Method for making purple yam chips through microwave vacuum low-temperature oil bath dehydration technology
A low-temperature oil bath and microwave vacuum technology, applied in the field of food processing, can solve the problems of increasing enterprise investment and operating costs, reducing heat transfer efficiency, increasing equipment investment, etc., achieving good market prospects, low production costs, and reducing equipment investment Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
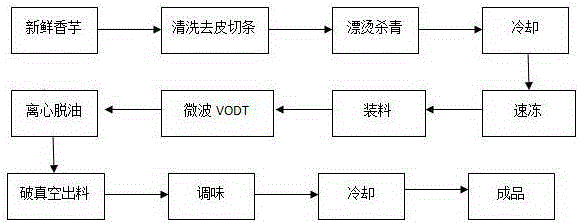
[0027] Wash and peel fresh taro and cut into long strips, 8~10cm long and 10~12mm wide, blanched in hot water at 95℃ for 90s, quickly remove and spray to cool to avoid overcooking, drain and put on a plate in - Quick-frozen at 35°C for 24 hours, and the thickness of the plate should not exceed 3cm. Take out the frozen taro strips and put them in the polytetrafluoroethylene material frame, shake the taro strips as much as possible, move the material frame into the microwave vacuum low-temperature oil bath dehydration machine, vacuumize to 0.097Mpa, turn on the microwave to heat the oil temperature to 95°C, immerse the material frame in hot oil to heat, the water contained in the taro sticks will sublimate and evaporate in large quantities, and the dehydration time will be 30 minutes. The hot oil is pumped to the storage tank for later use. The material box is centrifuged at 200rpm to remove the oil on the surface of the taro sticks. The time is 3 minutes. After stopping the cen...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Wash and peel the fresh taro and cut it into long strips, 6~8cm long and 12~15mm wide, blanched in 96℃ hot water for 70s, quickly remove and spray to cool to avoid over-cooking, drain and put on a plate in - Quick-frozen at 35°C for 24 hours, and the thickness of the plate should not exceed 3cm. Take out the frozen taro strips and put them in a polytetrafluoroethylene material frame, shake the taro strips as much as possible, move the material frame into the microwave vacuum low-temperature oil bath dehydration machine, vacuumize to 0.098Mpa, turn on the microwave to heat the oil to At 90°C, immerse the material frame in hot oil to heat. The water contained in the taro sticks will sublimate and evaporate in large quantities. The dehydration time is 40 minutes. The hot oil is pumped to the storage tank for later use. The material box is centrifuged at 150rpm to remove the oil on the surface of the taro sticks for 5 minutes. After stopping the centrifugation, break the va...
Embodiment 3
[0031] Wash and peel fresh taro and cut into long strips, 8~10cm long and 12~15mm wide, blanched in hot water at 96℃ for 90s, quickly remove and spray to cool to avoid overcooking, drain and put on a plate in - Quick-frozen at 35°C for 24 hours, and the thickness of the plate should not exceed 4cm. Take out the frozen taro strips and put them in a polytetrafluoroethylene material frame, shake the taro strips as much as possible, move the material frame into the microwave vacuum low-temperature oil bath dehydration machine, vacuumize to 0.098Mpa, turn on the microwave to heat the oil to 95°C, immerse the material frame in hot oil to heat, the water contained in the taro strips will sublimate and evaporate in large quantities, and the dehydration time will be 45min. The hot oil is pumped to the storage tank for later use. The material box is centrifuged at 250rpm to remove the oil on the surface of the taro sticks. The time is 3 minutes. Nitrogen-filled quantitative packaging i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com