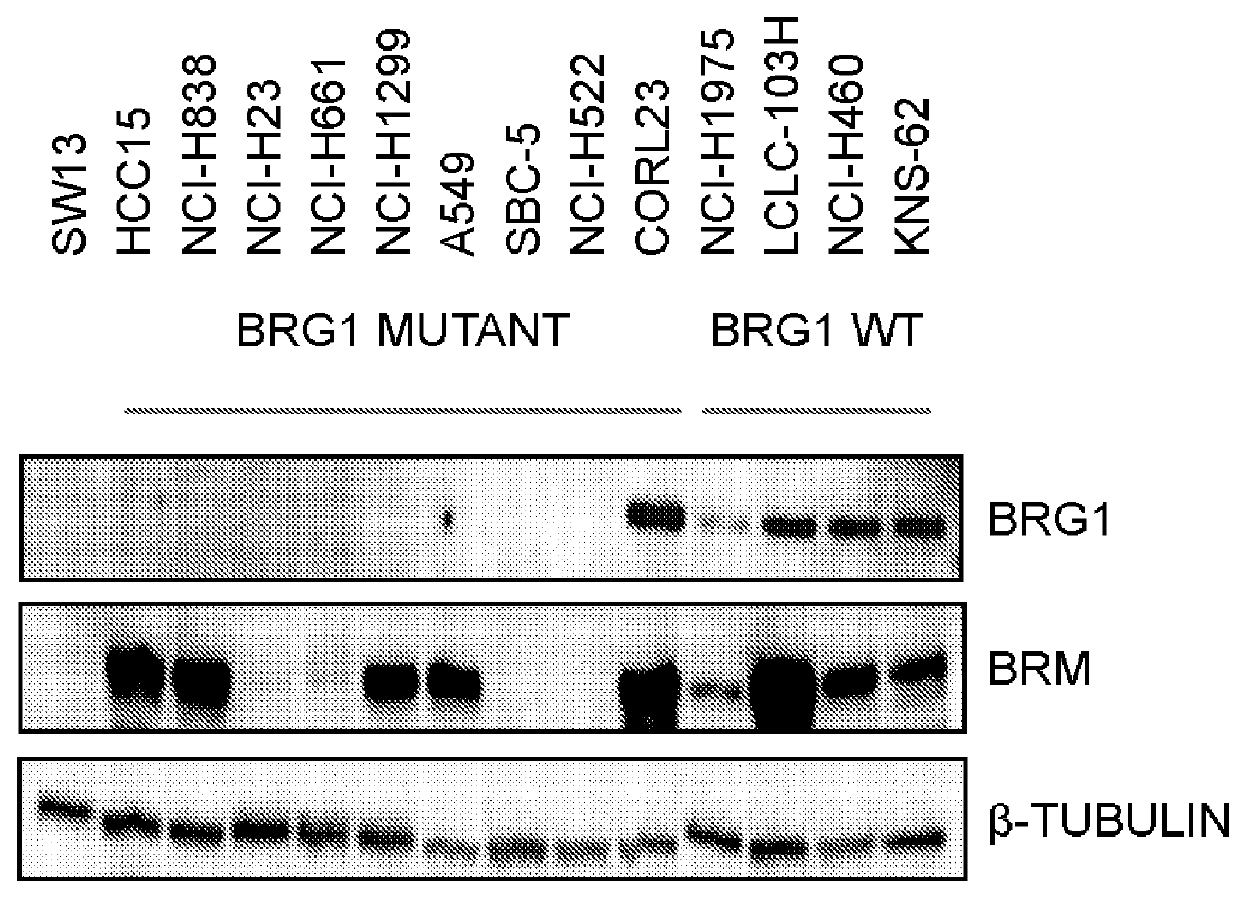
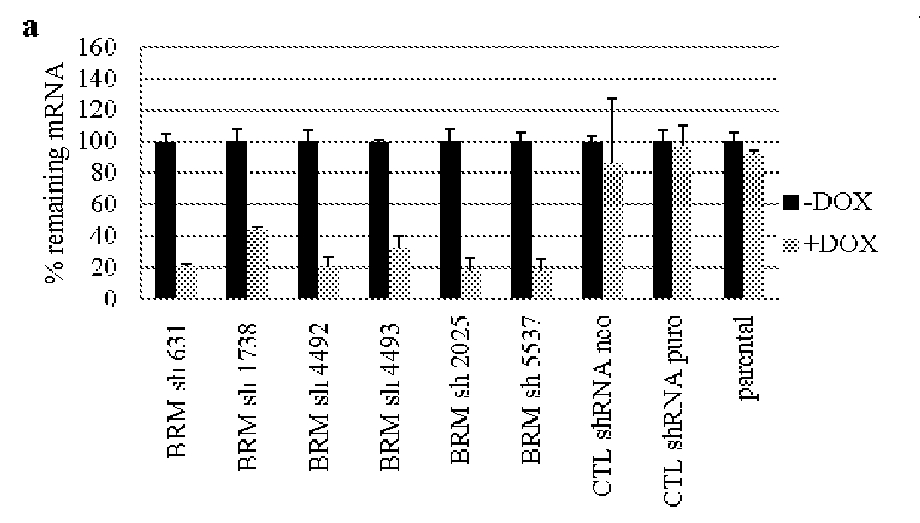
The invention provides methods of detecting cancer biomarkers, such as one or more SWI / SNF complex mutations, in order to determine a cancer subject's amenability to therapeutic treatment with a BRM inhibitor. Kits, methods of screening for candidate BRM inhibitors, and associated methods of treatment are also provided.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Colon cancer biomarkers
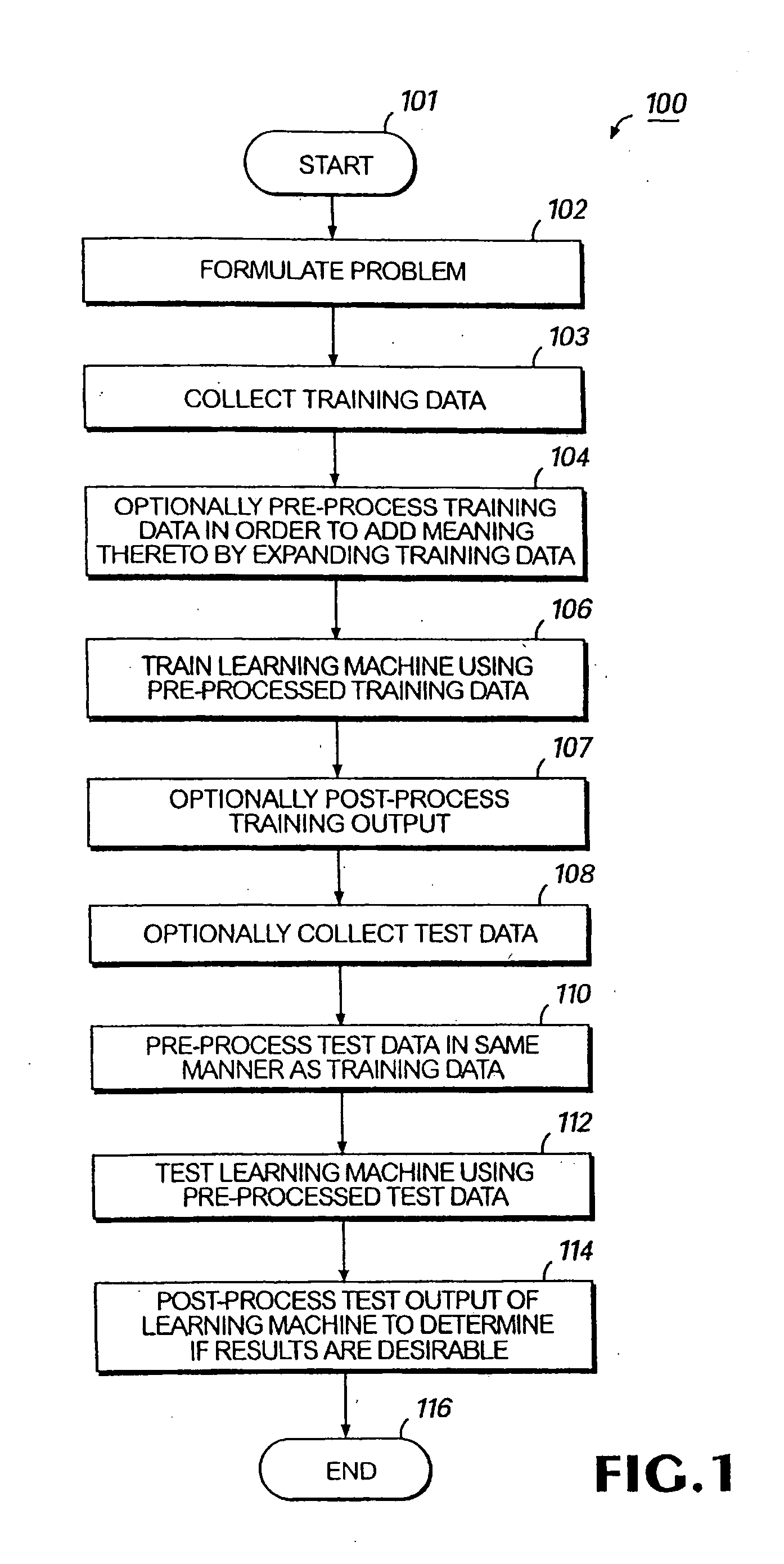
InactiveUS20050165556A1Improve abilitiesGreat dimensionalityImage analysisKernel methodsLearning machineFuzzy support vector machine
Owner:HEALTH DISCOVERY CORP +1
Cancer Biomarkers and Methods of Use
InactiveUS20150072349A1Increase probabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisPancreas CancersTumor Biomarkers
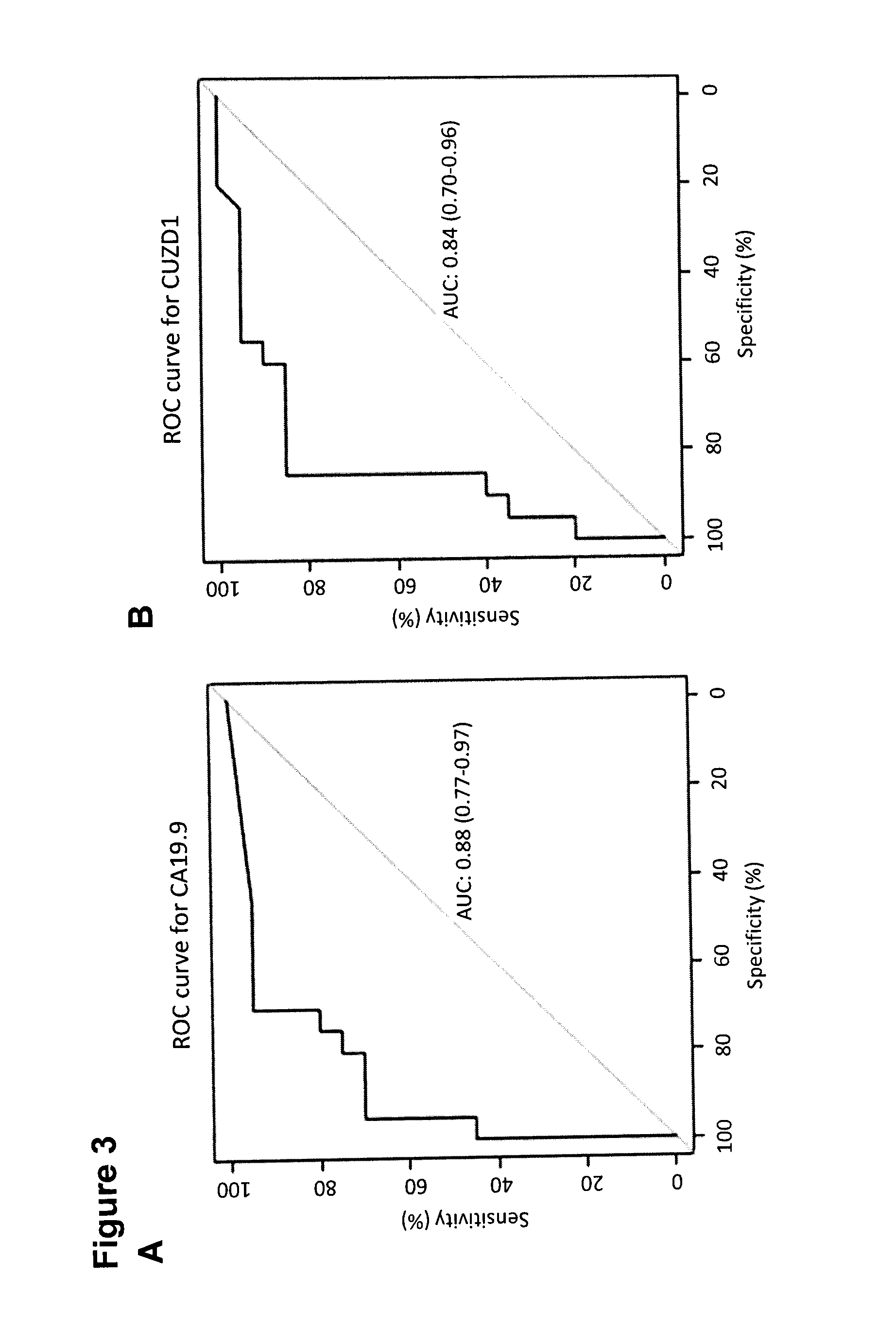
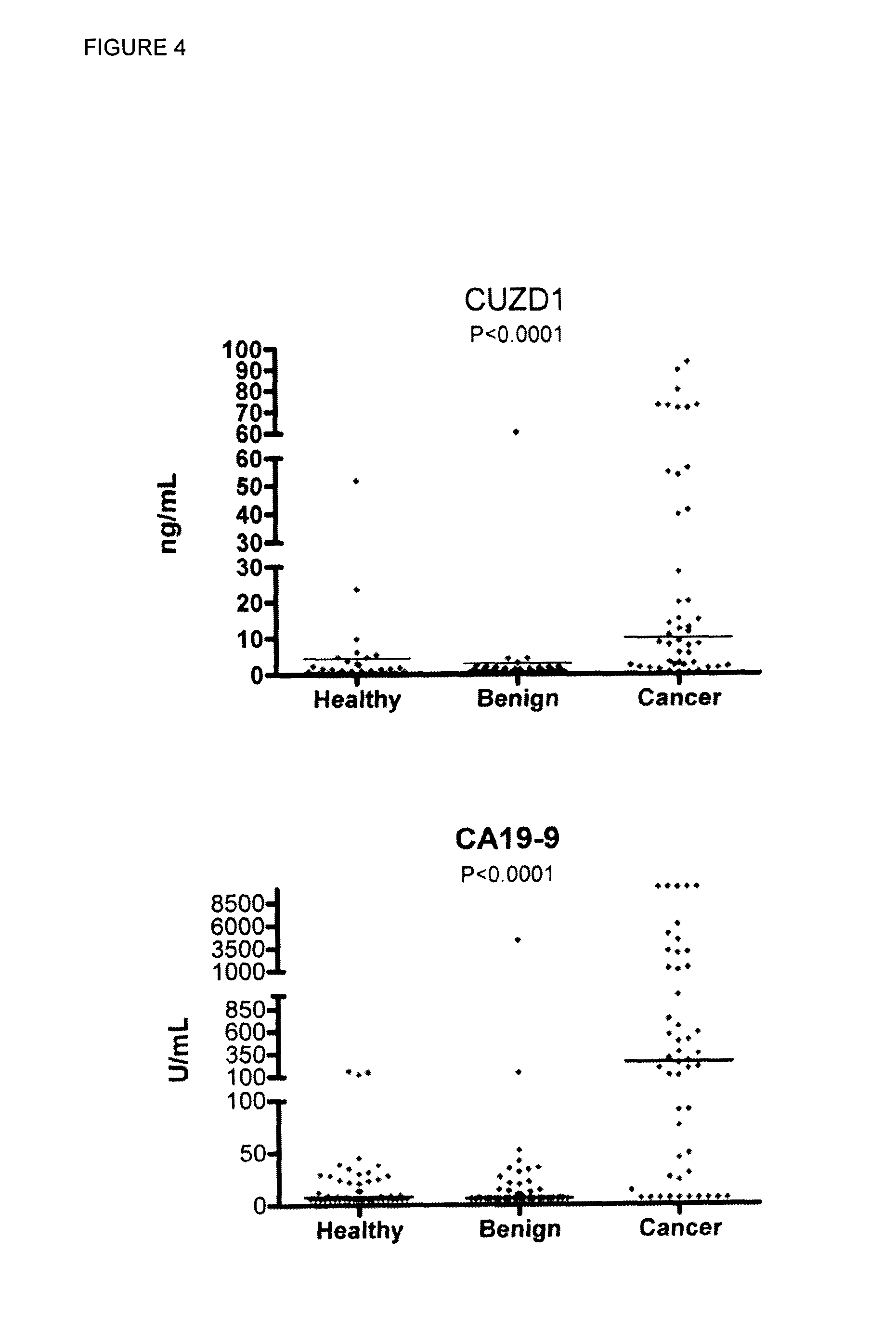
A method of evaluating a probability a subject has a cancer, diagnosing a cancer and / or monitoring cancer progression comprising: a. measuring an amount of a biomarker selected from the group consisting of CUZD1 and / or LAMC2 and / or the group CUZD1, LAMC2, AQP8, CELA2B, CELA3B, CTRB1, CTRB2, GCG, IAPP, INS, KLK1, PNLIPRP1, PNLIPRP2, PPY, PRSS3, REG3G, SLC30A8, KLK3, NPY, PSCA, RLN1, SLC45A3, DSP, GP73, DSG2, CEACAM7, CLCA1, GPA33, LEFTY1, ZG16, IRX5, LAMP3, MFAP4, SCGB1A1, SFTPC, TMEM100, NPY, PSCA, RLN1 and / or SLC45A3 in a test sample from a subject with cancer; wherein the cancer is pancreas cancer if CUZD1, LAMC2, AQP8, CELA2B, CELA3B, CTRB1, CTRB2, GCG, LAPP, INS, KLK1, PNLIPRP1, PNLIPRP2, PPY, PRSS3, REG3G, SLC30A8, DSP, GP73 and / or DSG2 is selected; the cancer is