Double-stranded antisense nucleic acid with exon-skipping effect
A double-stranded nucleic acid and nucleotide technology, applied to medical preparations containing active ingredients, organic active ingredients, drug combinations, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
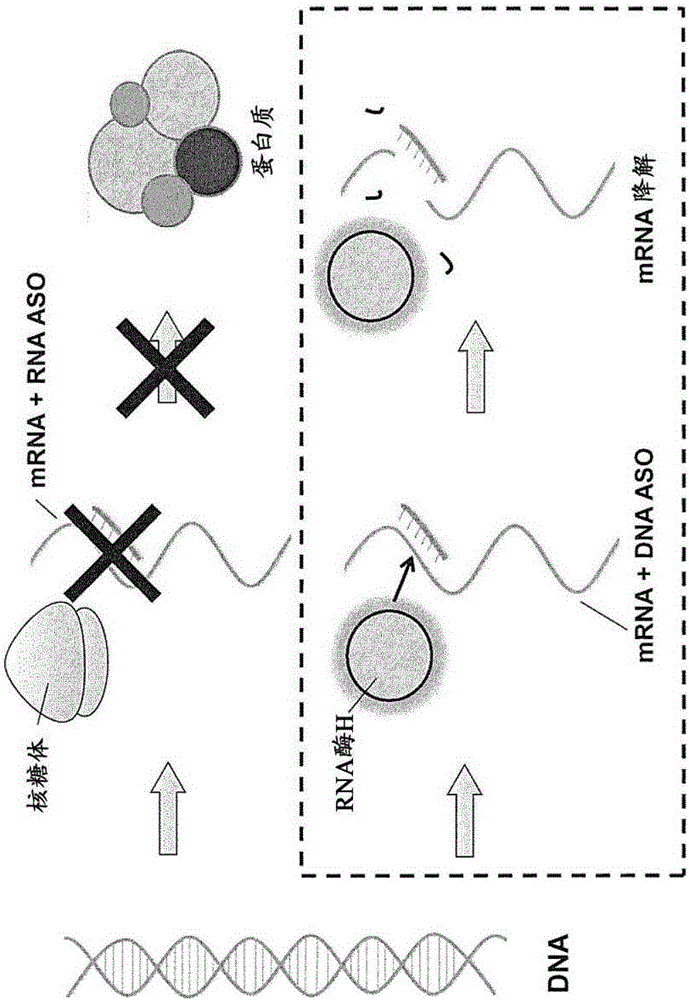
[0175] The accessibility of double-stranded antisense nucleic acid complexes to the nucleus of Huh-7 cells was tested and compared to the accessibility of single-stranded antisense oligonucleotides to the nucleus of Huh-7 cells. In experiments, to the extent that the antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) is able to reach the nucleus, the ASO should be able to inhibit the expression of the target gene ApoB, and thus, the amount of ApoB mRNA will show a corresponding decrease.
[0176] A single-stranded LNA / DNAgapmer antisense oligonucleotide (SEQ ID NO: 1 ) and a complementary RNA-based strand (SEQ ID NO: 2) were prepared with the following sequences and compositions:
[0177] 16merASO (targeting intron human apoB mRNA):
[0178] SEQ ID NO: 15'-C * T * C *c*c*a*c*c*a*c*a*t*a* G * C * A -3'
[0179] 16mercRNA (targeting intron human apoBmRNA):
[0180] SEQ ID NO: 25'-g*c*u*AUGUGGUGGG*a*u*g-3'
[0181] Lowercase italic letters represent DNA, underlined capital letter types repr...
Embodiment 2
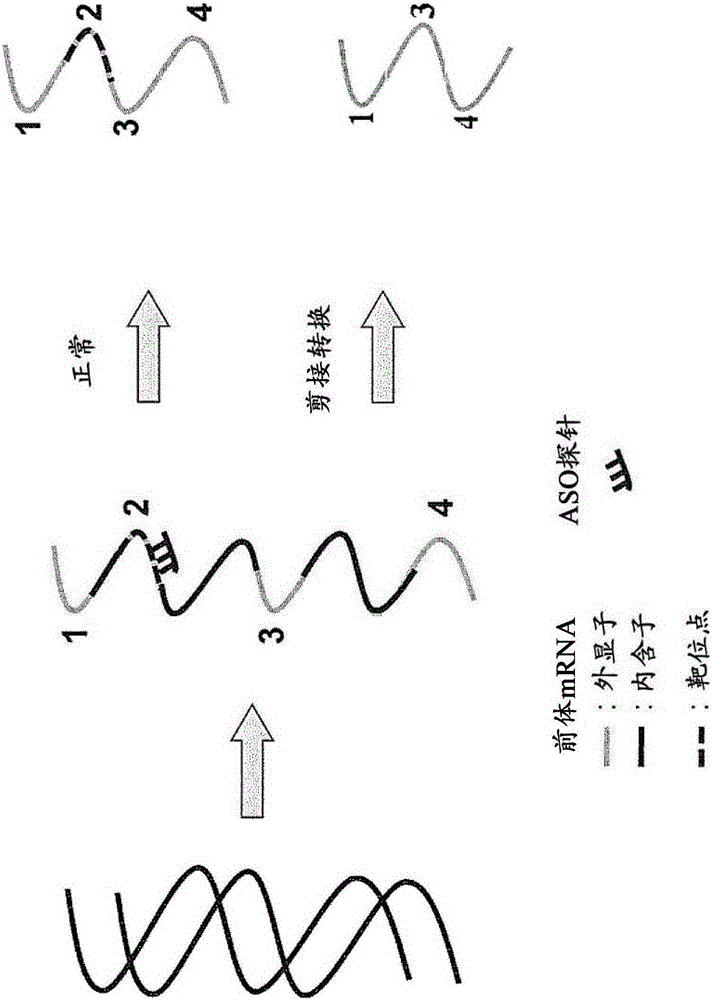
[0188] The double-stranded antisense nucleic acid complex according to one embodiment of the present invention was tested for its ability to cause exon skipping during the processing of pre-mRNA of part of the dystrophin gene and compared it with a single-stranded antisense oligonucleotide This ability of glycosides was compared.
