Method for preparing solid amorphous alloy thin strips with controllable microstructures
A technology of amorphous alloys and microstructures, which is used in instruments, material analysis by measuring secondary emissions, and material analysis, etc., can solve problems such as only being applicable, not knowing the main factors of the microstructure of solid-state amorphous alloys, and not understanding the effects, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
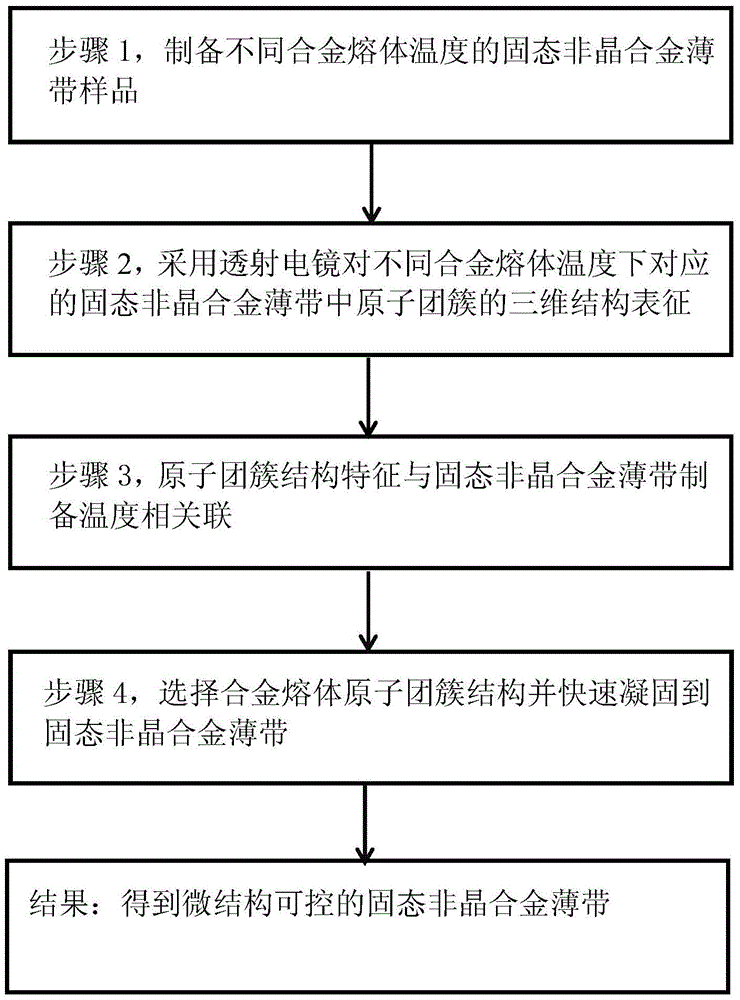
[0033] combine figure 1 , a method for preparing a solid amorphous alloy thin strip with controllable microstructure proposed by the present invention, comprising the following specific steps:
[0034] Step 1, preparing solid amorphous alloy thin strip samples at different alloy melt temperatures: the alloy melt is rapidly solidified into thin strips by high-speed planar flow continuous casting, and a series of alloy melts separated by a certain distance are prepared by changing the temperature of the alloy melt. Solid amorphous alloy thin strip sample at bulk temperature;
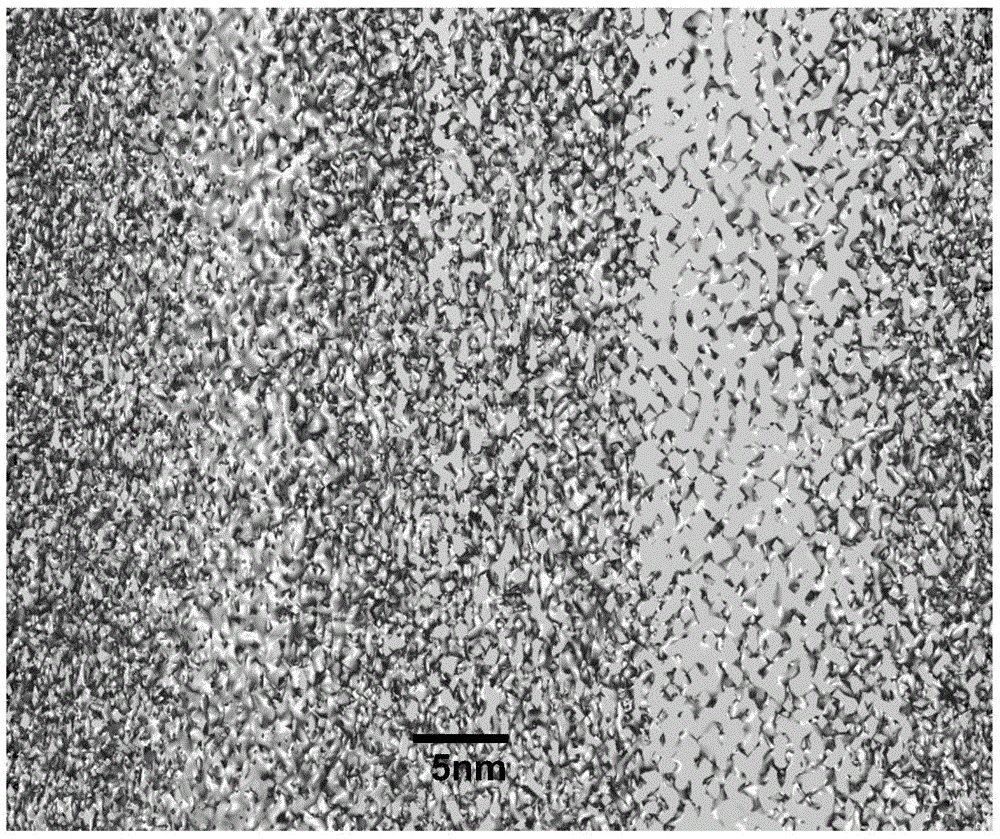
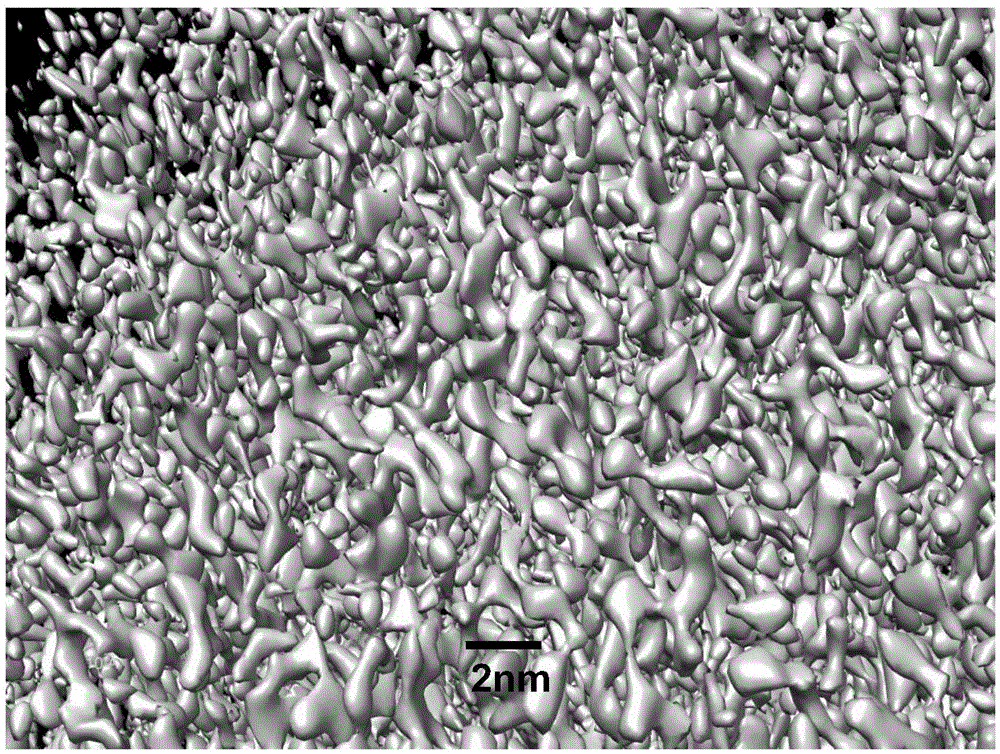
[0035] Step 2, use transmission electron microscopy to characterize the three-dimensional structure of atomic clusters in solid amorphous alloy ribbons corresponding to different alloy melt temperatures: install the solid amorphous alloy ribbon sample described in step 1 on a platform with tilting and rotating functions On the sample stage of the transmission electron microscope, in the case of a rotation...
Embodiment 1
[0039] Embodiment 1: adopt solid amorphous alloy Zr 48 Cu 45 Al 7 A thin strip (the subscript number in the chemical formula is at%), the solid amorphous alloy thin strip is prepared by the high-speed planar flow continuous casting method commonly used in this field.