colon cancer if CEACAM7, CLCA1, GPA33, LEFTY1 and / or ZG16 is selected, the cancer is lung cancer if IRX5, LAMP3, MFAP4, SCGB1A1, SFTPC and / or TMEM100 is selected; or the cancer is prostate cancer if NPY, PSCA, RLN1 and / or SLC45A3 is selected; b. comparing the measured amount to a control and detecting an increase in the amount of the biomarker compared to control; and c. identifying the subject as having or having an increased probability of having the cancer when an increase in the biomarker compared to control is detected.
Owner:UNIV HEALTH NETWORK
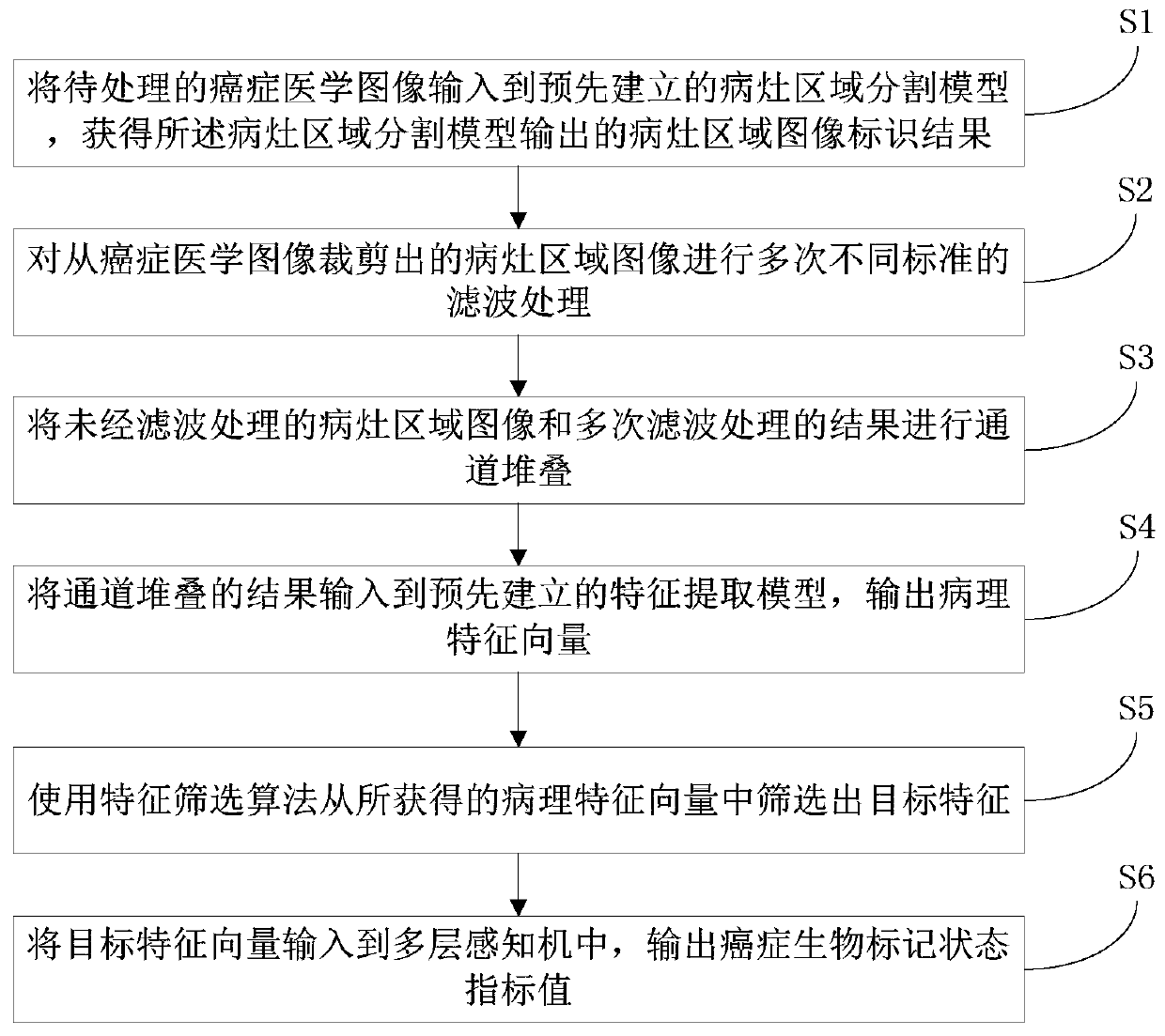
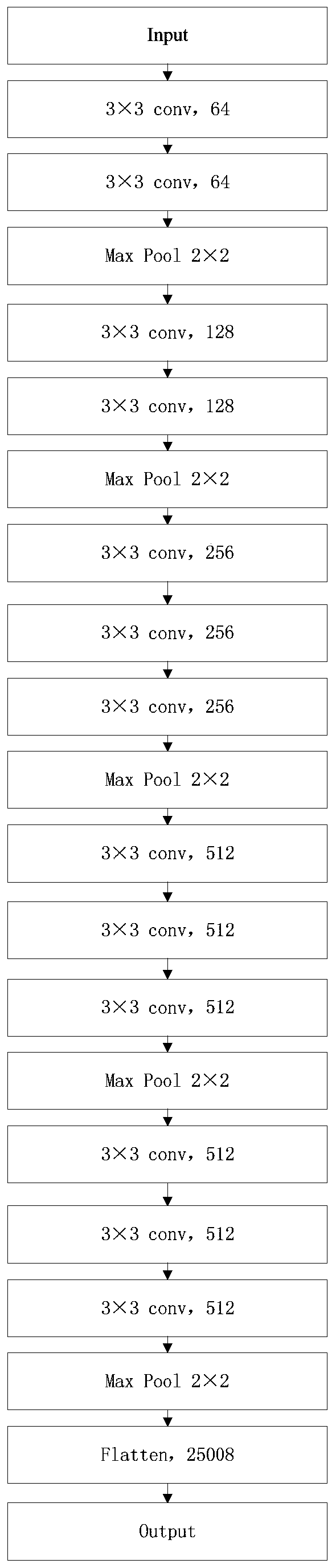
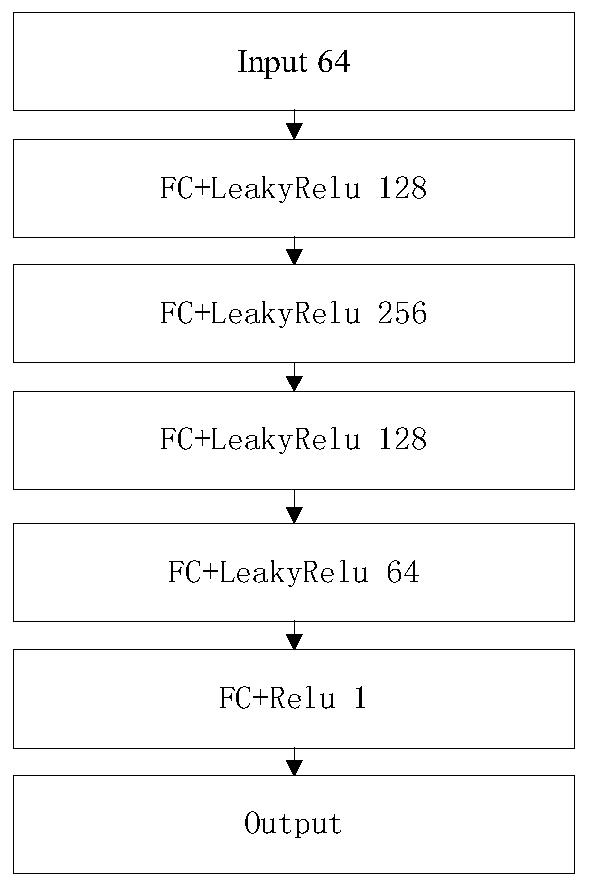
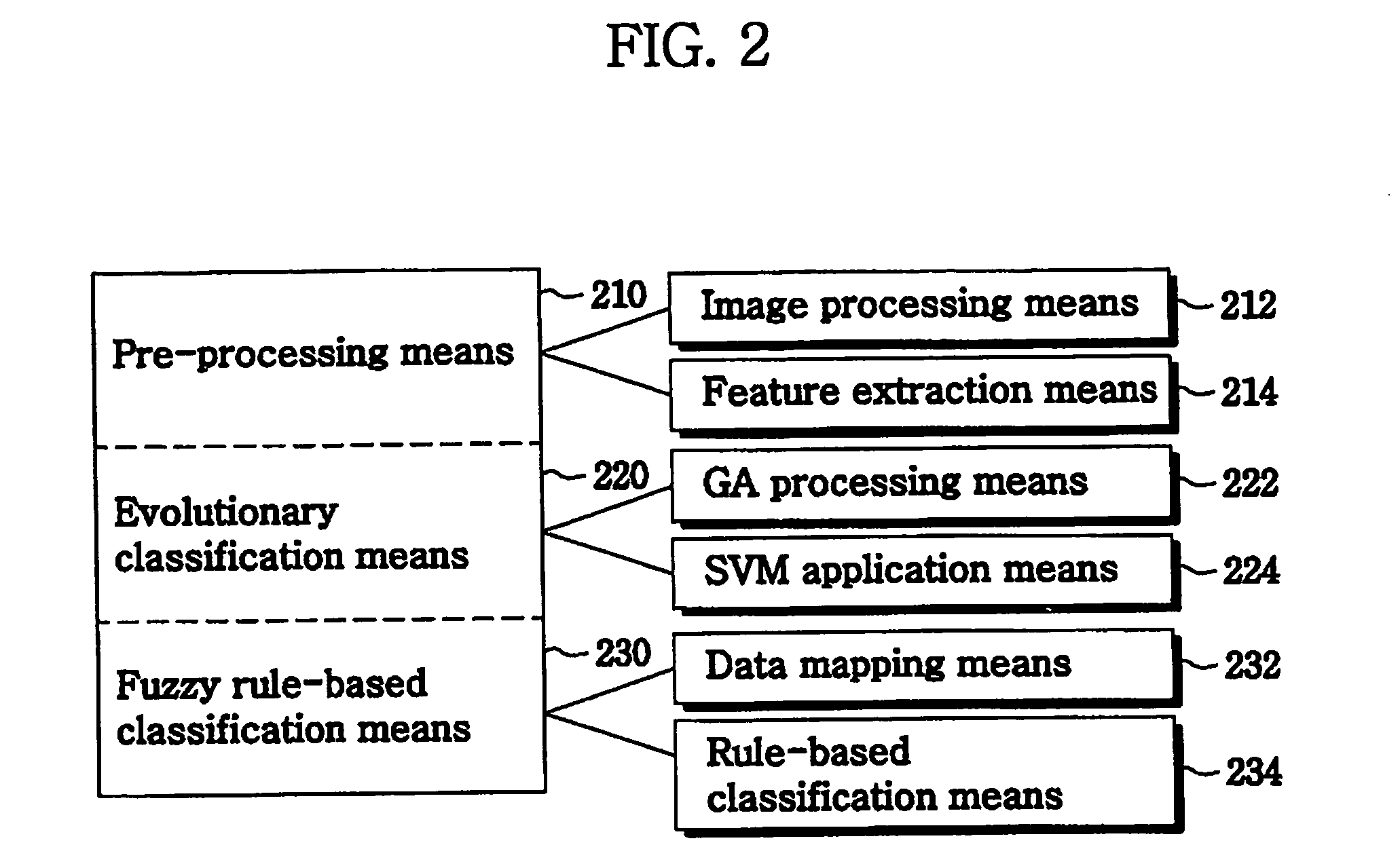
Cancer medical image data processing method, system and device and storage medium
InactiveCN109785300AImprove recognition efficiencyImprove cutting efficiencyImage analysisNeural architecturesFeature vectorImaging processing
The invention discloses a cancer medical image data processing method, system, device and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: inputting a to-be-processed cancer medical image into a pre-established focus area segmentation model, obtaining a focus area image identification result output by the focus area segmentation model, filtering processing of different standards is carried out on the focus area image cut from the cancer medical image for multiple times, channel stacking is carried out, a channel stacking result is input into a pre-established feature extraction model, and a feature screening algorithm is used for screening out target features from the obtained pathological feature vectors; inputting the target characteristics into a multilayer