Method for in-situ remediation of mercury pollution in underground water with magnetite and bauxite slag
An in-situ remediation and bauxite technology, applied in water pollutants, chemical instruments and methods, contaminated groundwater/leachate treatment, etc., can solve the problems of long-term effectiveness and high cost of groundwater, and increase hydraulic retention time , saving construction costs, good stability and safety
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
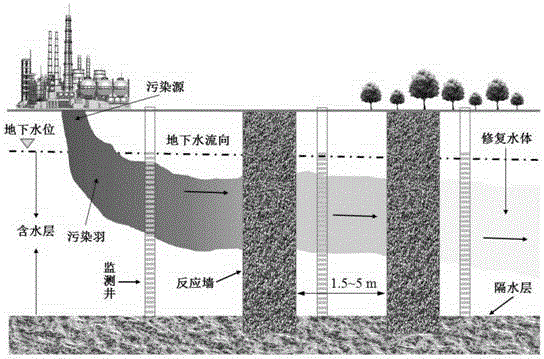
[0021] The hydrological and hydrogeological parameters of the aquifer at a mercury-polluted site are as follows: the medium type of the aquifer is coarse sand, the permeability coefficient is 20m / d, the maximum concentration of mercury pollution is 200μg / L, the width of the pollution plume is 1.6m, and the highest groundwater level is 3.8 m, the depth of the aquifer is 5m underground, and the hydraulic gradient is 0.001.
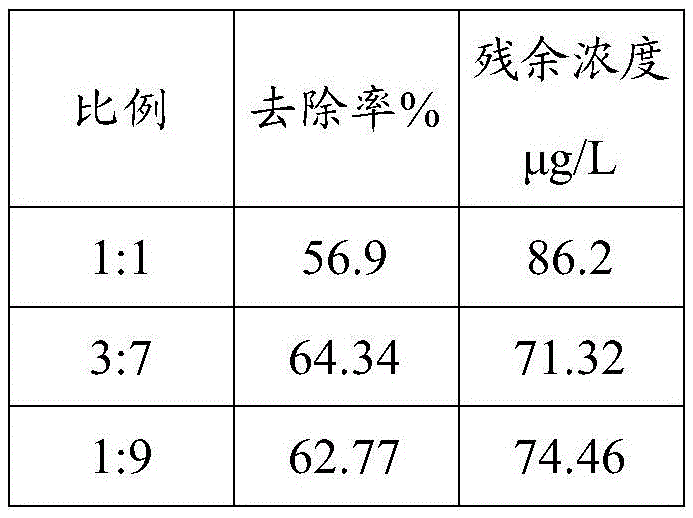
[0022] 1. Crushing and sieving the slag of natural magnetite and bauxite, the particle size is 0.5-1mm for later use, the mass ratio of natural magnetite and bauxite is 1:1, and the permeability coefficient is 75m / d .
[0023] 2. Take the sand from the natural river, dry it, sieve it, and take the sand with a particle size of 0.5-1mm for use.
[0024] 3. The reaction wall is set downstream of the groundwater pollution plume, perpendicular to the direction of groundwater flow, and the length is 1.2 to 1.5 times the width of the groundwater pollution plume; t...
Embodiment 2
[0038] The hydrological and hydrogeological parameters of the aquifer at a mercury-contaminated site are as follows: the medium type of the aquifer is coarse sand, the permeability coefficient is 20m / d, the maximum concentration of mercury pollution is 50μg / L, the width of the pollution plume is 1.6m, and the highest groundwater table is 3.8 m, the depth of the aquifer is 5m underground, and the hydraulic gradient is 0.001.
[0039] 1. Crushing and sieving the slag of natural magnetite and bauxite, the particle size is 0.5-1mm for later use, the mass ratio of natural magnetite and bauxite is 1:1, and the permeability coefficient is 75m / d .
[0040] 2. Take the sand from the natural river, dry it, sieve it, and take the sand with a particle size of 0.5-1mm for use.
[0041] 3. The reaction wall is set downstream of the groundwater pollution plume, perpendicular to the direction of groundwater flow, and the length is 1.2 to 1.5 times the width of the groundwater pollution plume...
Embodiment 3
[0055] The hydrological and hydrogeological parameters of the aquifer at a mercury-contaminated site are as follows: the medium type of the aquifer is coarse sand, the permeability coefficient is 20m / d, the maximum concentration of mercury pollution is 50μg / L, the width of the pollution plume is 1.6m, and the highest groundwater table is 3.8 m, the depth of the aquifer is 5m underground, and the hydraulic gradient is 0.001.
[0056] 1. Crushing and sieving the slag of natural magnetite and bauxite, take the particle size of 1-1.5mm for later use, the addition ratio of natural magnetite and bauxite is 1:9, and the permeability coefficient is 120m / d .
[0057] 2. Take the sand from the natural river, dry it, sieve it, and take the sand with a particle size of 1-1.5mm for use.
[0058] 3. The reaction wall is set downstream of the groundwater pollution plume, perpendicular to the direction of groundwater flow, and the length is 1.2 to 1.5 times the width of the groundwater pollu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| osmotic coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| osmotic coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com