Method for rapidly identifying or screening microorganisms producing bacteriostatic active substances
A technology of antibacterial activity and active substances, which is applied in the field of rapid identification of microorganisms producing antibacterial active substances and active substances, which can solve the problems of low efficiency and cumbersome steps, so as to improve efficiency, shorten experimental time, and save screening costs Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
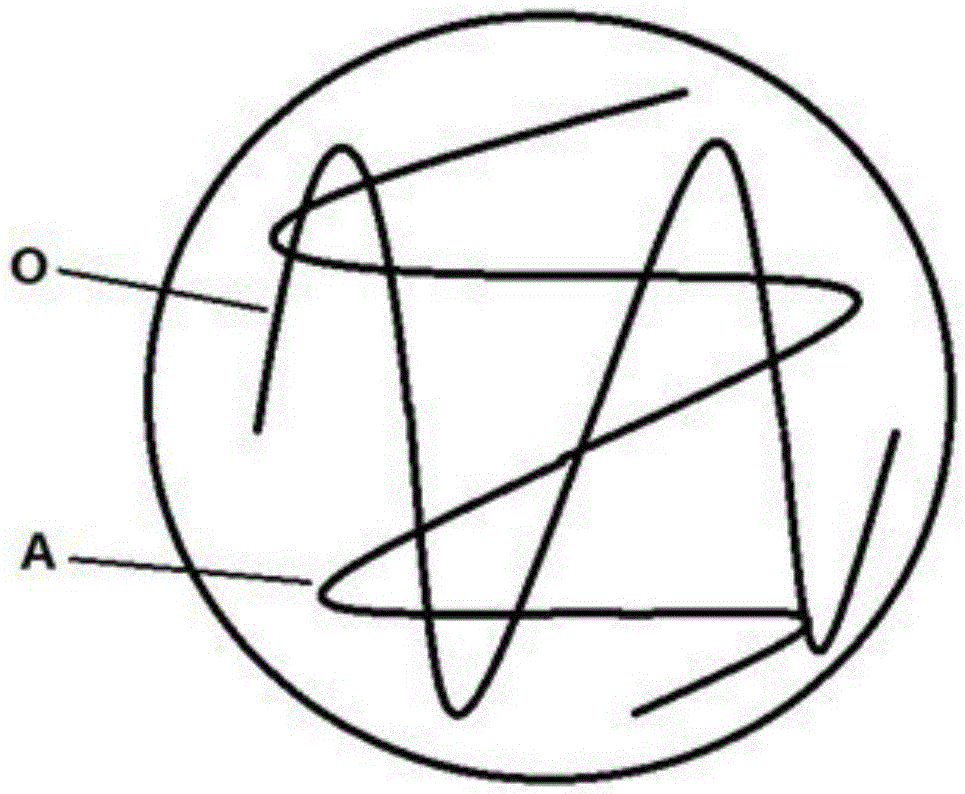
[0016] A kind of method that the present invention proposes to quickly identify or screen the microorganisms that produce antibacterial active substances comprises the steps:
[0017] S1, prepare solid medium culture dish (LB medium or PDA medium etc.);
[0018] S2. Under aseptic conditions, inoculate the test microorganisms and indicator microorganisms by cross-streaking on the same petri dish;
[0019] S3. After inoculation, the culture dish is placed in an incubator for culture (culture conditions: 26-40° C., culture time 12-240 h);
[0020] S4. Determine whether the test microorganism produces an active substance that inhibits the indicator microorganism.
[0021] Such as figure 1 as shown, figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of Embodiment 1 of the present invention. Depend on figure 1 It can be seen that the test microorganism A does not produce the active substance that inhibits the indicator microorganism O, and the test microorganism A and the indicator microorgani...
