Patents
Literature
38 results about "Nuclear weapon" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
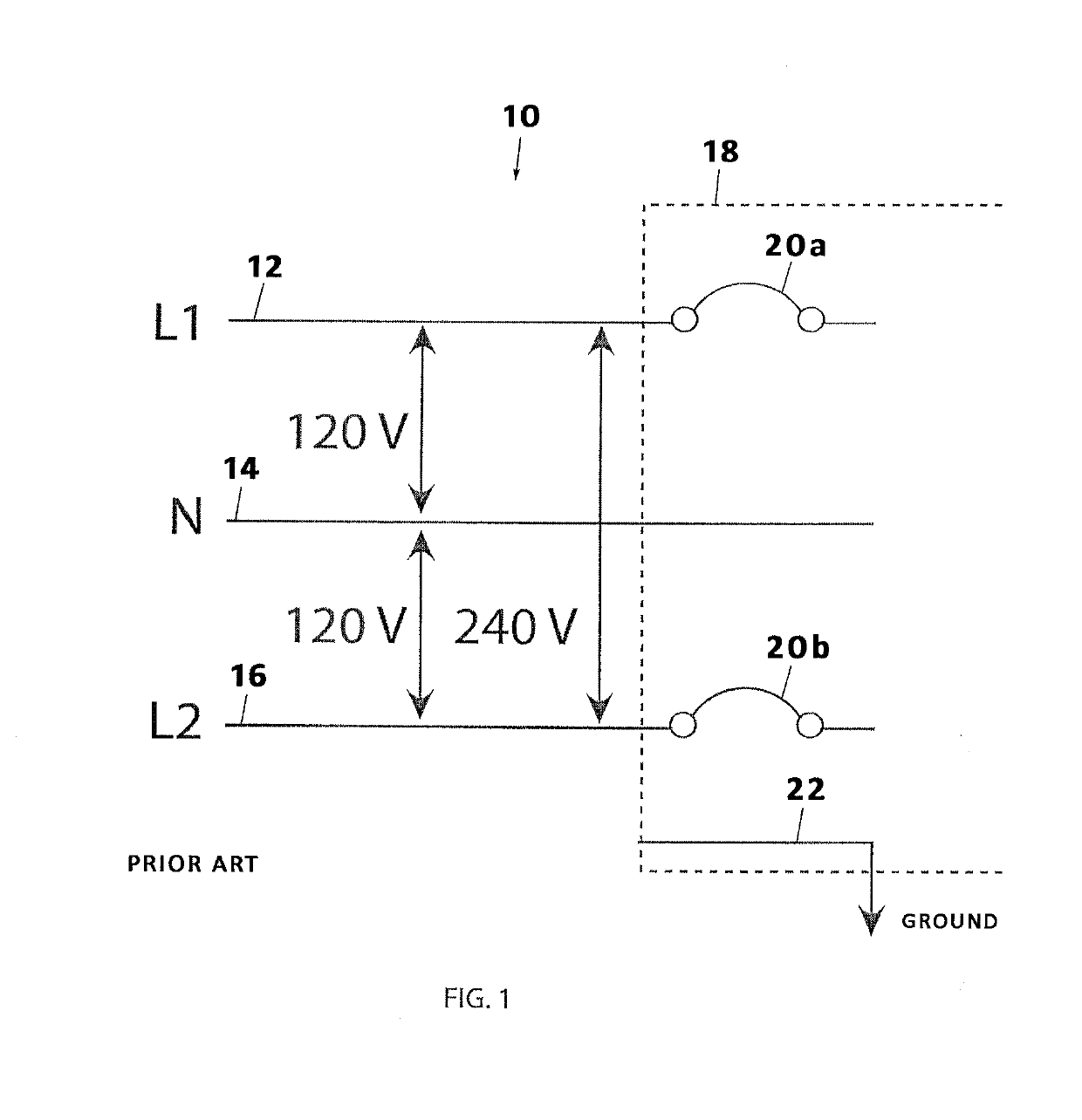
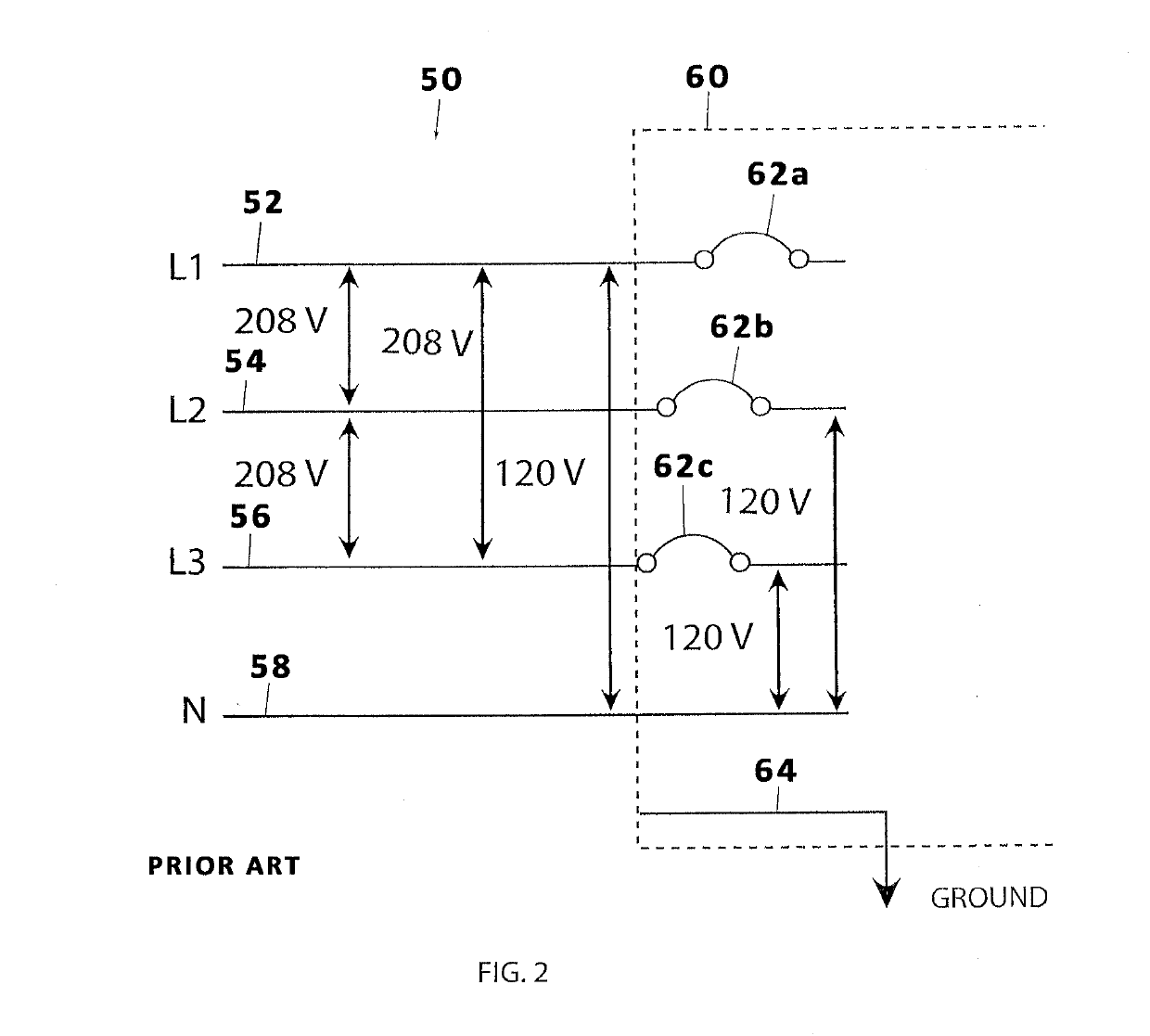
A nuclear weapon (also called an atom bomb, nuke, atomic bomb, nuclear warhead, A-bomb, or nuclear bomb) is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or from a combination of fission and fusion reactions (thermonuclear bomb). Both bomb types release large quantities of energy from relatively small amounts of matter. The first test of a fission ("atomic") bomb released an amount of energy approximately equal to 20,000 tons of TNT (84 TJ). The first thermonuclear ("hydrogen") bomb test released energy approximately equal to 10 million tons of TNT (42 PJ). A thermonuclear weapon weighing little more than 2,400 pounds (1,100 kg) can release energy equal to more than 1.2 million tons of TNT (5.0 PJ). A nuclear device no larger than traditional bombs can devastate an entire city by blast, fire, and radiation. Since they are weapons of mass destruction, the proliferation of nuclear weapons is a focus of international relations policy.
