Rare earth treated normalized Q460GJ steel plate for buildings and production method of steel plate
A production method and construction technology, applied in the field of normalized Q460GJ construction steel plate and its production method, can solve the problems of different chemical composition and production process, and achieve excellent laminar tear resistance and low yield strength ratio. , the effect of improving the overall performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
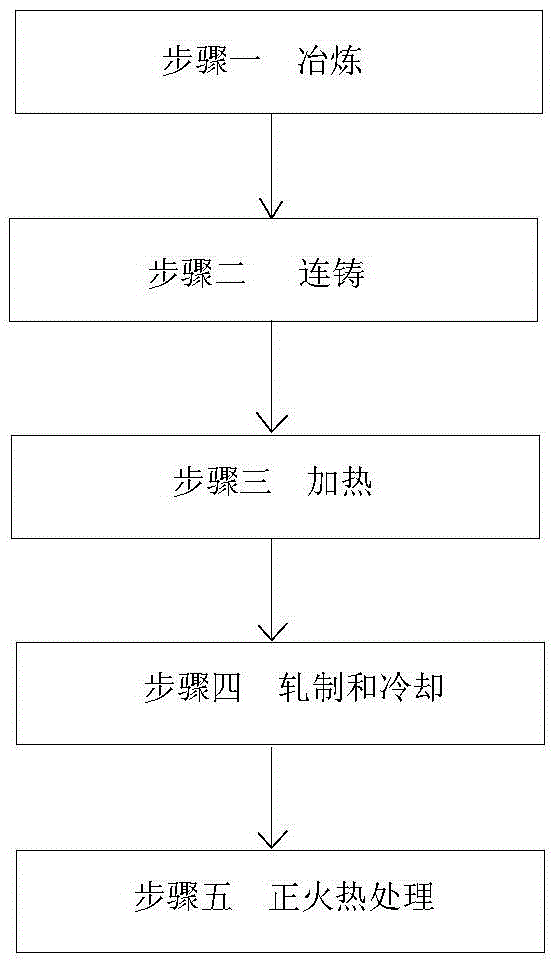
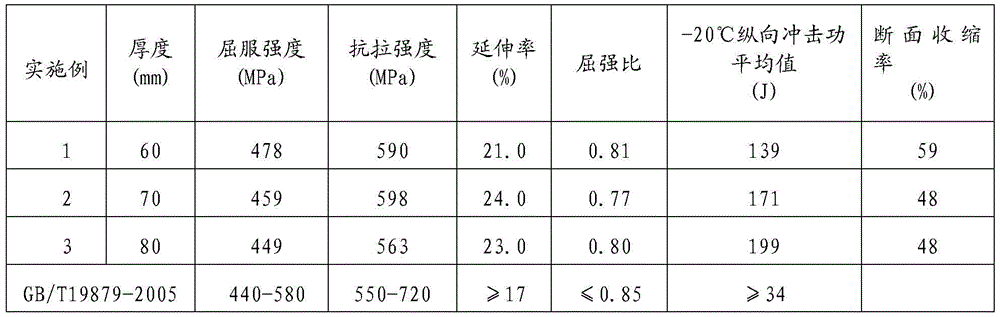
[0026] The raw material molten iron is subjected to deep desulfurization of molten iron, top-bottom blowing of converter, argon blowing of ladle, external refining of LF furnace, RH vacuum treatment and continuous casting process to obtain 300mm thick slab with chemical composition weight percentage shown in Table 1. The slab heating temperature is 1220°C, the heating time is 243min, the rolling start temperature of the first stage is 1190°C, and the relative reduction ratio of a single pass is controlled at least 20% in at least two passes. When the thickness of the rolled piece is 120mm, After the temperature reaches 910°C, the second-stage rolling is carried out, the final rolling temperature is 840°C, and the thickness of the finished steel plate is 60mm. After rolling, the steel plate enters the accelerated cooling (ACC) equipment and is cooled to 680°C at a rate of 5°C / s. After hot straightening, the cooling bed is cooled. After finishing and shot blasting, it is sent to...