[0189] For this experiment, a stable expression plasmid for the human dystrophin gene fragment was constructed and a stable cell line containing the construct was established. The human dystrophin gene fragment has the full-length sequence of exon 57 to exon 59 except for intron 57, which is truncated for convenience due to its length.
[0190] Expression of dystrophin fragments in stable cell lines would generally be expected to produce mRNA comprising exons 57, 58 and 59. However, in the presence of a splice-switch oligonucleotide with the ability to cause exon 58 skipping during pre-mRNA processing, the expressed mRNA would be expected to contai...
Embodiment 3
[0240] Materials and methods
[0241] Synthesis of splicing-switching oligonucleotides (SSOs)
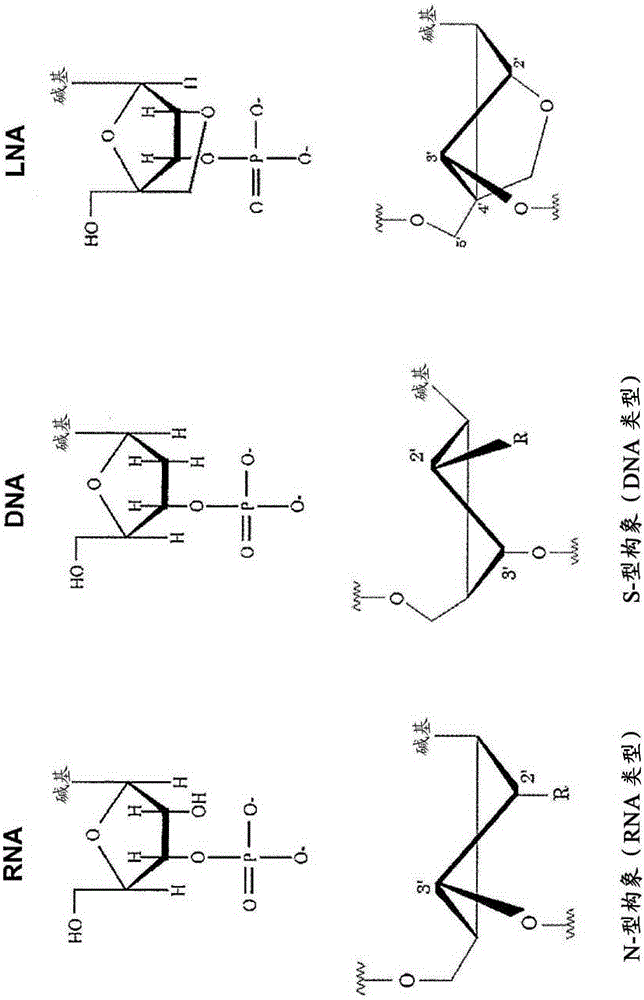
[0242]All SSOs used in this study are shown in Table 1. The sequence of the SSO was optimized by systematic screening as shown in the literature Shimo.T. et al. Two types of modifications, 2',4'-BNA and 2'-OMe, are incorporated into the SSO sequence, where the phosphodiester linkage is completely replaced by a phosphorothioate linkage. All SSOs were designed to have a sequence complementary to the human dystrophin gene, and were synthesized and purified by GeneDesign Inc. (Osaka, Japan).
[0243] Synthesis of modified complementary RNA
[0244] All modified complementary RNAs (modified cRNAs) used in this study are shown in Table 2. A 2'-OMe modification is incorporated into the modified cRNA sequence in which the phosphodiester linkage is partially replaced by a phosphorothioate linkage. Modified cRNA was synthesized and purified by GeneDesign Inc. (Osaka, Japan).
[0245] Pr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com