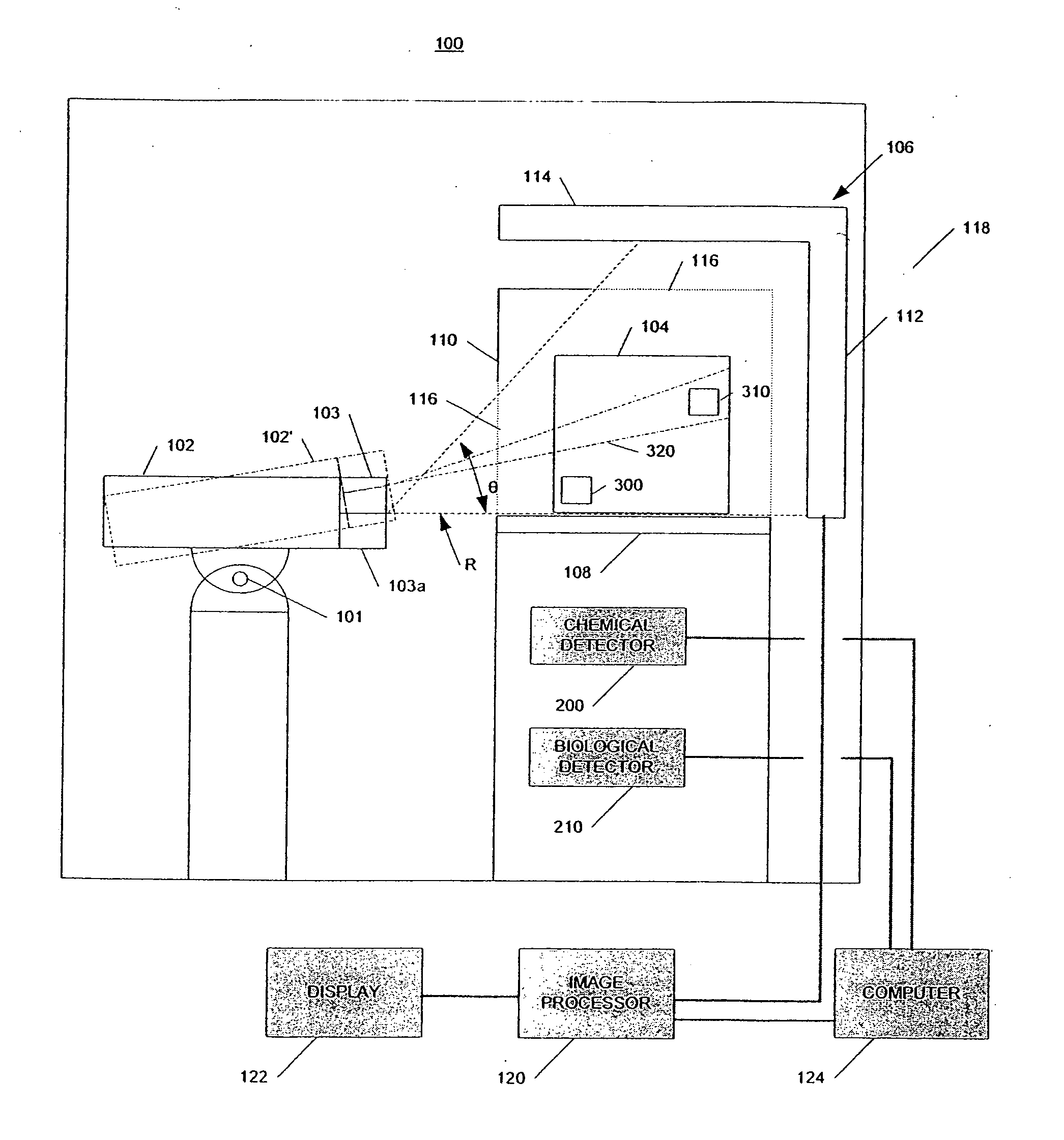
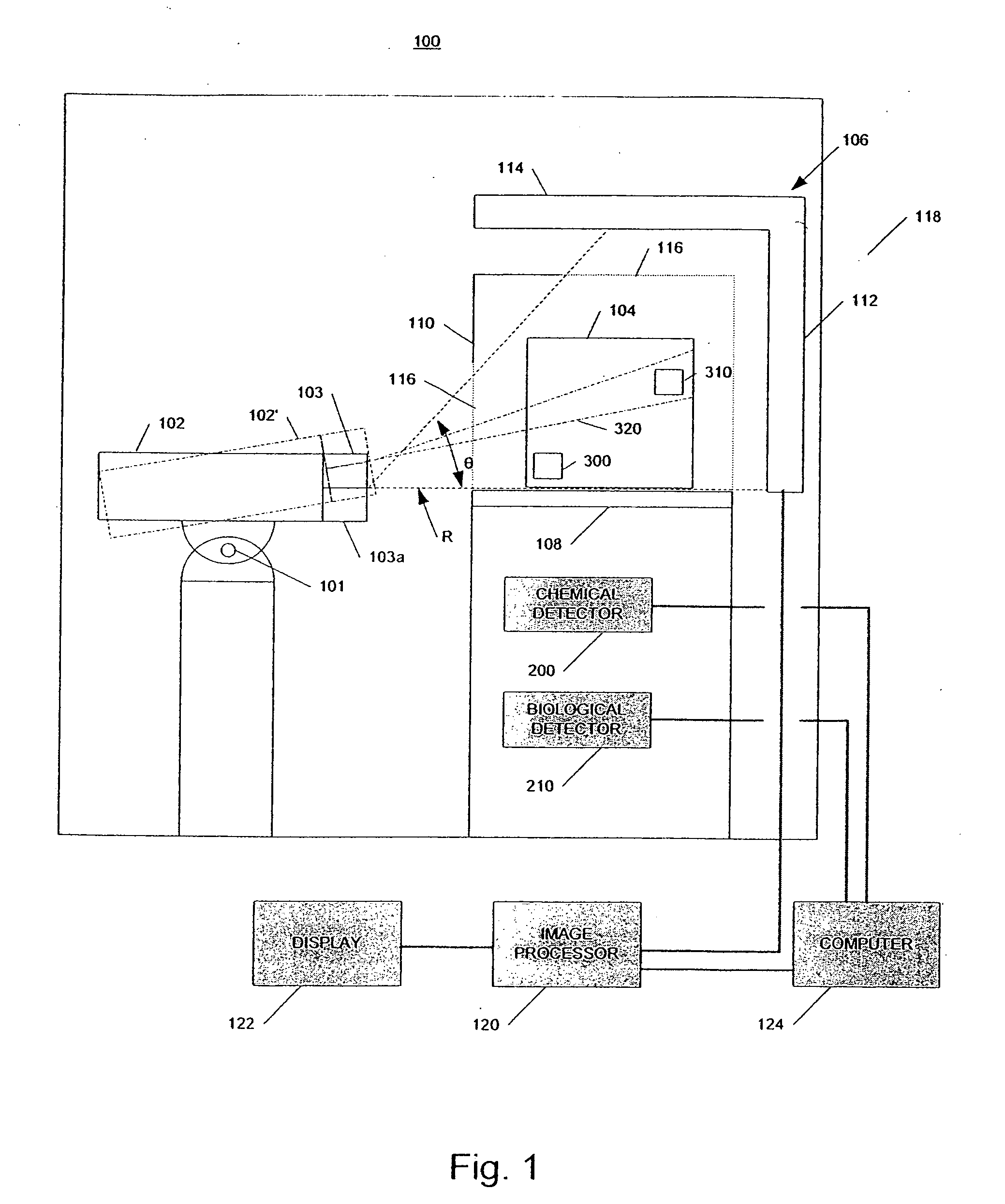
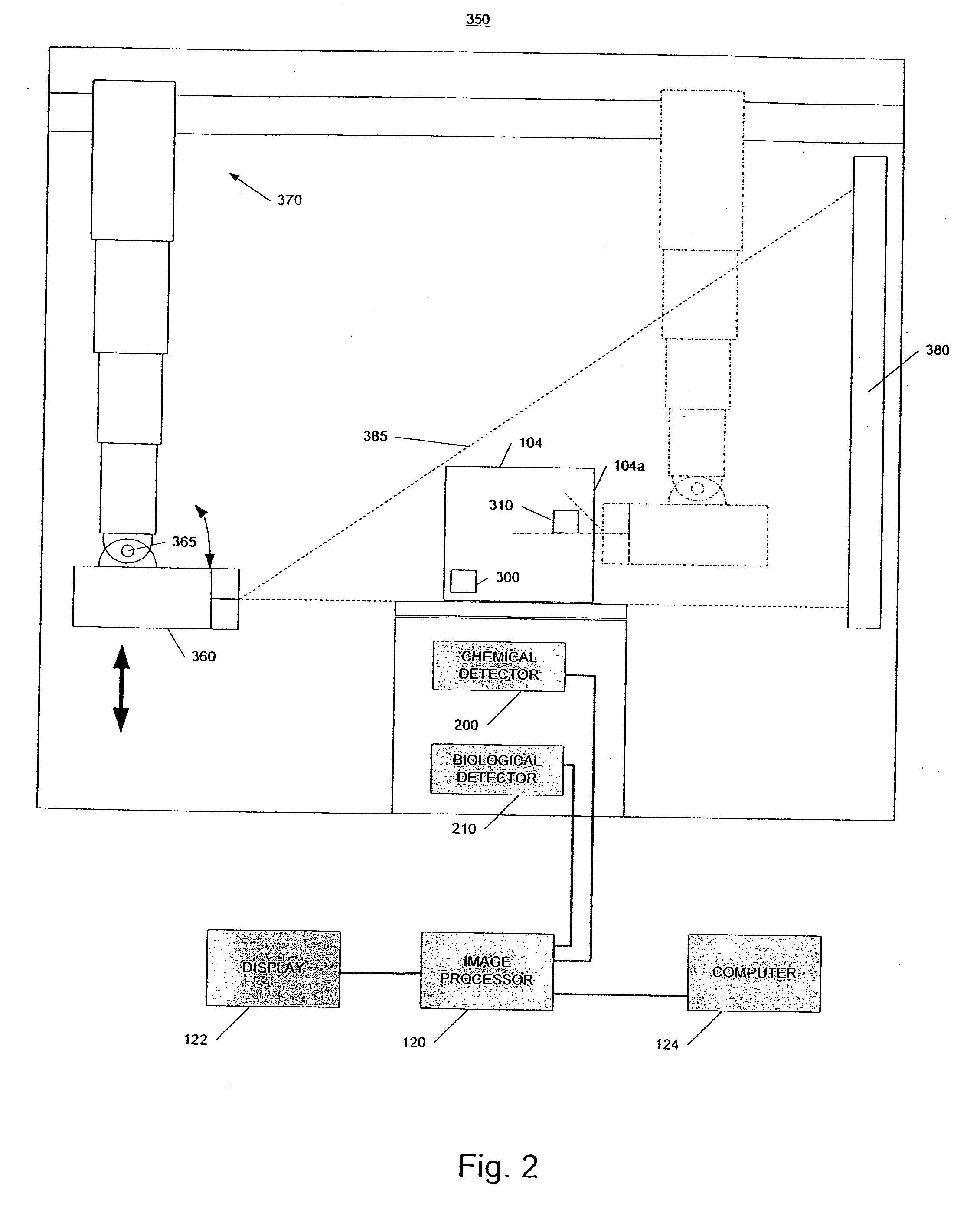
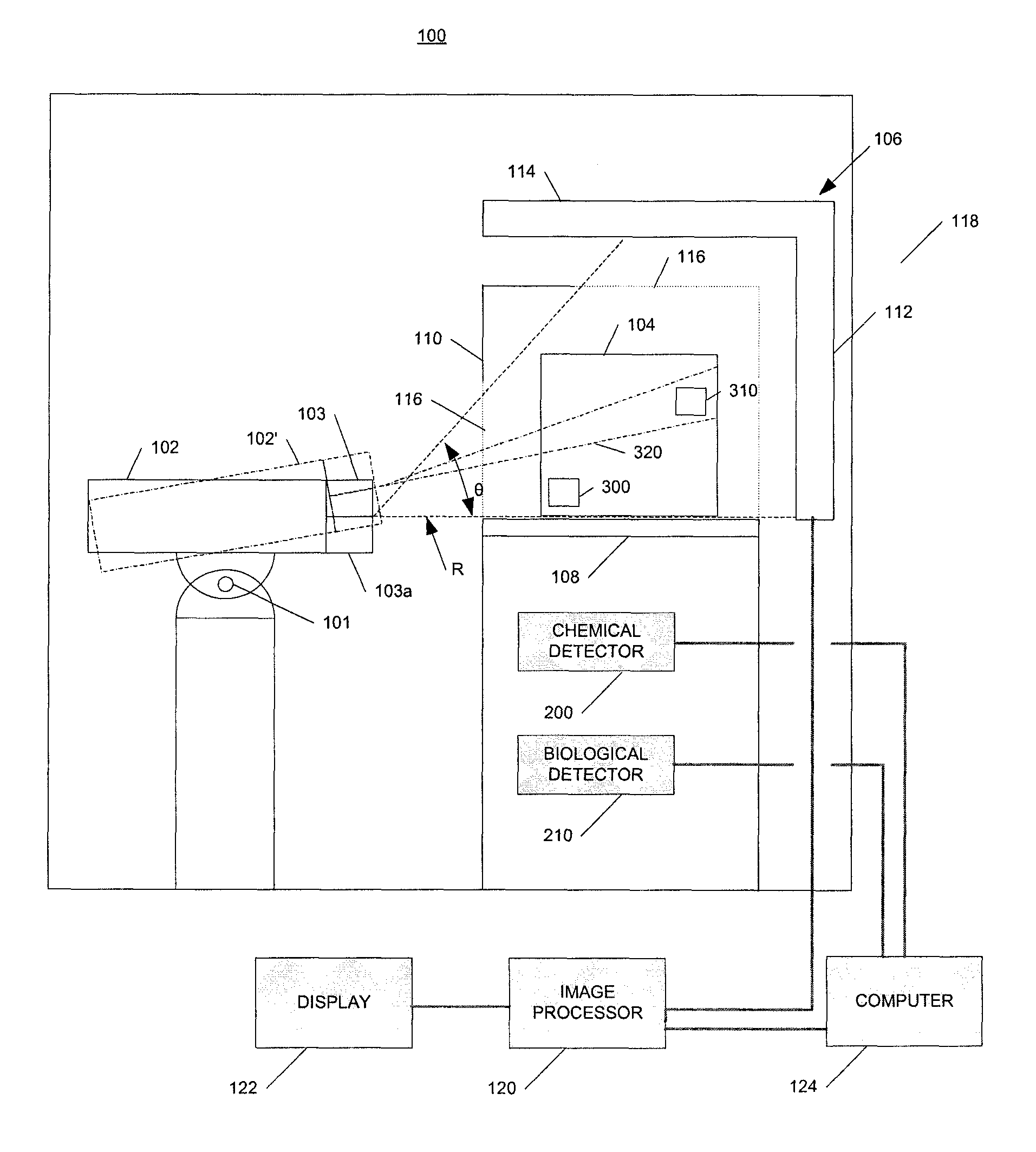
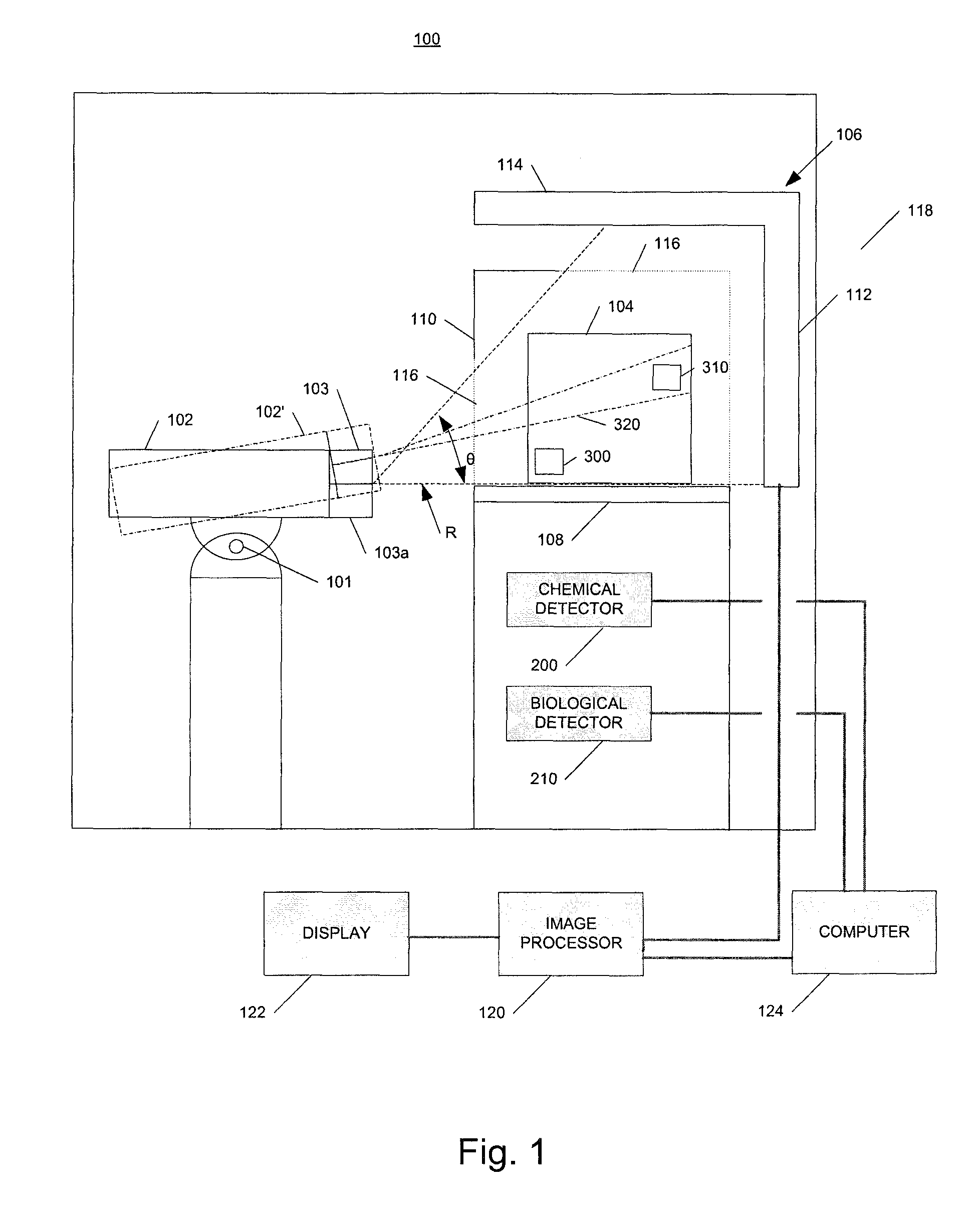
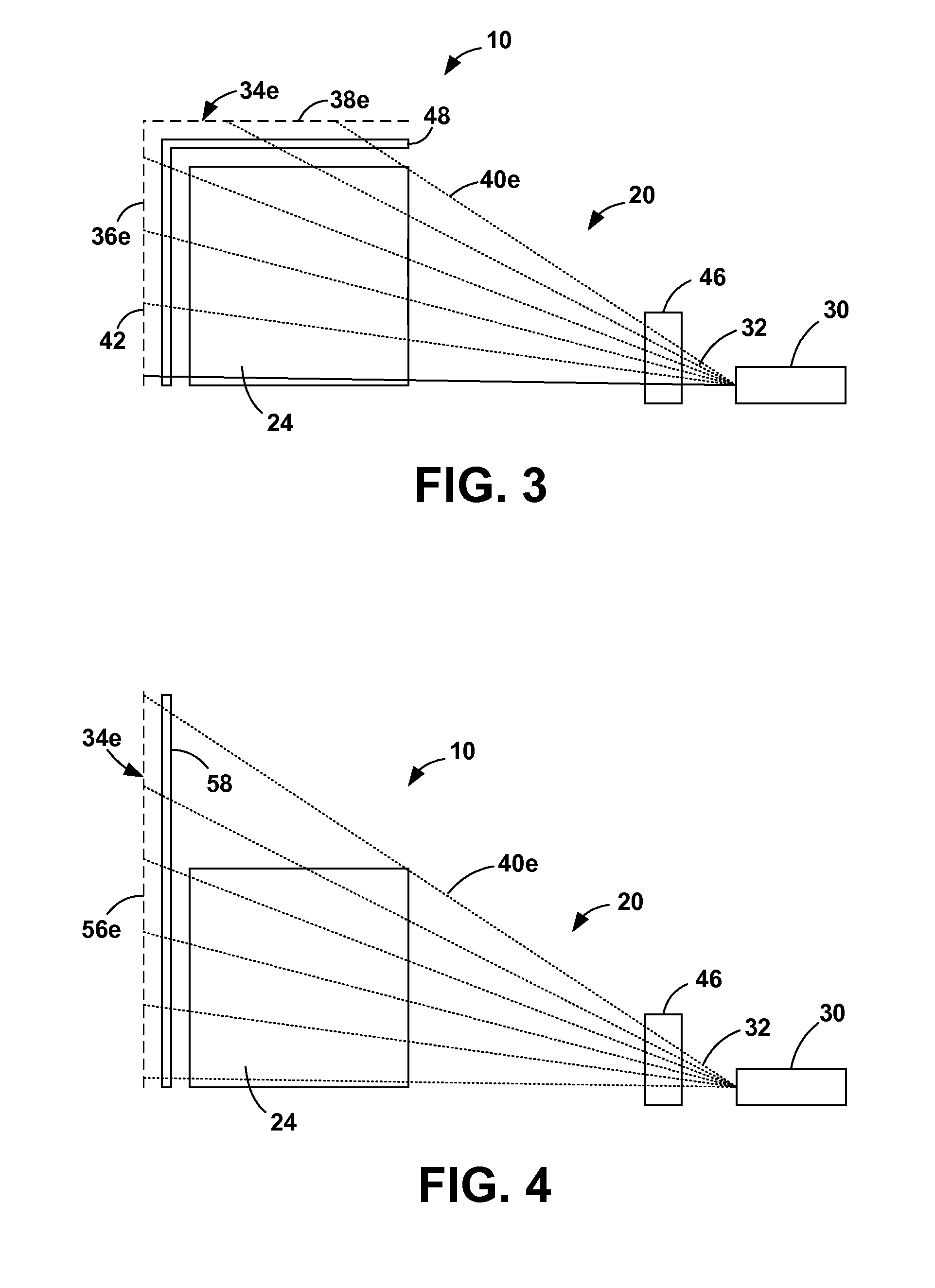