Embodiment 2
[0028] The implementation is the same as in Example 1, wherein the heating temperature is 1215°C, the heating time is 230min, the rolling start temperature of the first stage rolling is 1185°C, the starting rolling temperature of the second stage rolling is 900°C, and the thickness of the rolled piece is 126mm. The final rolling temperature is 850°C, and the thickness of the finished steel plate is 70mm. The cooling rate of the steel plate is 6°C / s, and the final cooling temperature is 670°C. After hot straightening, the cooling bed is cooled. After finishing and shot blasting, it is sent to the normalizing furnace for normalizing treatment. The normalizing temperature is 880°C, and the time T in the furnace is 1.5t+10. The unit of T is min, and t is the thickness of the steel plate in mm. Finally, the finished steel plate can be obtained.
Embodiment 3
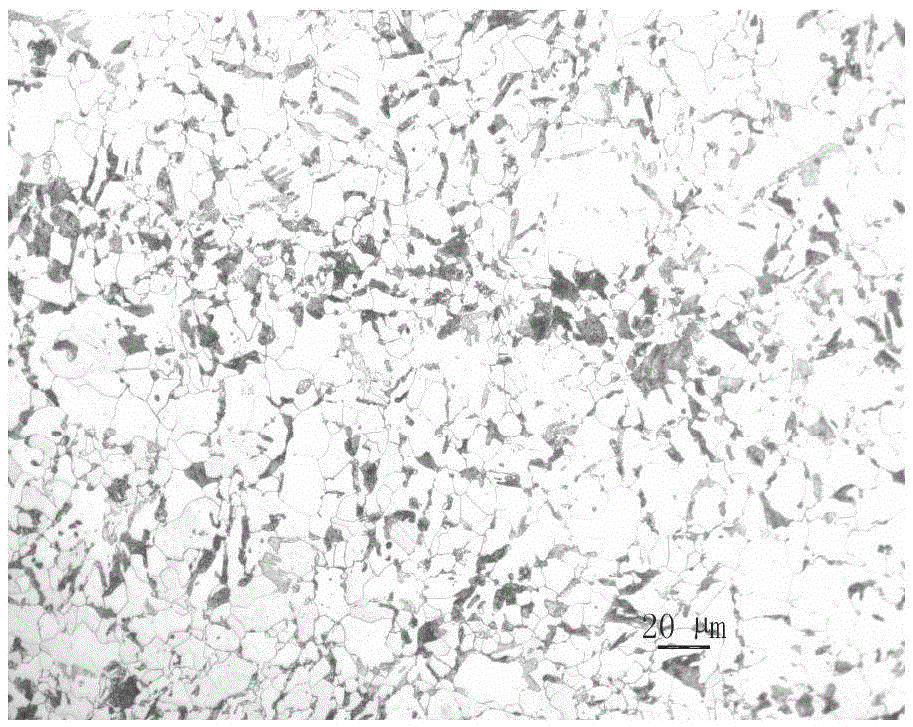
[0030] The implementation is the same as in Example 1, wherein the heating temperature is 1210°C, the heating time is 230min, the rolling start temperature of the first stage rolling is 1190°C, the starting rolling temperature of the second stage rolling is 890°C, and the thickness of the rolled piece is 128mm. The final rolling temperature is 860°C, and the thickness of the finished steel plate is 80mm. The cooling rate of the steel plate is 8°C / s, and the final cooling temperature is 660°C. After hot straightening, the cooling bed is cooled. After finishing and shot blasting, it is sent to the normalizing furnace for normalizing treatment. The normalizing temperature is 880°C, and the time T in the furnace is 1.5t+10. The unit of T is min, and t is the thickness of the steel plate in mm. Finally, the finished steel plate can be obtained. The metallographic structure diagram of embodiment 3 steel plate 1 / 2 thickness place is as figure 2 As shown, the metallographic struct...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com