perceptron to obtain cancer biomarker state index values output by the multilayer perceptron, and the like. According to the method, the focus area on the cancer medical image can be automatically identified, and the focus area image is cut out, so that the identification and cutting efficiency and accuracy are greatly improved. The method is widely applied to the technical field of image processing.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
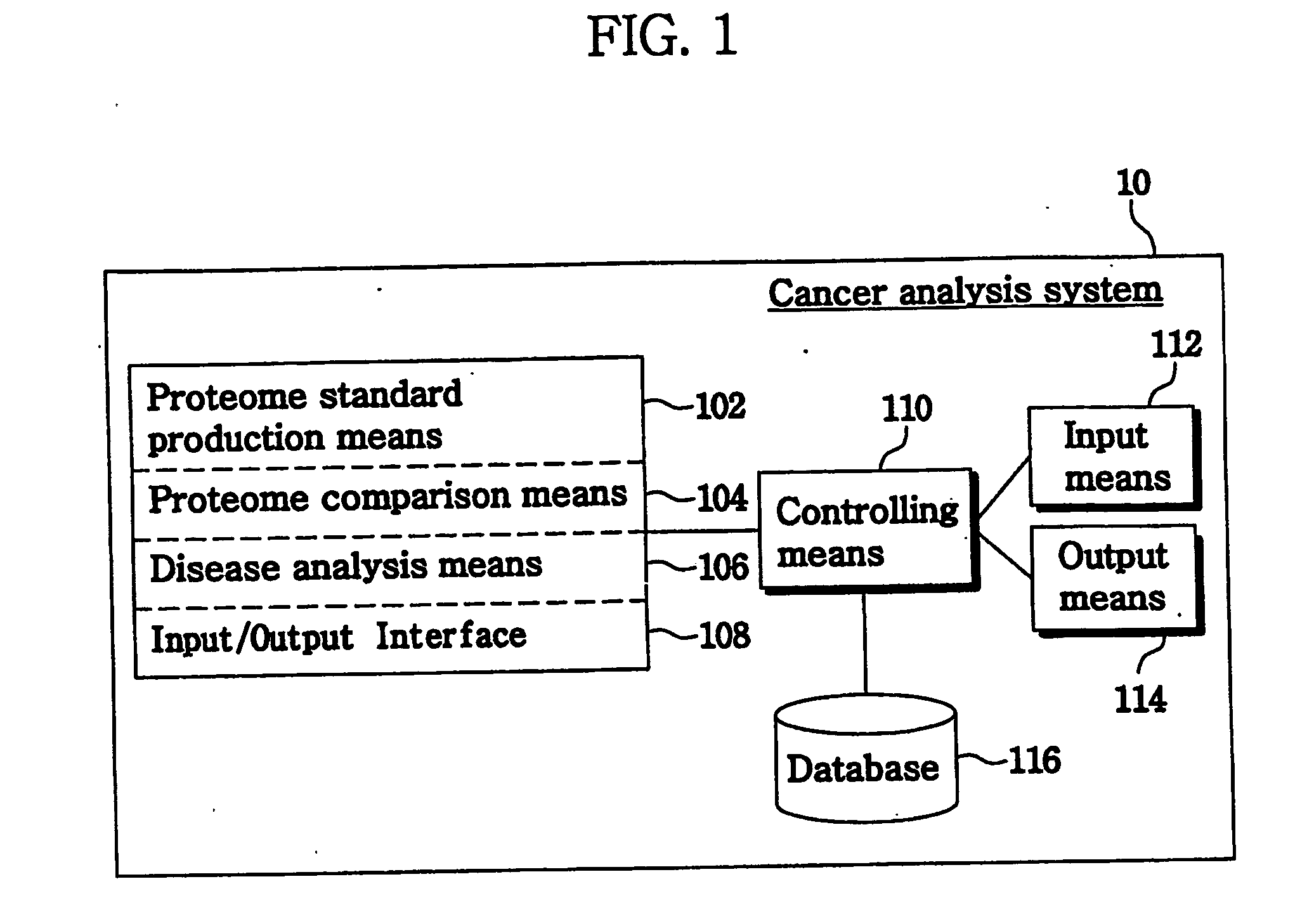
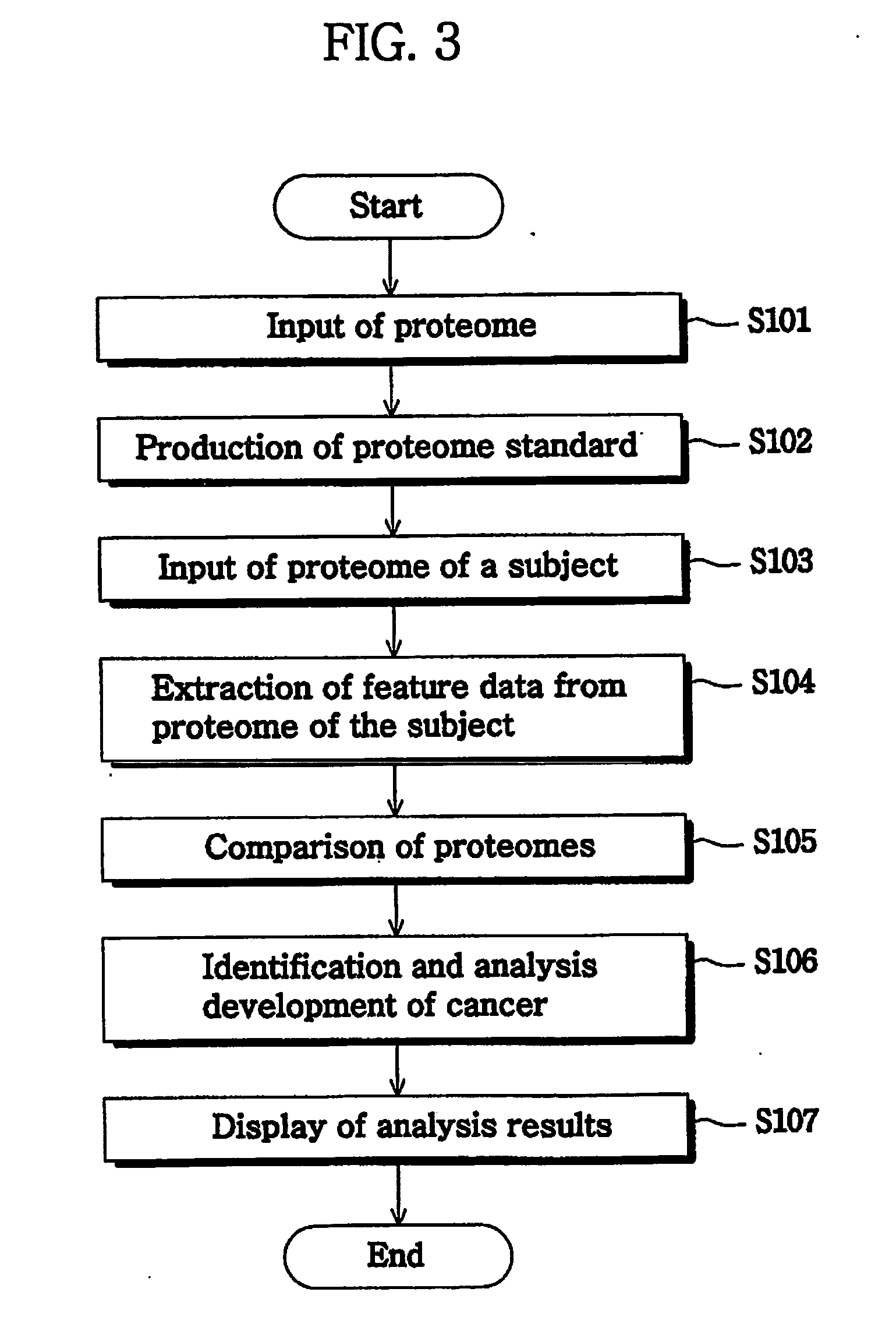
Method and system for analysis of cancer biomarkers using proteome image mining
InactiveUS20070072250A1The analysis result is accurateEasy to distinguishBiostatisticsProteomicsTumor BiomarkersImaging technique
The present invention provide a system and a method for detection of cancer, by producing a serum proteome standard by an image mining technique, and provide cancer-specific biomarkers. Disclosed is a method of analyzing cancer, comprising the steps of transforming serum proteomes from normal individuals and individuals having cancer into two-dimensional images, and constructing a database consisting of the proteome standard by an image mining technique; inputting a serum proteome from a subject of interest, transforming the serum proteome into a image and comparing the structure of the serum proteome pattern of the subject with the proteome standard and determining whether the serum proteome of the subject is normal or abnormal. The system and method for cancer analysis facilitates detection of cancer by constructing a database from a plurality of serum proteome using an image technique and comparing serum proteome of a subject with a proteome standard.