Radiation scanning and disabling of hazardous targets in containers
ActiveUS8223918B2Material analysis by transmitting radiationIrradiation devicesNuclear weaponElectron
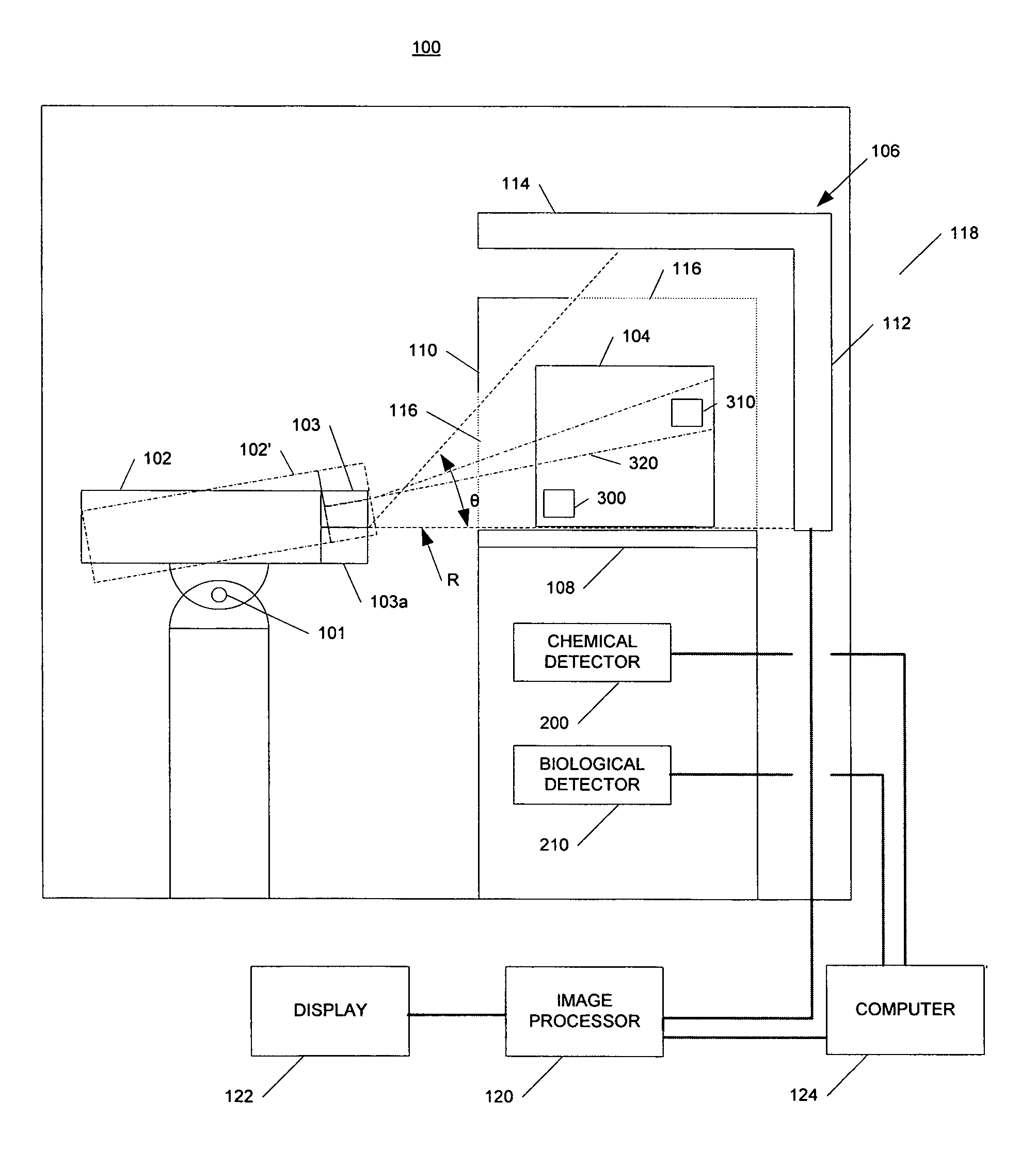
In one example, a method of examining a container is disclosed comprising detecting a potential threat within contents of a container using radiation scanning and disabling the potential threat with radiation. In another example, a method of examining a container is disclosed comprising scanning at least a portion of the container with a first radiation beam, detecting radiation interacting with contents of the container, identifying a potential threat contained based, at least in part, on the detected radiation, and disabling the potential threat with a dose of radiation from a second radiation beam. The potential threat may be a nuclear, chemical, and / or biological weapon, for example. Chemical and / or biological detectors may also be provided. The threat and / or electronics associated with the threat, may be disabled. Systems are also disclosed.