[0040] The specific operation steps of using the microstructure-controllable solid-state amorphous alloy thin strip preparation method according to the present invention are as follows:
[0041] Step 1: including the following sub-steps in turn: (1) select the temperature of the alloy melt to be 1200° C., and use a high-speed planar flow continuous casting method to prepare a solid amorphous alloy thin strip with a thickness of 25 microns; (2) use an ultrasonic cutting machine (Gatan Inc. .Model: 601) Cut the six kinds of solid amorphous alloy thin strips into discs with a diameter of 3 mm; (3) place the discs in acetone for 10 minutes of ultrasonic treatment; (4) use a pit instrument (Gatan Inc.) to The cent...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Step 1: In order to obtain the microstructural characteristics of the solid amorphous alloy corresponding to the 1400°C alloy melt, first adjust the temperature of the alloy melt to 1400°C to prepare a solid amorphous alloy thin strip. The difference from Example 1 is that due to The temperature of the alloy melt increases by 200°C, which is about 17% higher than that of the alloy melt at 1200°C. Due to the increase of the temperature of the alloy melt, the cooling rate of the copper roll should be increased accordingly, so that the alloy melt at 1400 ° C can be rapidly solidified into a solid amorphous alloy strip within the same solidification time as the alloy melt at 1200 ° C, so To retain the atomic cluster structure of the 1400°C alloy melt in the solid amorphous alloy, the cooling rate needs to be increased by about 20%. In the process of preparing solid amorphous alloy thin strips with an alloy melt temperature of 1400°C, in order to improve the cooling capacity...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com