Owner:BIOINFRA
Novel method for the detection of cancer biomarkers in cervical specimens
InactiveUS20050136405A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisTumor BiomarkersProper treatment
Owner:CYTYC CORP
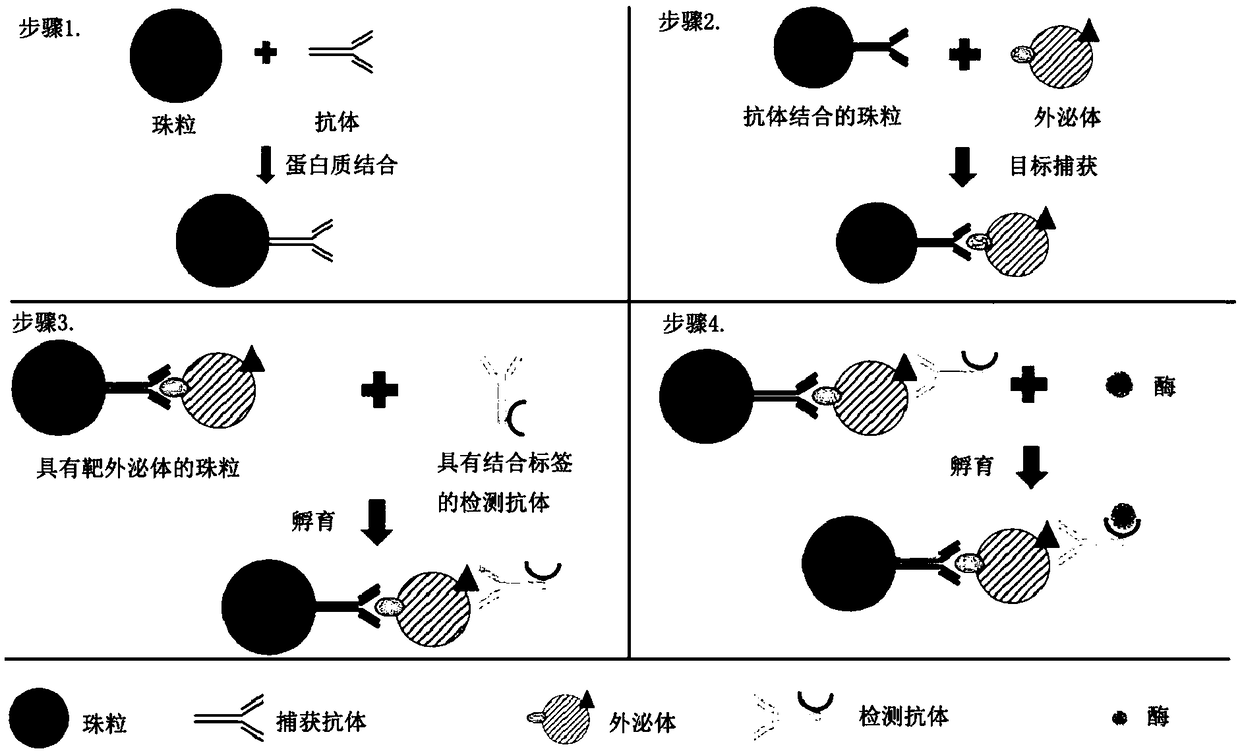
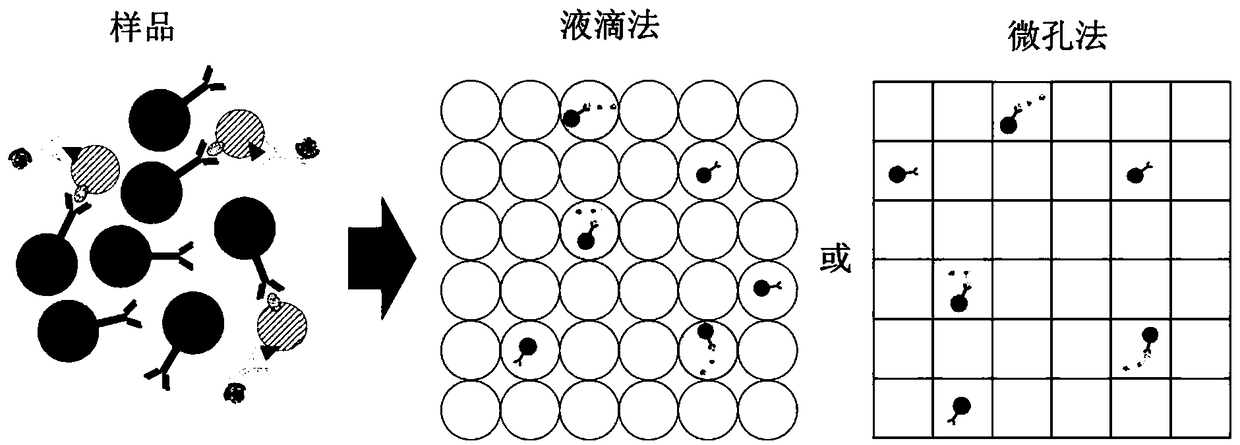
Analysis of exosomes and methods of diagnosing cancer
InactiveCN109490528ABiological material analysisMedical automated diagnosisTumor BiomarkersCancers diagnosis
The invention relates to quantification, isolation, and characterization of exosomes. In some embodiments, exosomes can be quantified by contacting a sample with a capture bead comprising a bead and afirst binding agent, and a second binding agent. The first binding agent binds to a first biomolecule in the exosomes to produce a first complex and the second binding agent binds to a second biomolecule in the exosomes of the first complex to produce a second complex. The first complexes and the second complexes are quantified based on a detectable signal conjugated to the second binding agent.A microwell or a droplet generation is utilized to quantify the first complexes and the second complexes. In optional embodiments, quantification of the exosomes is used to diagnose a cancer in a subject. In such methods, the first and the second binding agents bind to cancer biomarkers present in the exosomes.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Early Detection and Prognosis of Colon Cancers
InactiveUS20080221056A1Organic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsGenes mutationBiomarker (petroleum)
We have developed a transcriptome-wide approach to identify genes affected by promoter CpG island hypermethylation and transcriptional silencing in colorectal cancer (CRC). By screening cell lines and validating tumor specific hypermethylation in a panel of primary human CRC samples, we estimate that nearly 5% of all known genes may be promoter methylated in an individual tumor. When directly compared to gene mutations, we find a much larger number of genes hypermethylated in individual tumors, and much higher frequency of hypermethylation within individual genes harboring either genetic or epigenetic changes. Thus, to enumerate the full spectrum of alterations in the human cancer genome, and facilitate the most efficacious grouping of tumors to identify cancer biomarkers and tailor therapeutic approaches, both genetic and epigenetic screens should be undertaken. The genes we identified can be used inter alia diagnostically to detect cancer, pre-cancer, and likelihood of developing cancer.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
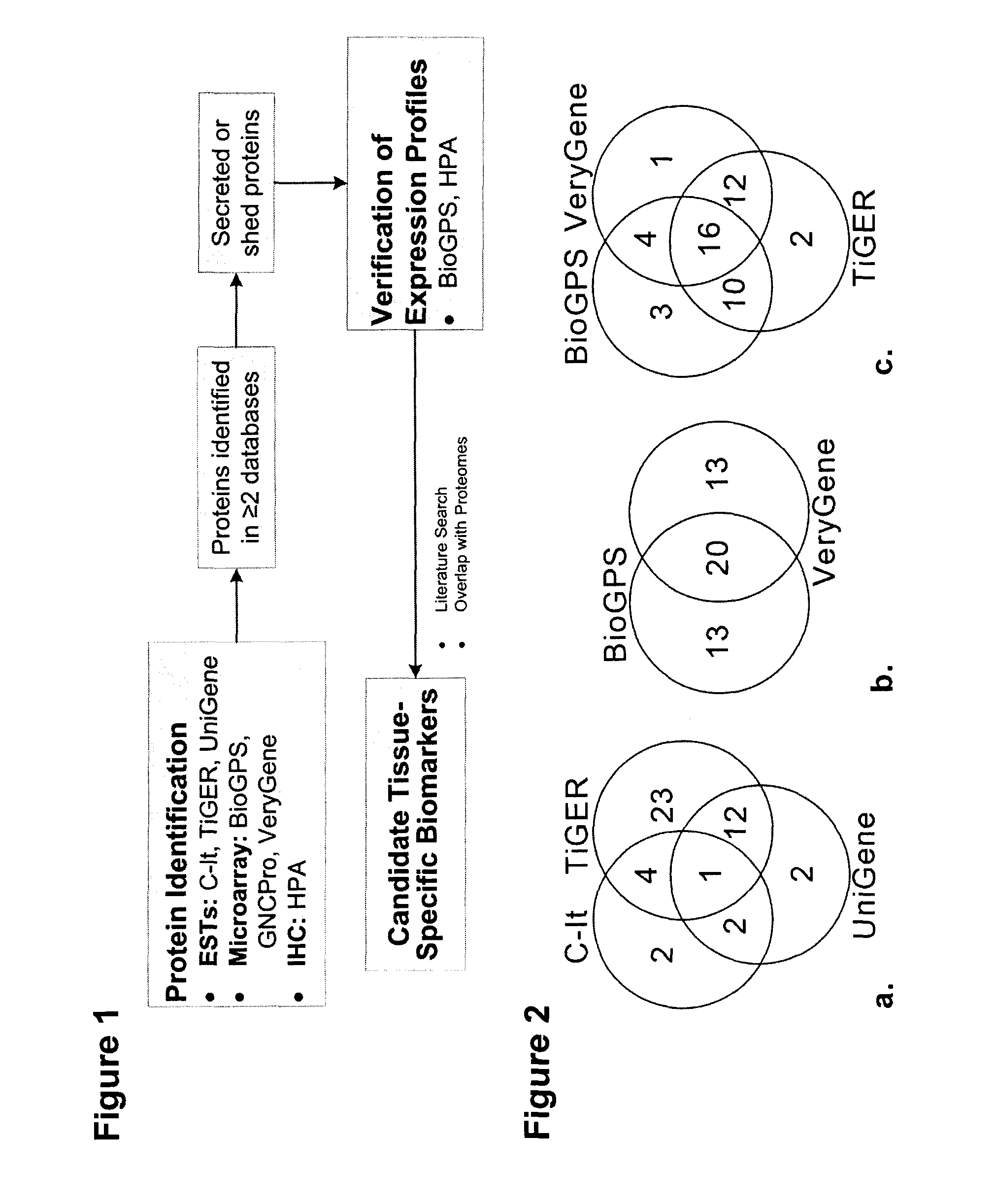
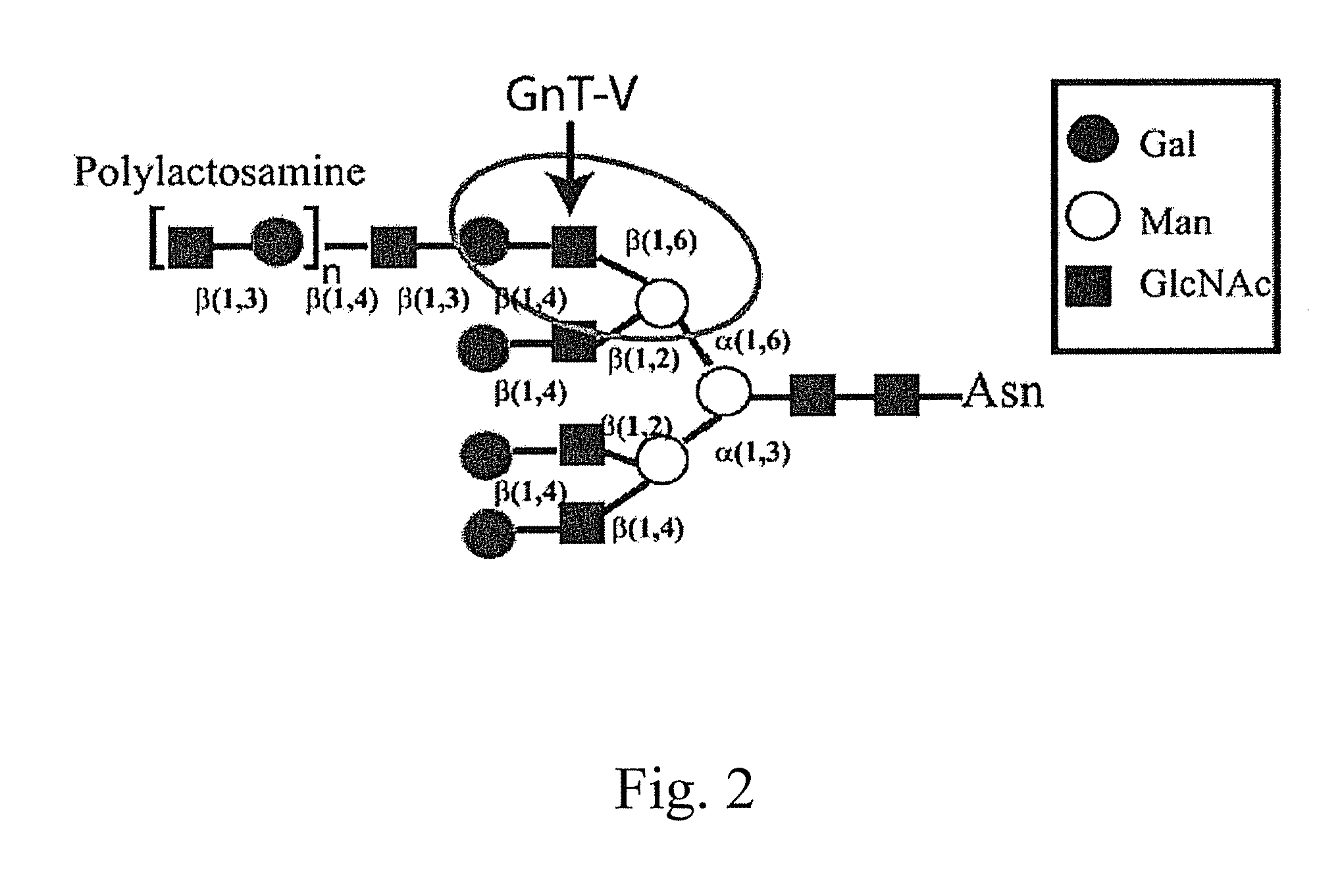
Glycoprotein cancer biomarker
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
Device and method for detection and identification of immunological proteins, pathogenic and microbial agents and cells
