Integrated heat sink based on metal phase-change material and heat pipes
A technology of metal phase change and phase change materials, which is applied in the direction of cooling/ventilation/heating transformation, electrical components, and structural parts of electrical equipment, etc., to achieve the effects of simplifying the structure, strengthening conduction, and prolonging the action time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
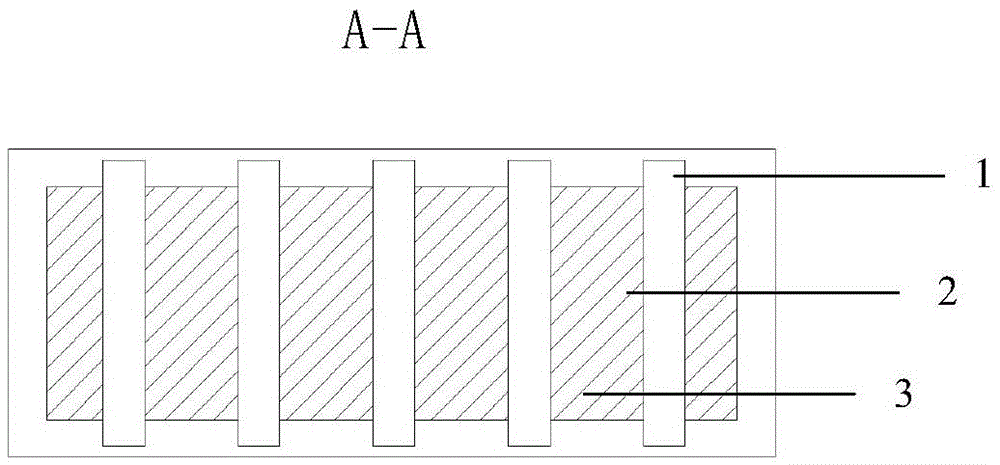
[0041] Embodiment 1 of the present invention is an integrated radiator in the form of a flat plate, and its specific structure is as follows: figure 1 with figure 2 As shown, it includes a cavity 1, a phase change material 2 and five heat pipes 3, the phase change material and heat pipes are packaged in the cavity, the end of the heat pipe is buried in the cavity, and the heat release end is inserted between the phase change materials middle;
[0042] The appearance of the cavity 1 in this embodiment is a flat rectangle, made of nickel, stainless steel or graphite.
[0043] The phase-change material 2 of this embodiment is any of gallium, gallium-indium alloy, bismuth-indium-tin alloy, and other low-melting-point alloys prepared with gallium and / or bismuth and / or indium as basic metals. The interior space is completely filled.
[0044] The heat pipe of this embodiment adopts conventional heat pipe products that match the size of the cavity (for example, for the heat dissip...
Embodiment 2
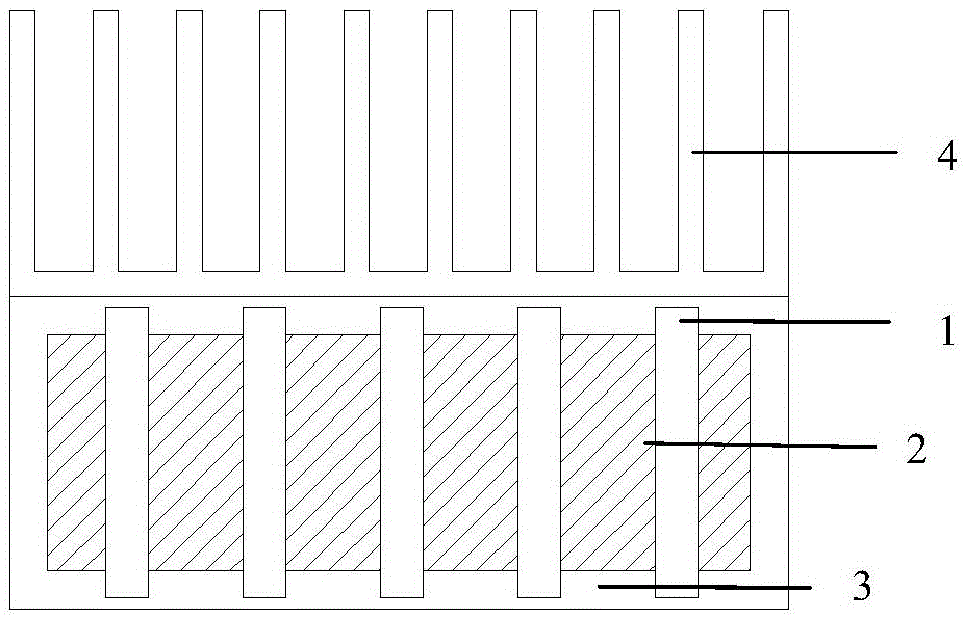
[0047] The concrete structure of present embodiment 2 is as image 3 As shown, in this embodiment, on the basis of the structure of the above-mentioned embodiment 1, cooling fins 4 are installed on the outer side of the cavity. The cooling fins can be conventional products whose size matches the cavity. The surface on the outer side of the cavity is bonded. The heat of this structural heat source is absorbed by the phase change material on the one hand, and on the other hand, is transferred from the heat pipe to the external heat dissipation fins, and is dissipated from the fins to the environment, so as to reduce the heat dissipation load of the phase change material and prolong its action time. The rest of the structure and working principle are exactly the same as that of Embodiment 1.
Embodiment 3
[0049] The concrete structure of present embodiment 3 is as Figure 4 As shown, heat dissipation fins 4 are installed on the outside of the heat pipe on the structure of embodiment 2: for example, 1 mm thickness, 5 cm length, and 3 cm width sheet are used to make them with a spacing of 8 mm, and five fins 31 are installed on each heat pipe 3 ; Installing fins on the heat pipe can further strengthen the heat exchange between the heat pipe and the phase change material, and can reduce the number of heat pipes used. The rest of the structure and working principle are exactly the same as the basic structure of Embodiment 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The inside diameter of | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com