Establishment and application of brewing yeast engineering bacterium strain for producing L-malic acid
A technology of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and engineering bacteria, applied in the direction of enzymes, fermentation, fungi, etc., can solve the problems of long fermentation cycle, overexpression of large fragment genes, and low bacterial concentration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
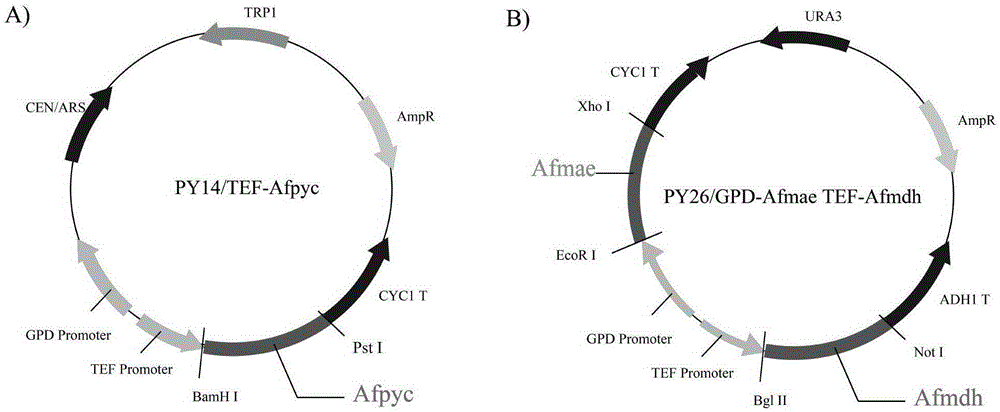
[0035] Example 1: Construction of Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering strains producing malic acid
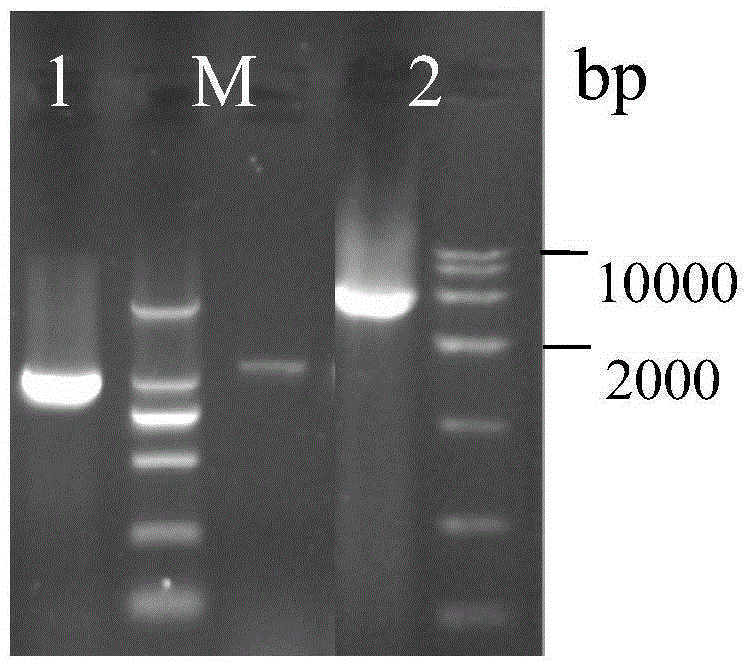
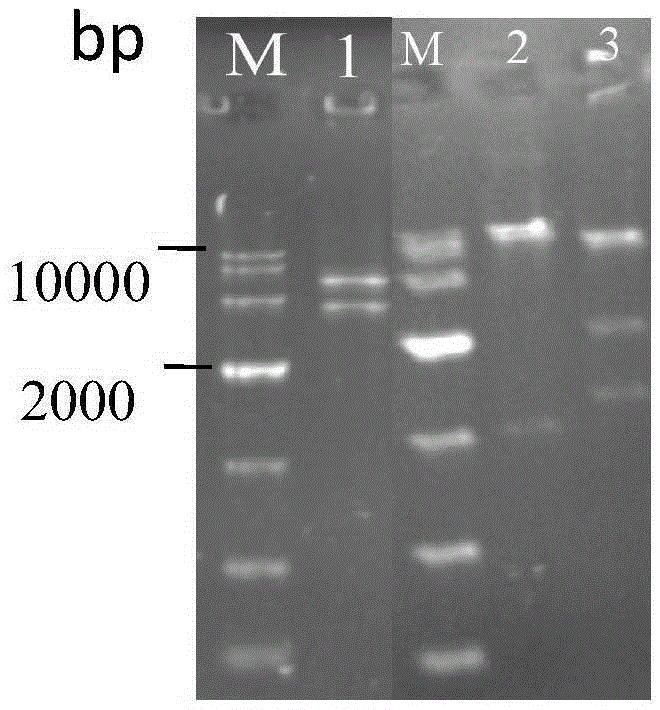
[0036] (1) Using the cDNA of A.flavusATCC13697 as a template, the pyruvate carboxylase gene (NCBIaccessionnumble: XM_002377040, 3582bp) to carry out PCR amplification, utilize primer 3 (sequence such as SEQIDNO.3) and primer 4 (sequence such as SEQIDNO.4) to amplify malate dehydrogenase gene (NCBIaccessionnumble: XM_002378178,996bp), utilize primer 5 (sequence such as SEQIDNO. .5) and primer 6 (sequence such as SEQ ID NO.6) for PCR amplification of the malate transporter gene (NCBI accessionnumble: XM_002376564, 1197bp);
[0037] The primer sequences are as follows:
[0038] Primer 1: 5'-CGGGATCCATGGCGGCTCCGTTTCGT-3'
[0039] Primer 2: 5'-AACTGCAGTTGCTTACGCTTTGACGAT-3'
[0040] Primer 3: 5'-ATTTGCGGCCGCATGGTCAAAGCTGCGGTACT-3'
[0041] Primer 4: 5'-GAAGATCTTCAAAGCTTTGGTGGTGGGTT-3'
[0042] Primer 5: 5'-CGGAATTCATGTTCAATAACGAACACC-3'
[0043] Primer 6: 5'-CCGCTCGAGCTAATCAG...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Embodiment 2: utilize Saccharomyces cerevisiae to produce L-malic acid
[0054] Inoculate the engineered strains stored in the glycerol tube on the slant of the YNB medium, take a ring to the seed medium (100mL / 500mL Erlenmeyer flask), and cultivate it at 30°C and 200r / min for 48h, then inoculate with 10% inoculum (V / V ) to inoculate the fermentation medium (100mL / 500mL Erlenmeyer flask), the temperature is 30°C, the rotation speed is 800rpm, the ventilation rate is 1.5vvm, the pH is adjusted to 5.0 by 8mM KOH, and the fermentation time is 84h. Measured by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC): the malic acid output of the genetically engineered bacteria (W1101) of the present invention is 27.3 g / L, while the starting strain (WT) accumulates a small amount of malic acid. The yield of malic acid relative to glucose was 0.41mol / mol.
[0055] Table 1 product output (unit: g / L)
[0056]
[0057] Advantages of the present invention: 1) Compared with the reported...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com