ActiveUS20130078620A1Low costReduce complexityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluid pressure measurementPsa antigenCancer cell
The present invention provides a method and device for detecting and quantifying the concentration of magnetic-responsive micro-beads dispersed in a liquid sample. Also provided is a method and microfluidic immunoassay pScreen™ device for detecting and quantifying the concentration of an analyte in a sample medium by using antigen-specific antibody-coated magnetic-responsive micro-beads. The methods and devices of the present invention have broad applications for point-of-care diagnostics by allowing quantification of a large variety of analytes, such as proteins, protein fragments, antigens, antibodies, antibody fragments, peptides, RNA, RNA fragments, functionalized magnetic micro-beads specific to CD4+, CD8+ cells, malaria-infected red blood cells, cancer cells, cancer biomarkers such as prostate specific antigen and other cancer biomarkers, viruses, bacteria, and other pathogenic agents, with the sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of bench-top laboratory-based assays.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
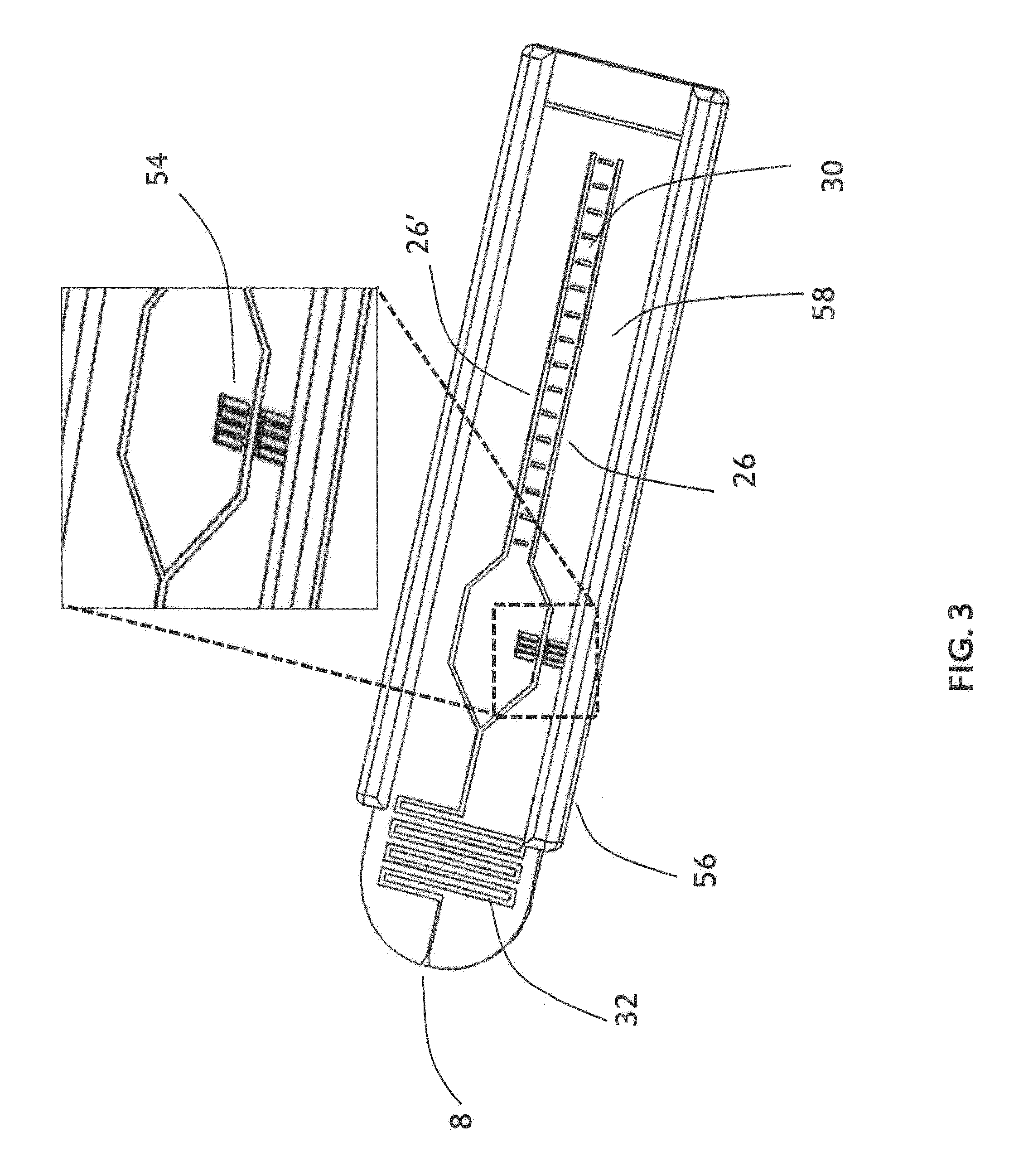
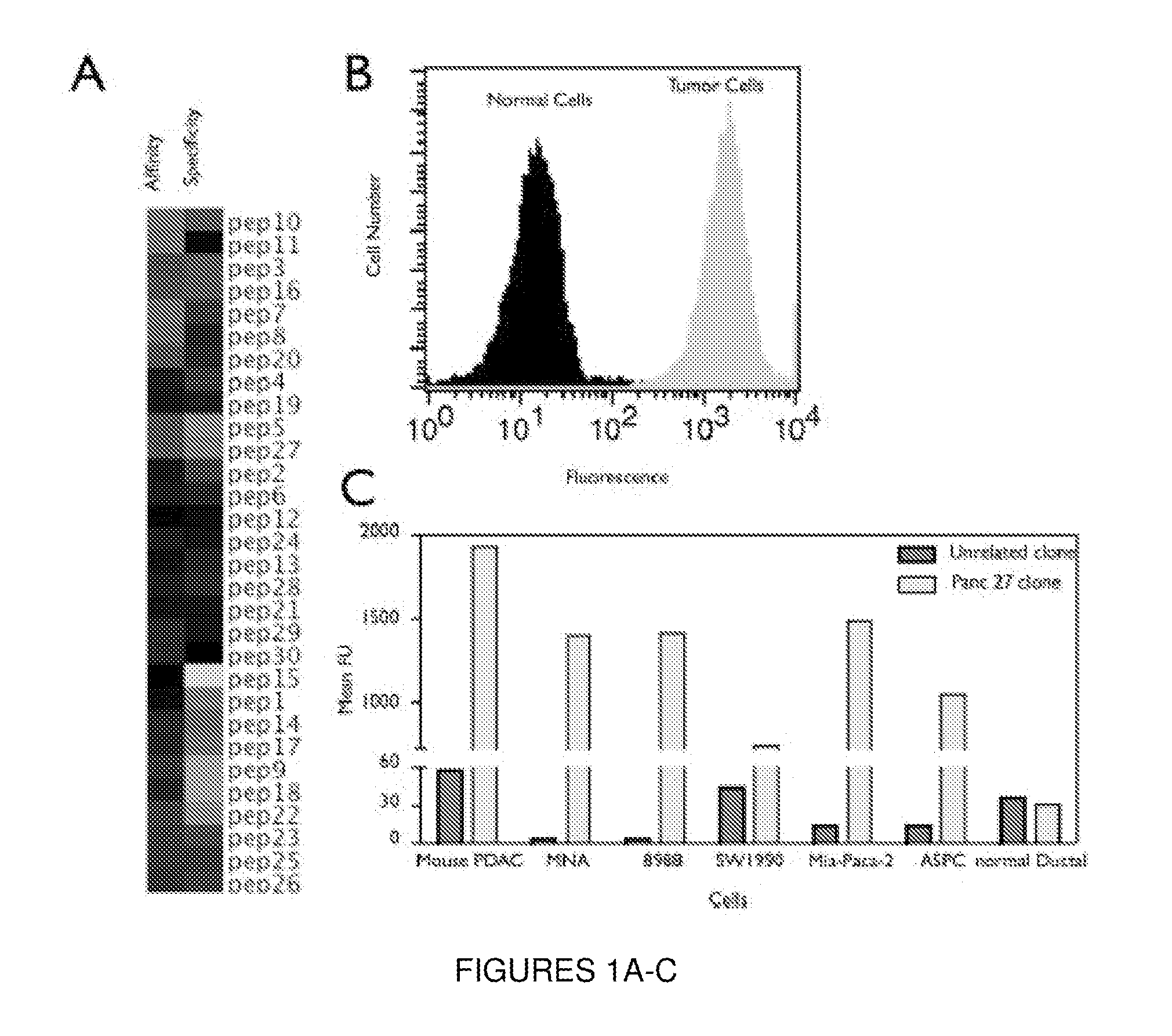
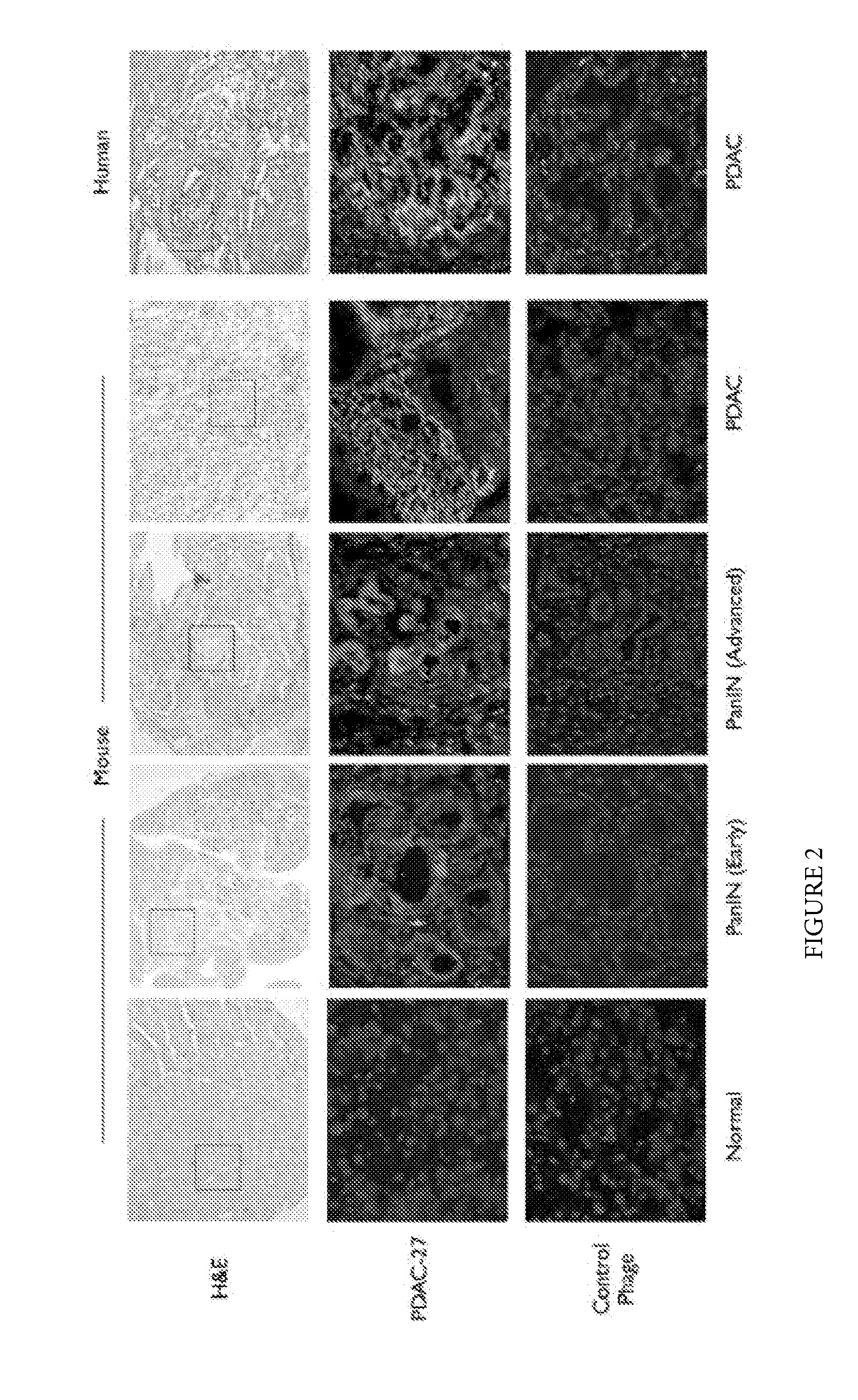
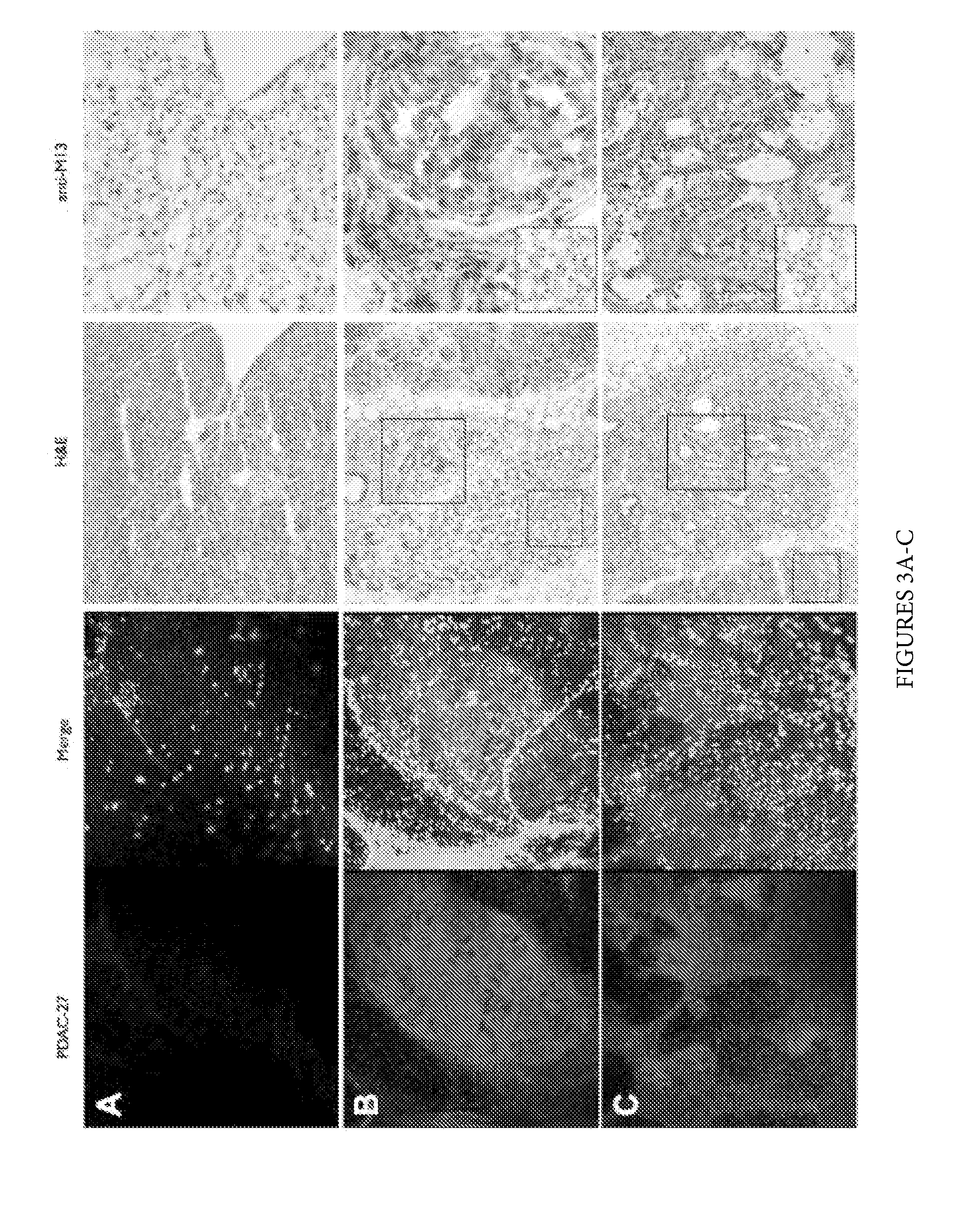
Plectin-1 Targeted Agents for Detection and Treatment of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
ActiveUS20150151010A1Fast wayQuick identificationPeptide/protein ingredientsGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsCancer cellTumor Biomarkers
Described herein are compositions and methods for cancer cell biomarkers, such as pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cell biomarkers, and binding molecules for diagnosis and treatment of cancer, e.g., PDAC. Methods of identifying “accessible” proteomes are disclosed for identifying cancer biomarkers, such as plectin-1, a PDAC biomarker. Additionally, imaging compositions are provided comprising magnetofluorescent nanoparticles conjugated to peptide ligands for identifying PDACs.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
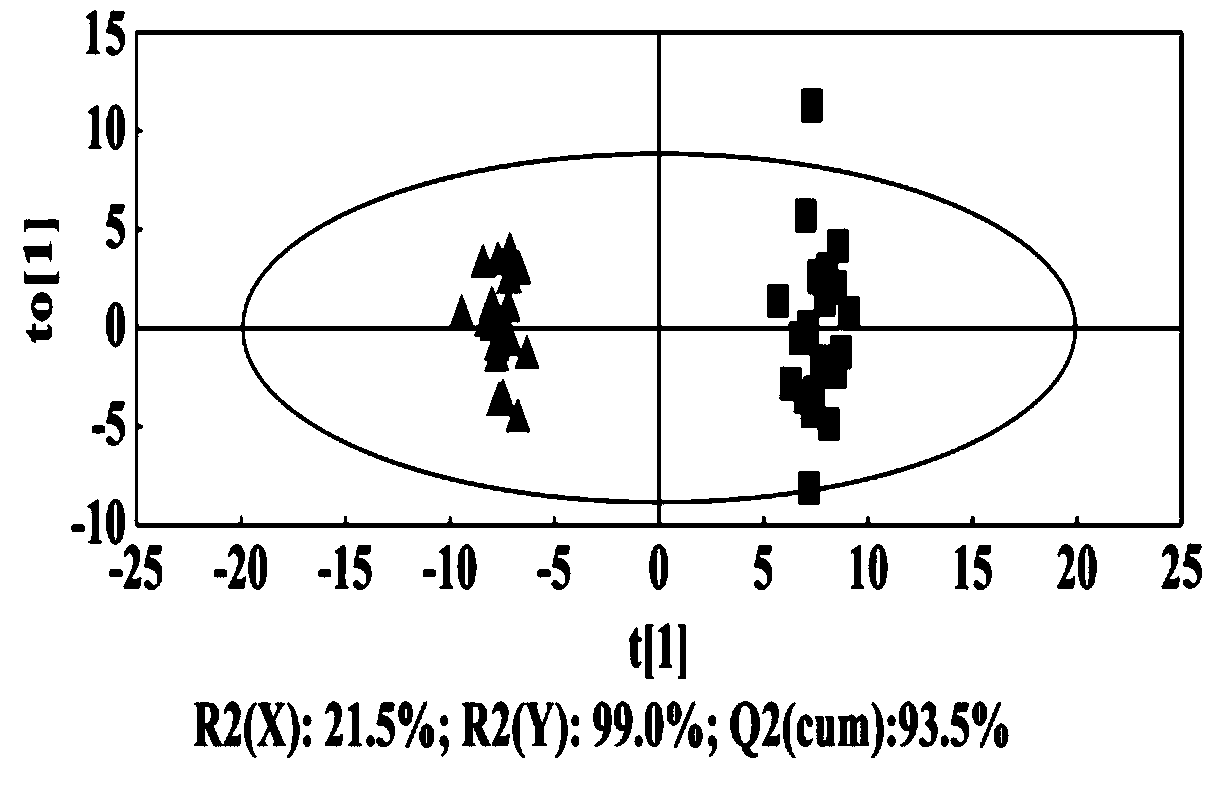
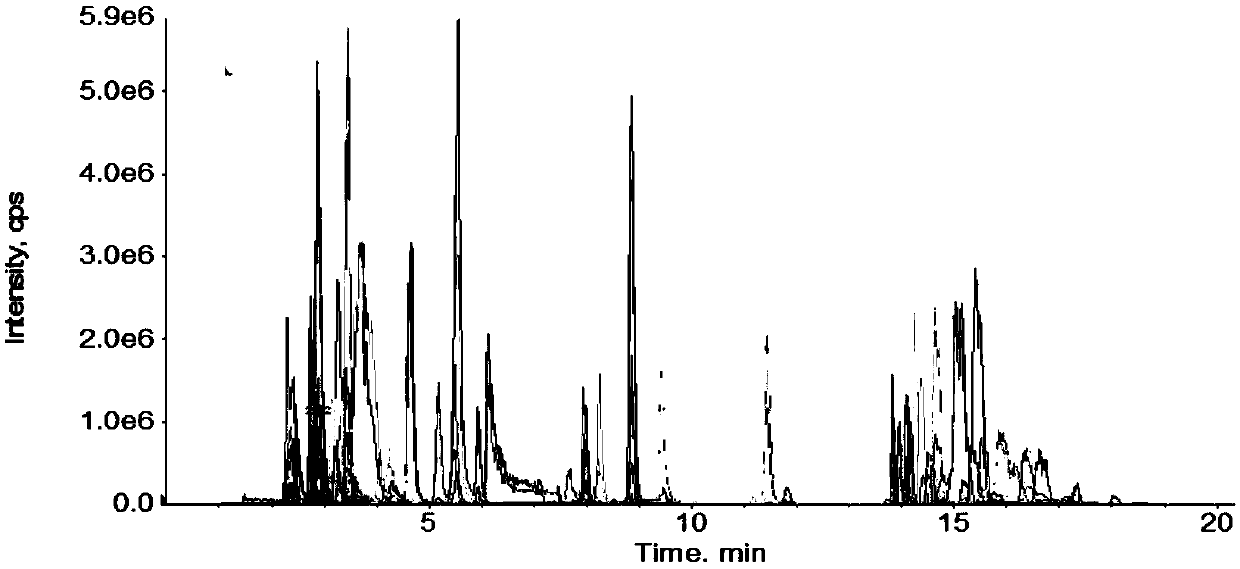
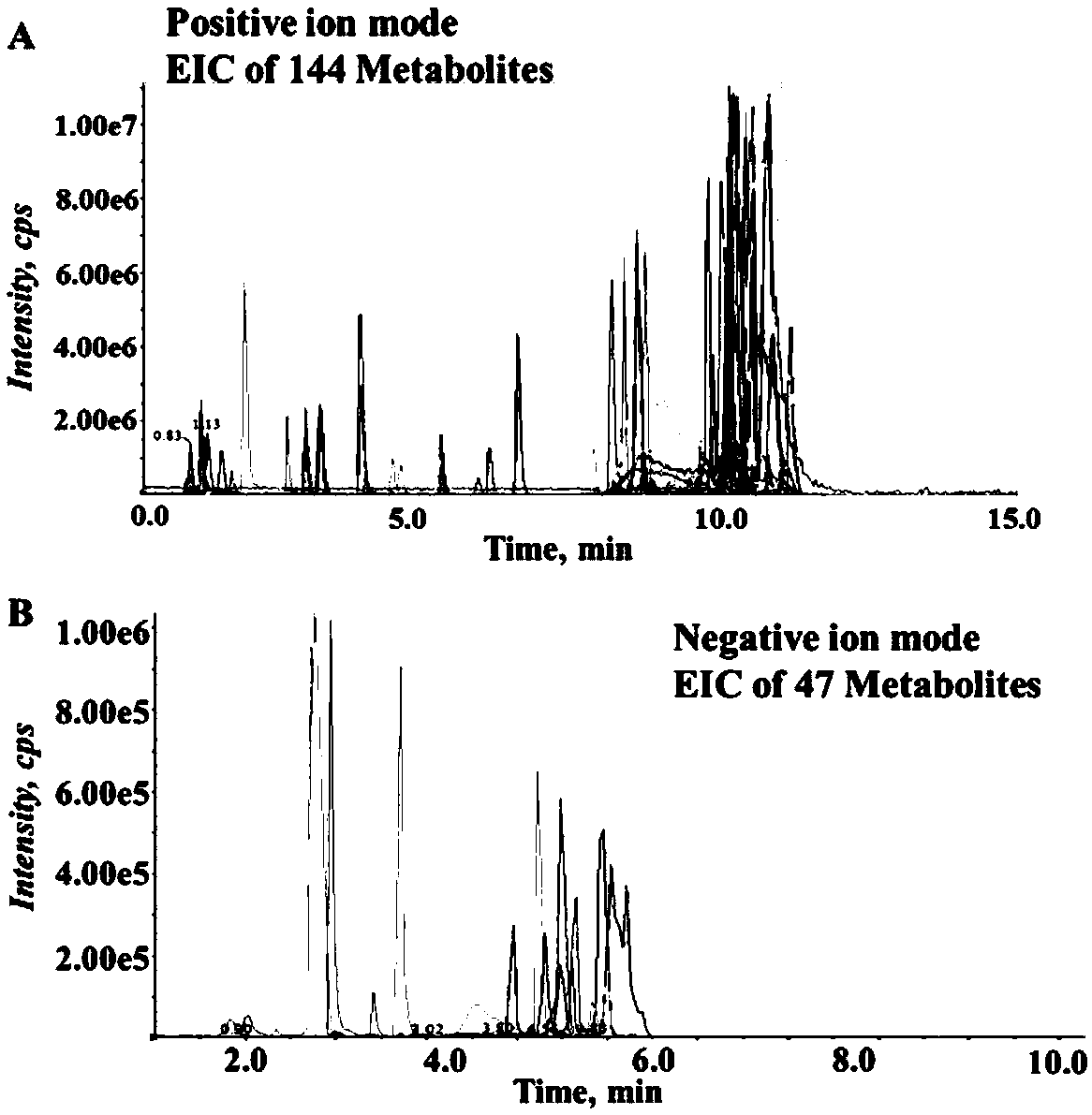
Targeting qualitative and quantitative metabonomic analysis method used for screening cancer biomarkers based on LC-MS/MS technology
