Retinal cell microscopic image segmentation and counting method
A technology of retinal cells and microscopic images, applied in the field of image processing, can solve the problems of difficult selection and matching of pit points, differences in segmentation results, and failure to use grayscale information, etc., achieving good accuracy, small amount of calculation, and simple operation Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings. The following examples are only used to illustrate the technical solutions of the present invention more clearly, and cannot be used to limit the protection scope of the present invention.
[0025] The specific steps of this method are as follows:
[0026] (1) Image preprocessing:
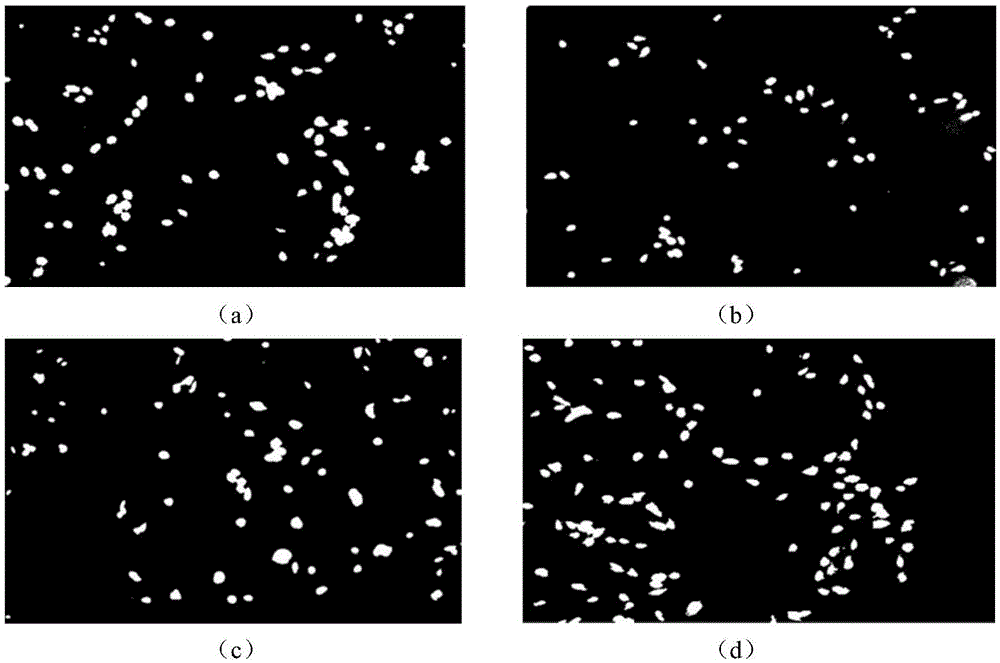
[0027] Since retinal cells are co-cultured with polymer materials, which will lead to irregular cell staining, the acquired fluorescence microscopic images have different degrees of noise. The images are preprocessed by threshold filtering and digital morphological transformation. The filtered image is eroded and expanded using a 3*3 template, which can effectively filter out noise points in the image. Moreover, this method is simple, has low computational cost and high processing efficiency, and can achieve good image denoising and enhancement effects.
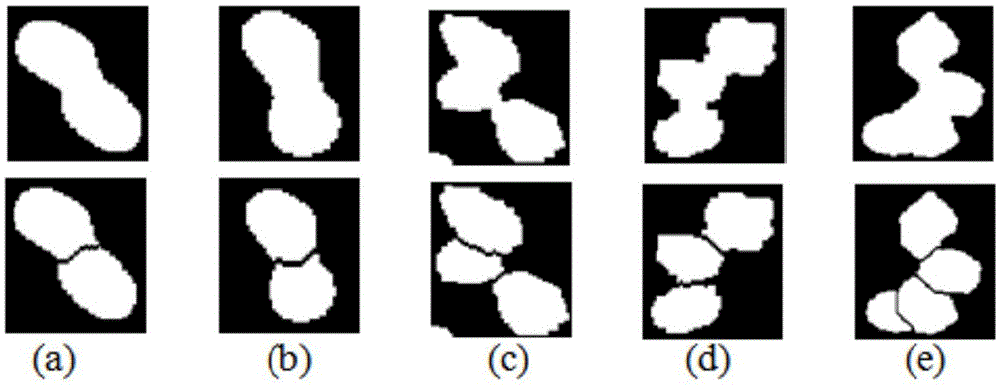
[0028] (2) Shape classification: ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com