Light-emitting diode chip and manufacturing method thereof
A technology for light-emitting diodes and a manufacturing method, which is applied to semiconductor devices, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as low yield, and achieve the effects of improving yield, VF optimization, and LOP optimization.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
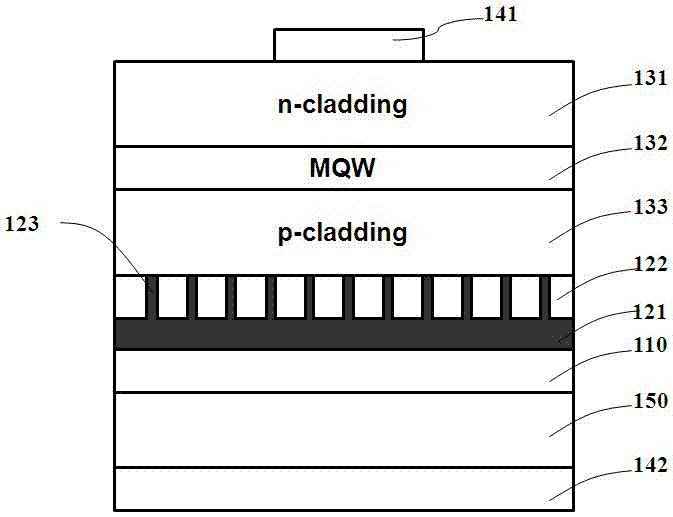
[0037] figure 1A light-emitting diode chip with a mirror system is disclosed, and its specific structure includes: a light-emitting epitaxial stack, a bonding layer 110 , a metal conductive layer 121 , a dielectric layer 122 , a first electrode 141 , a second electrode 142 and a conductive substrate 150 . Wherein, the light-emitting epitaxial stack is at least composed of a first-type semiconductor layer 131, an active layer 132 and a second-type semiconductor layer 133. When the first-type semiconductor layer 131 is a p-type semiconductor, the second-type semiconductor layer 133 can be different Electrical n-type semiconductor, on the contrary, when the first type semiconductor layer 131 is an n-type semiconductor, the second type semiconductor layer 133 can be a p-type semiconductor with different electrical properties, and the active layer 132 is located between the first type semiconductor layer 131 and the Between the second type semiconductor layers 133, there can be neu...
Embodiment 2
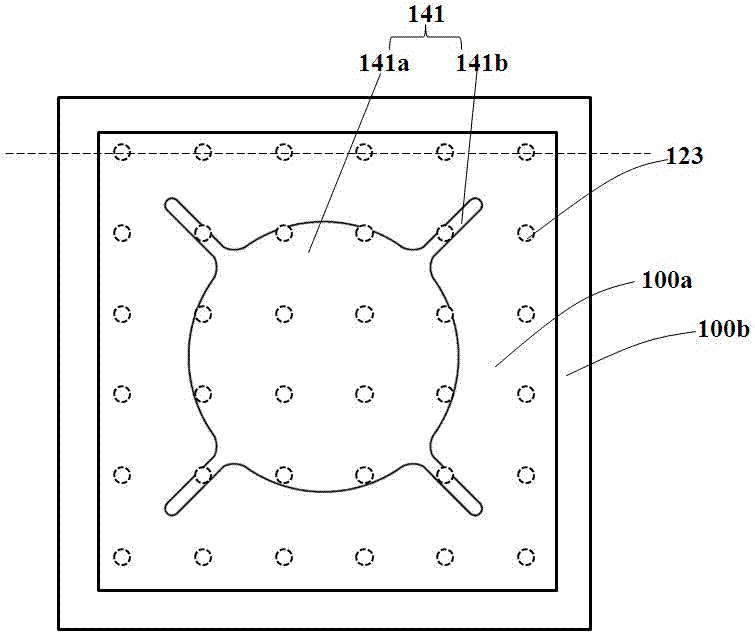
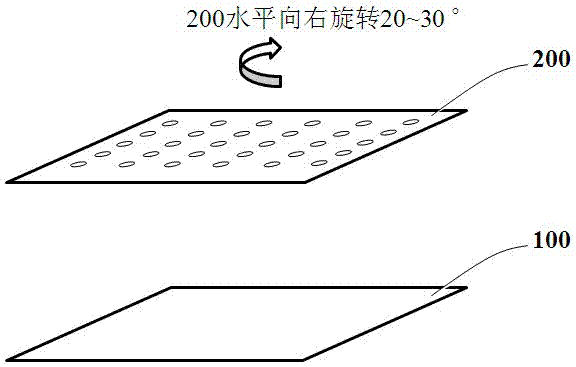
[0045] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the shape of the first electrode of the LED chip is different, please refer to the attached Figure 4~5 . exist Figure 4 In the figure shown, there is no rotation angle between the conductive via array and the finger electrodes of the first electrode. There are 36 conductive vias in the light-emitting area, 8 of which are covered by the first electrode, and the effective utilization rate is 77.8%; exist Figure 5 In the figure shown, the rotation between the conductive via array and the top first electrode is 23°. There are 35 conductive vias in the light emitting area 100a, of which only 4 are completely covered by the first electrode, and the effective utilization rate reaches 88.9%. .
Embodiment 3
[0047] This embodiment discloses a method for manufacturing the light-emitting diode chip shown in the foregoing embodiments 1-2, which includes steps S100-S500, which will be described in detail below.
[0048] Step S100 : providing a light-emitting epitaxial stack, including at least a first-type semiconductor layer 131 , an active layer 132 and a second semiconductor layer 133 , which are generally formed on a growth substrate such as sapphire or gallium arsenide. The light-emitting epitaxial stack can adopt a general structure, and it is preferable that the growth substrate is easy to remove.
[0049] Step S200 : forming a dielectric layer 122 on the lower surface of the light-emitting epitaxial stack 100 , which has a conductive via array 123 . Figure 7 A specific method for this step is shown. First, a layer such as SiO is deposited on the lower surface of the light-emitting epitaxial stack 100 2 A light-transmitting insulating material layer as a dielectric layer, su...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com