The invention relates to a targeting qualitative and quantitative metabonomic technical analysis method used for screening cancer biomarkers based on the LC-MS / MS technology. The method is characterized in that a structure prediction function of multi-reaction monitoring-dependent information acquisition-enhanced daughter ion detection on correlative metabolites and a structure identification function of a high-resolution mass spectrum are predicted by fully utilizing a multi-reaction monitoring quantitation function of the high performance liquid-tandem mass spectrum, and the analysis methodsuitable for screening biomarkers of various cancers is formed. The method has the advantages of high flux, good stability and high adaptability, and improves sensitivity and accuracy of screening andfinding of metabonomic biomarkers.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA AN INST OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Devices and Methods for Detection and Quantification of Immunological Proteins, Pathogenic and Microbial Agents and Cells
ActiveUS20170370921A1High sensitivityMaintain accuracyLaboratory glasswaresMaterial analysisPsa antigenCancer cell
The present invention provides a method and microfluidic immunoassay pScreen™ device for detecting and quantifying the concentration of an analyte in a liquid sample by using antigen-specific antibody-coated magnetic-responsive micro-beads. The methods and devices of the present invention have broad applications for point-of-care diagnostics by allowing quantification of a large variety of analytes, such as proteins, protein fragments, antigens, antibodies, antibody fragments, peptides, RNA, RNA fragments, functionalized magnetic micro-beads specific to CD4+, CD8+ cells, malaria-infected red blood cells, cancer cells, cancer biomarkers such as prostate specific antigen and other cancer biomarkers, viruses, bacteria, and other pathogenic agents, with the sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of bench-top laboratory-based assays.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
Detection, screening, and diagnosis of HPV-associated cancers
ActiveUS8968995B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisScreening methodSpecific protein
Embodiments of the invention provide methods, polyclonal antibodies, monoclonal antibodies, assays, and kits for detecting HPV infection, including infection by various HPV genotypes, early and / or late HPV-associated or HPV-specific proteins or antibodies. Mononoclonal antibodies are used to detect oncogenic high risk and low risk HPV types in a single assay, which is not limited to assay type or format. Useful tools for specific detection of various HPV associated cancers are provided. HPV associated cancer biomarkers are identified and can be used in a screening method for early stage precancerous lesions as well as late stage cancer progression.
Owner:HEER MEDICAL TECH DEV CO LTD
Biomarkers and methods of treatment
InactiveUS20140037625A1Effective treatmentIncreased riskOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderTumor BiomarkersC-Met
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Devices and Methods for Detection and Quantification of Immunological Proteins, Pathogenic and Microbial Agents and Cells
