Regulating method for distributed MEMS phase shifter working voltage based on phase shift magnitude electromechanical coupling
A technology of working voltage and electromechanical coupling, which is applied in the coupling of optical waveguides, generators/motors, and components of TV systems, etc. It can solve problems such as the inability to determine the height of MEMS bridges
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0071] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
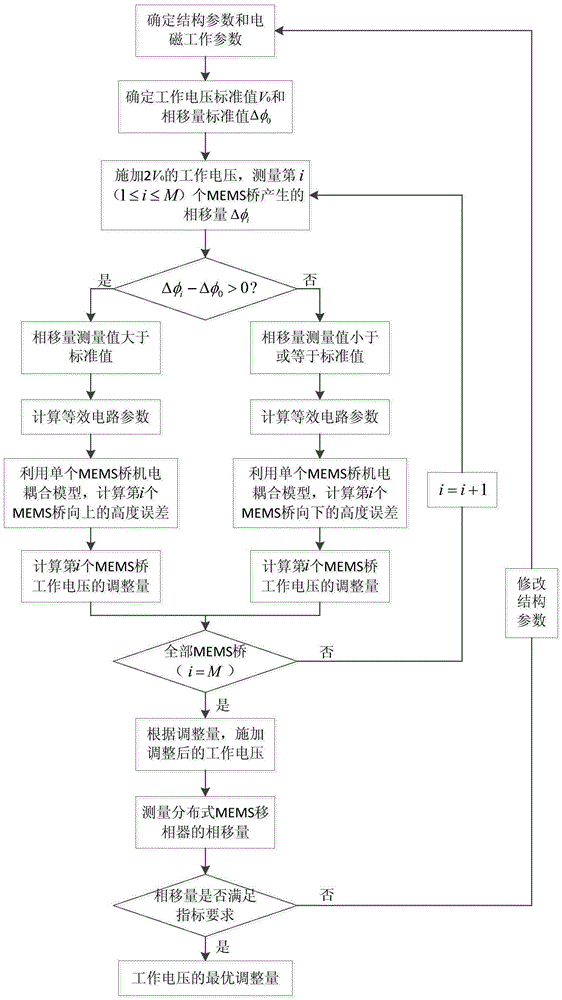
[0072] refer to figure 1 , the present invention is a method for adjusting the operating voltage of a distributed MEMS phase shifter based on the electromechanical coupling of the phase shift, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0073] Step 1, determine the structural parameters and electromagnetic working parameters of the distributed MEMS phase shifter.
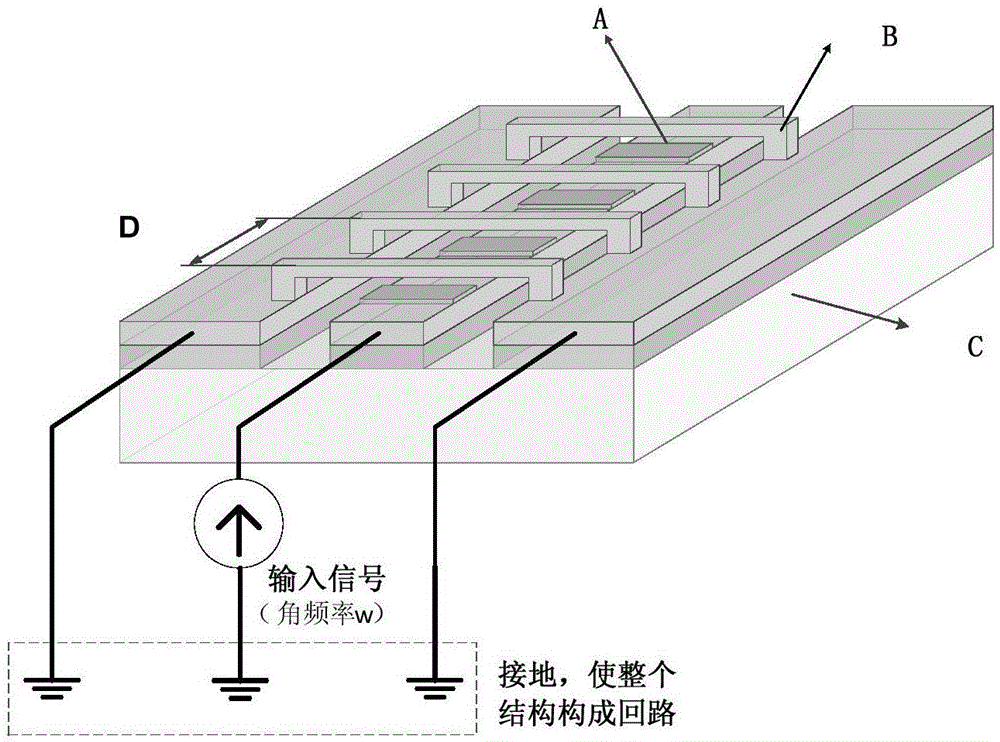
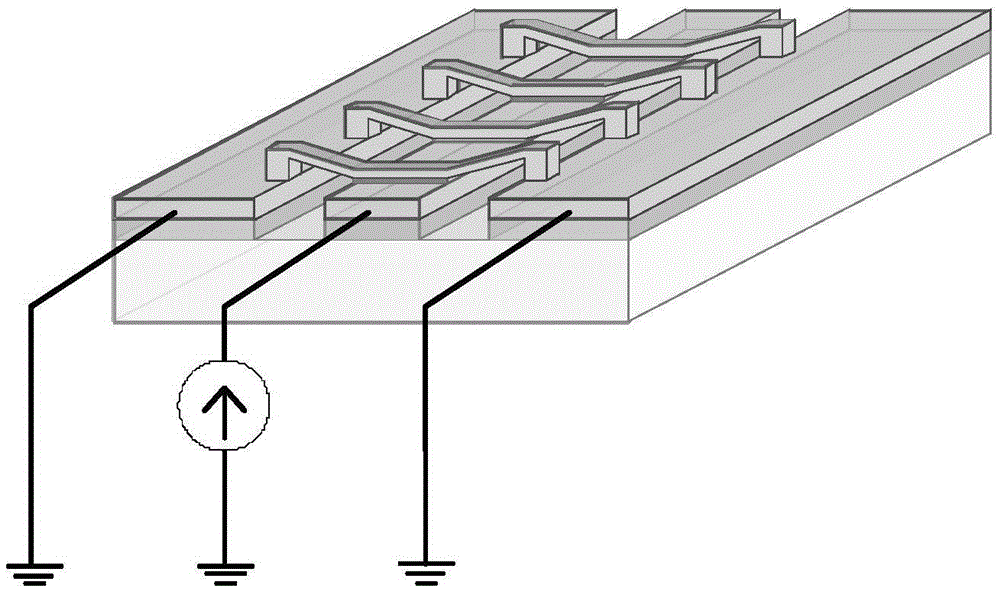
[0074] The structural parameters of the distributed MEMS phase shifter are as follows figure 2 As shown, it includes the length, width and thickness of the coplanar waveguide transmission line, MEMS bridge and dielectric layer, the distance between two adjacent bridges, and the height of the MEMS bridge from the dielectric layer. Material properties of distributed MEMS phase shifters, including relative permittivity of dielectric layers. The electromagnetic working parameters of the distribu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com