Embodiment 2
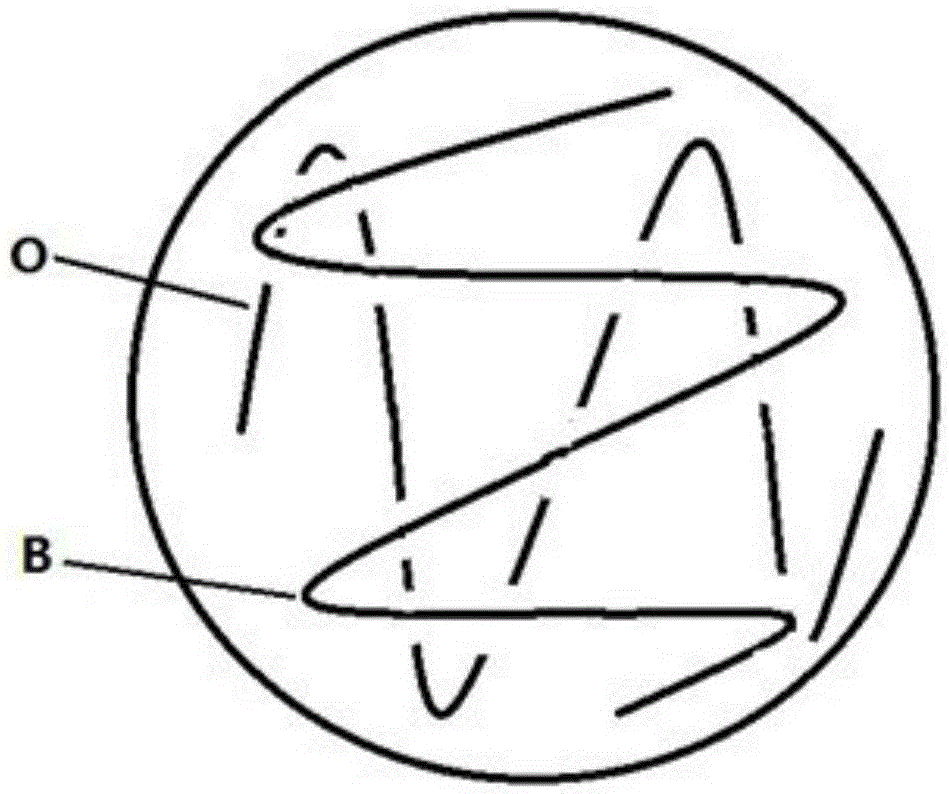
[0023] A kind of method that the present invention proposes to quickly identify or screen the microorganisms that produce antibacterial active substances comprises the steps:
[0024] S1, prepare solid medium culture dish (LB medium or PDA medium etc.);
[0025] S2. Under aseptic conditions, inoculate the test microorganisms and indicator microorganisms by cross-streaking on the same petri dish;
[0026] S3. After inoculation, the culture dish is placed in an incubator for culture (culture conditions: 26-40° C., culture time 12-240 h);
[0027] S4. Determine whether the test microorganism produces an active substance that inhibits the indicator microorganism.
[0028] Such as figure 2 as shown, figure 2 It is a schematic diagram of Embodiment 2 of the present invention. Depend on figure 2 It can be seen that the test microorganism B produces an active substance that inhibits the indicator microorganism O, and only the test microorganism B grows at the intersection, whi...
Embodiment 3
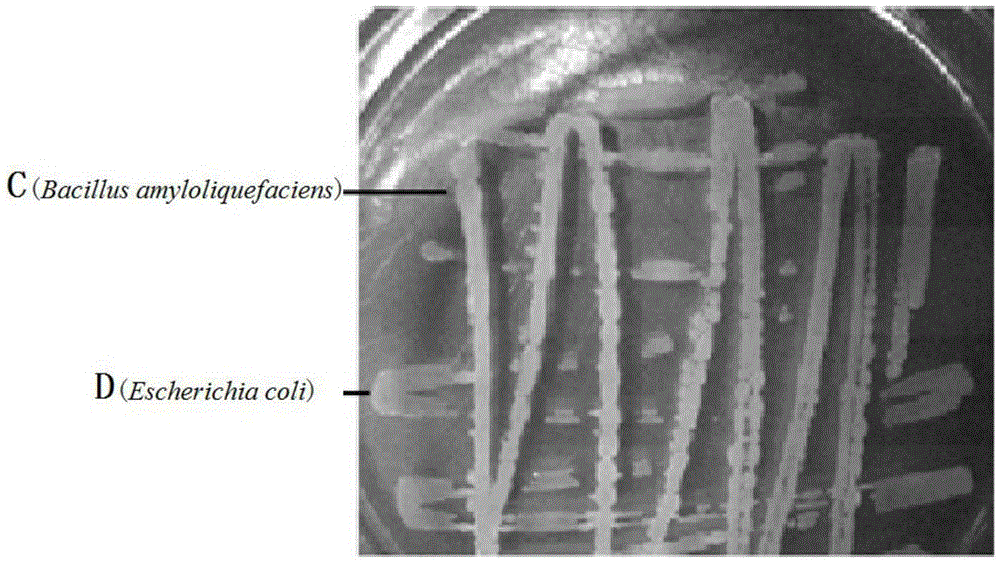
[0030] A kind of method that the present invention proposes to quickly identify or screen the microorganisms that produce antibacterial active substances comprises the steps:
[0031] S1, prepare solid medium culture dish (LB medium or PDA medium etc.);
[0032] S2. Inoculate the test microorganism C (Bacillus amyloliquefaciens) and the indicator microorganism D (Escherichiacoli) cross-streaked on the same petri dish under aseptic conditions;
[0033] S3. Place the culture dish inoculated with microorganisms in an incubator for cultivation (cultivation conditions: 26-40° C., cultivation time 12-240 h);
[0034] S4. Determine whether the test microorganism produces an active substance that inhibits the indicator microorganism.
[0035] Such as image 3 as shown, image 3 It is the result photo of Example 3 of the present invention. Depend on image 3 It can be seen that the test microorganism C (Bacillus amyloliquefaciens) produced an active substance that inhibited the in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com