ActiveUS20140120633A1Low costReduce complexityComponent separationLaboratory glasswaresBacteroidesPoint of care
The present invention provides a method and microfluidic immunoassay pScreen™ device for detecting and quantifying the concentration of an analyte in a liquid sample by using antigen-specific antibody-coated magnetic-responsive micro-beads. The methods and devices of the present invention have broad applications for point-of-care diagnostics by allowing quantification of a large variety of analytes, such as proteins, protein fragments, antigens, antibodies, antibody fragments, peptides, RNA, RNA fragments, functionalized magnetic micro-beads specific to CD4+, CD8+ cells, malaria-infected red blood cells, cancer cells, cancer biomarkers such as prostate specific antigen and other cancer biomarkers, viruses, bacteria, and other pathogenic agents, with the sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of bench-top laboratory-based assays.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
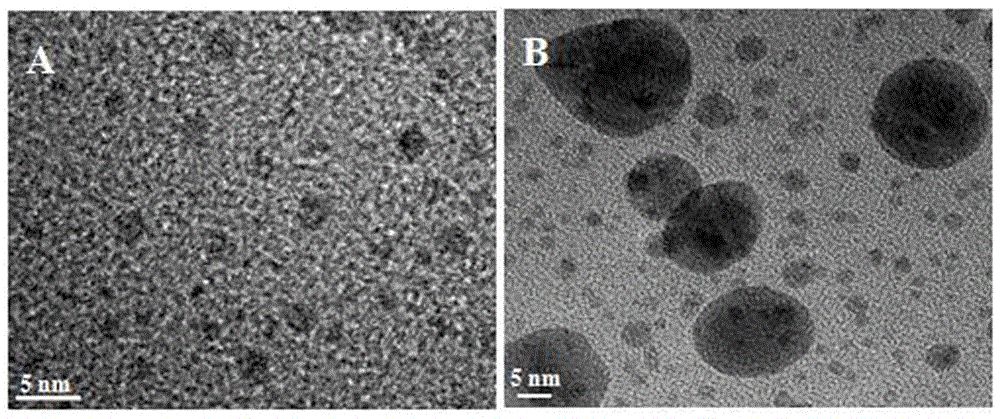
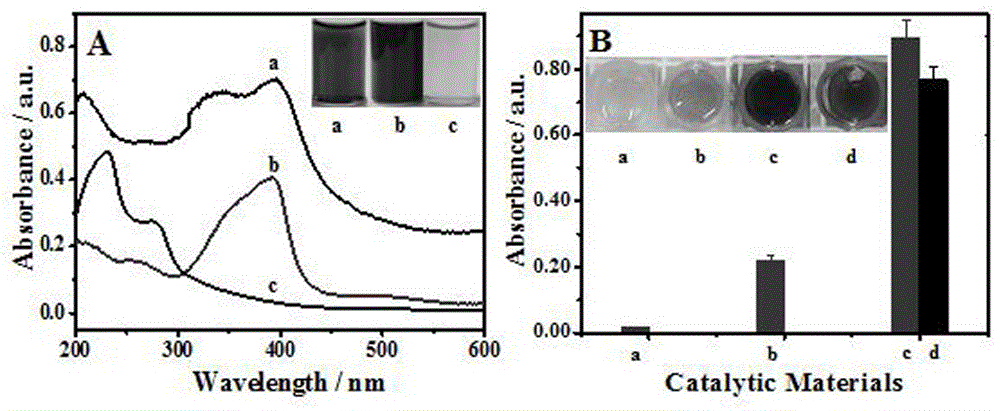
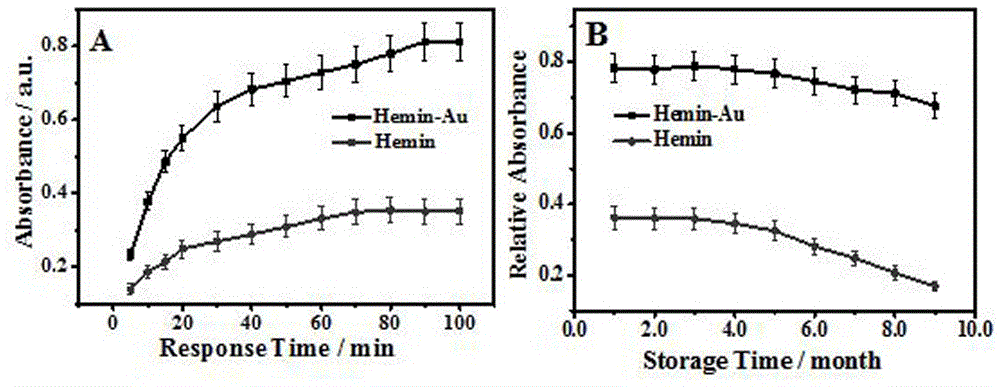
Preparing method and application of mimic enzyme with double catalysis functions based on hemin mediation gold mineralization path
ActiveCN106582848AHigh catalytic activityEasy to operateOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsBiological testingElectronic transmissionSynthesis methods
The invention provides a preparing method and application of mimic enzyme with double catalysis functions based on a hemin mediation gold mineralization path. The one-pot type in-situ synthesis method is adopted, the hemin and chloroauric acid are mixed under the alkaline condition, then gold in-situ biological mineralization is achieved with the hemin as a reducing agent and a stabilizing agent, and a Hemin-AuNCs compound with Hemin peroxidase catalysis and gold catalysis activity is prepared. The function of a nano wire of the Hemin-AuNCs compound is brought into play, the electronic transmission capability of the Hemin catalysis reaction is promoted, meanwhile, the adsorption capability for a substrate is enhanced, and the catalysis activity of the Hemin-AuNCs compound is obviously higher than that of common Hemin by four or more times. Complex photoelectric instrument usage is not involved in the preparing method, and the beneficial effects that the catalysis activity is high, operation is simple, response is fast and cost is low are achieved. The cancer biomarker alpha fetoprotein immunoassay serves as the example, the Hemin-AuNCs compound is applied to marking of an AFP antibody, then, the enzyme linked immunosorbent assay is adopted, and high-sensitivity detection on the cancer biomarker alpha fetoprotein in blood is achieved through the enzymatic catalysis and gold catalysis silver deposition signal amplification path.
Owner:QUFU NORMAL UNIV
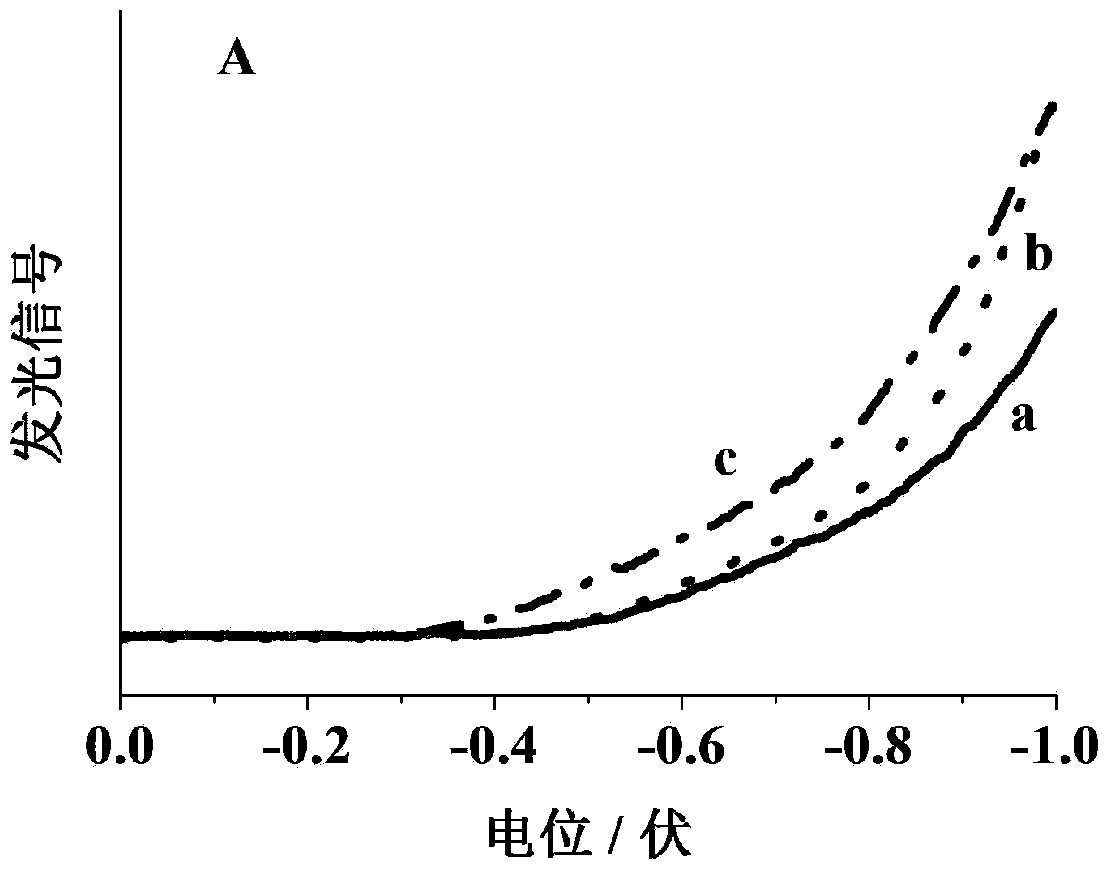
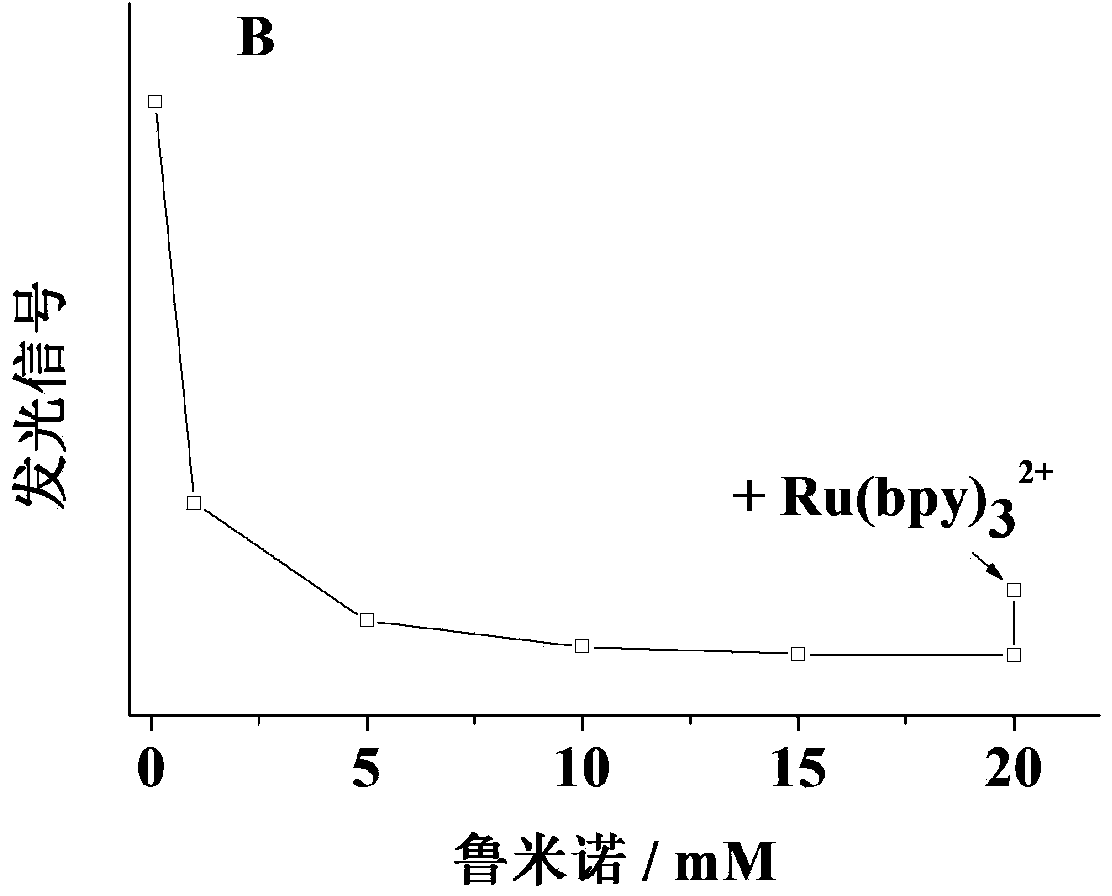
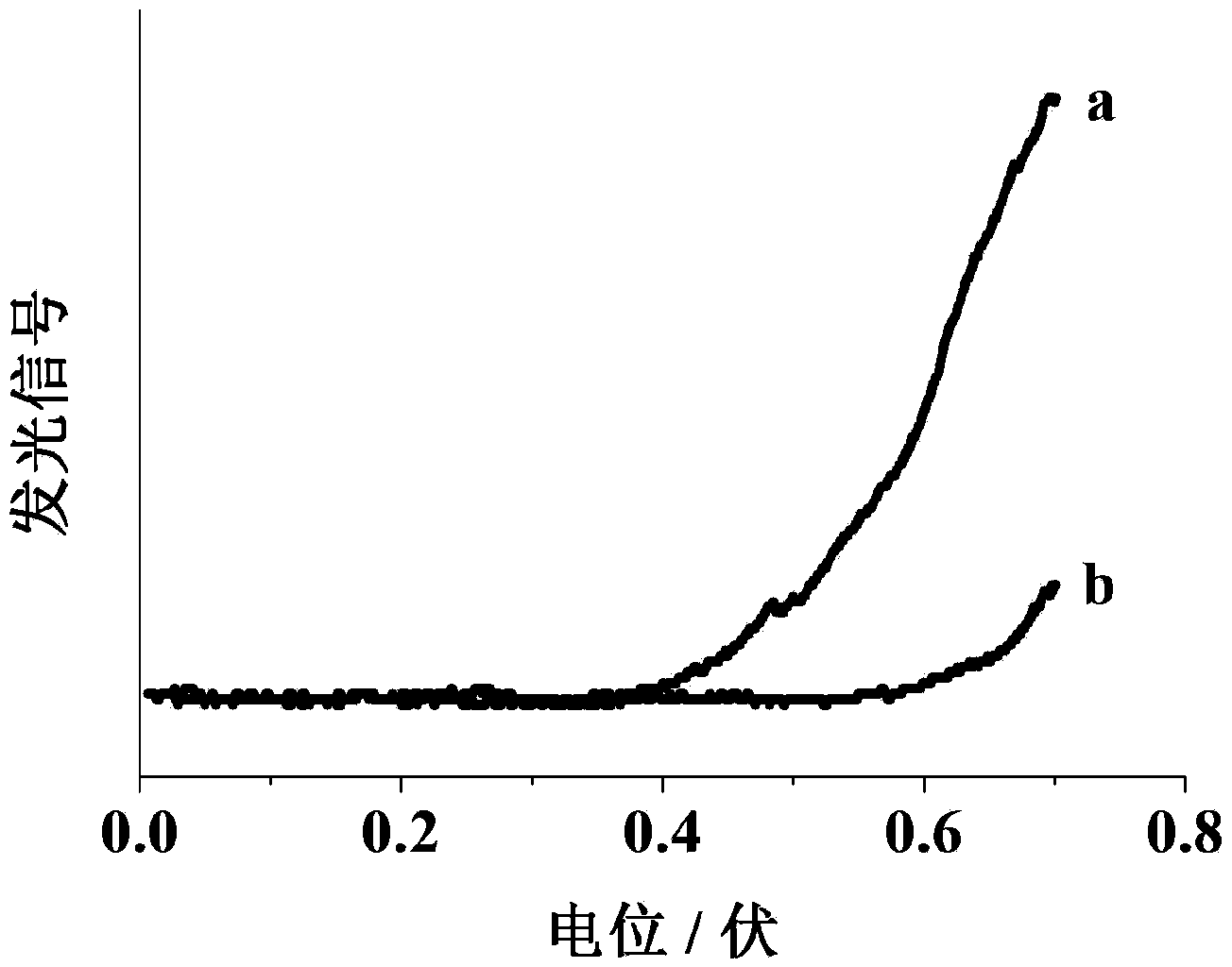
Luminol and trisruthenium-based potential-resolved electrochemiluminescence detection method and application thereof
ActiveCN103884707ARealize one-step analysis and detectionEliminate mutual interferenceChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceAntigenPeroxydisulfate
The invention discloses a luminol and trisruthenium-based potential-resolved electrochemiluminescence detection method. Luminal and trisruthenium are used as luminescent probes. During detection, an ITO (indium tin oxide) electrode is used as a working electrode for luminescence detection, a silver-silver chloride electrode is used as a reference electrode, a potassium electrode is used as a counter electrode, and a luminescent signal from luminol is detected by performing scanning from 0.6V to 0.0V; peroxydisulfate and an excessive amount of luminol are added into a detection system, and a luminescent signal from trisruthenium is detected by performing scanning from 0.0V to -1.0V. The invention also discloses a simple and effective method for simultaneously detecting two cell surface cancer biomarkers. According to the methods, two antigens on the surfaces of cells can be analytically detected by one step by double-tagging and potential resolving methods, the mutual interference of signals under different potentials is eliminated, and carcinoembryonic antigens and alpha fetoprotein antigens on surfaces of cells are successfully detected at the same time.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Biomarkers predictive of therapeutic responsiveness to chimeric antigen receptor therapy and uses thereof
PendingUS20210172020A1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisAntigen receptorTumor Biomarkers
Owner:NOVARTIS AG +1
Cancer biomarker genes and gene products and methods for using the same
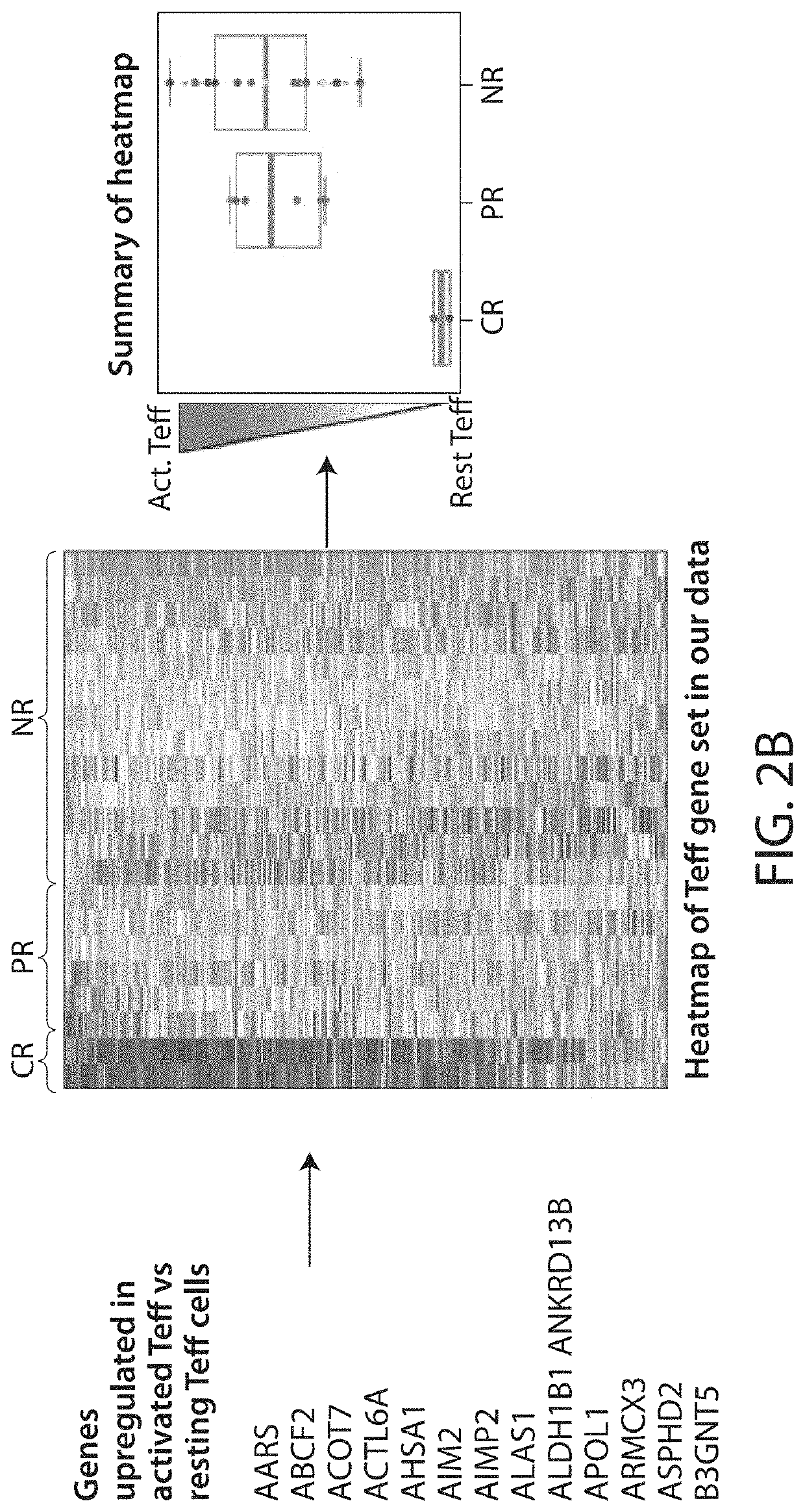
Using gene expression analysis, specific biomarker genes and gene products have been identified which are activated in transformed cells, but suppressed in nontransformed cells; or suppressed in transformed cells, but activated in transformed cells affected by Contact Normalization. Thus, the present invention features compositions and methods for detecting, diagnosing, treating and prognosing cancer.
Owner:ROWAN UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com