Owner:VAREX IMAGING CORP
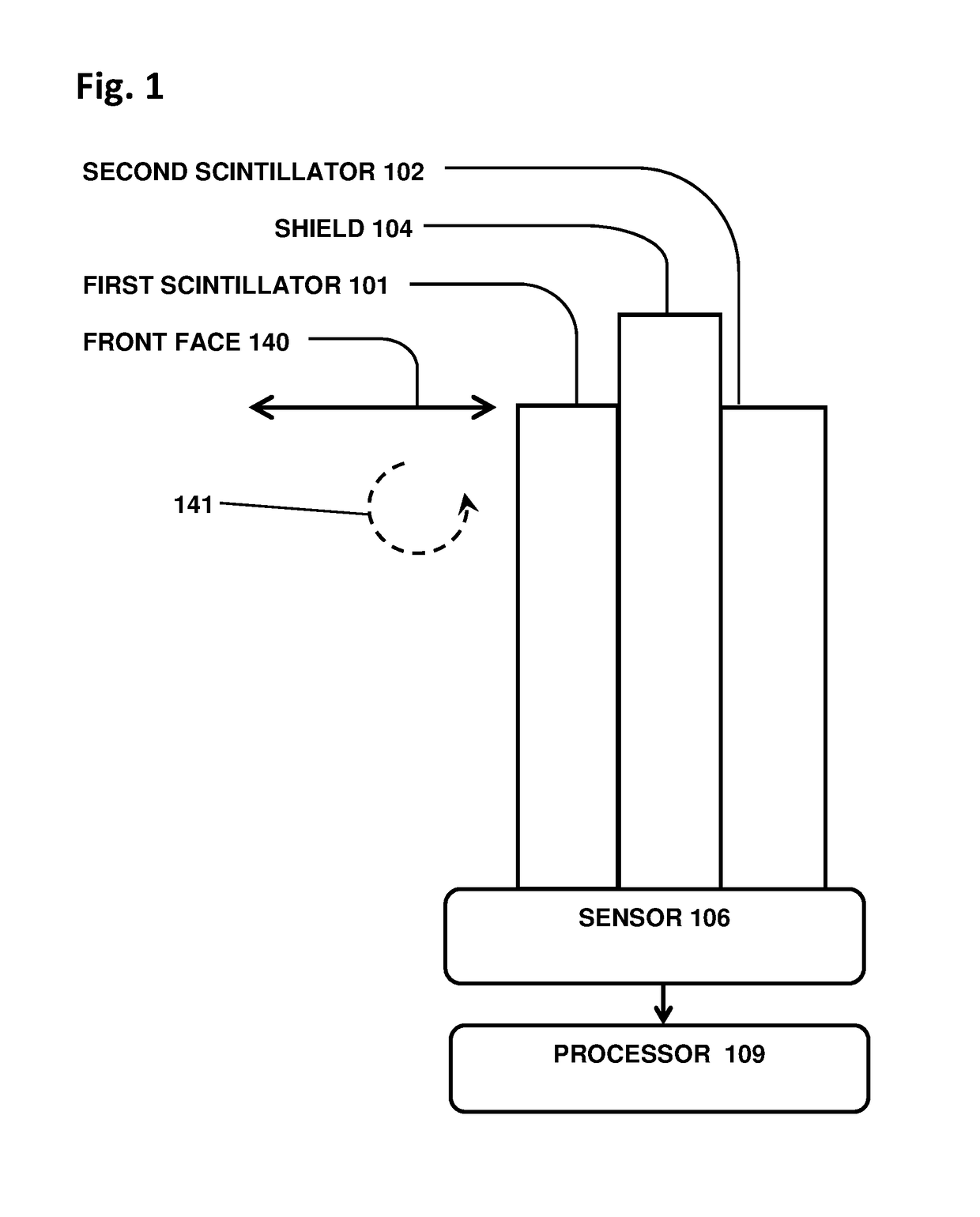
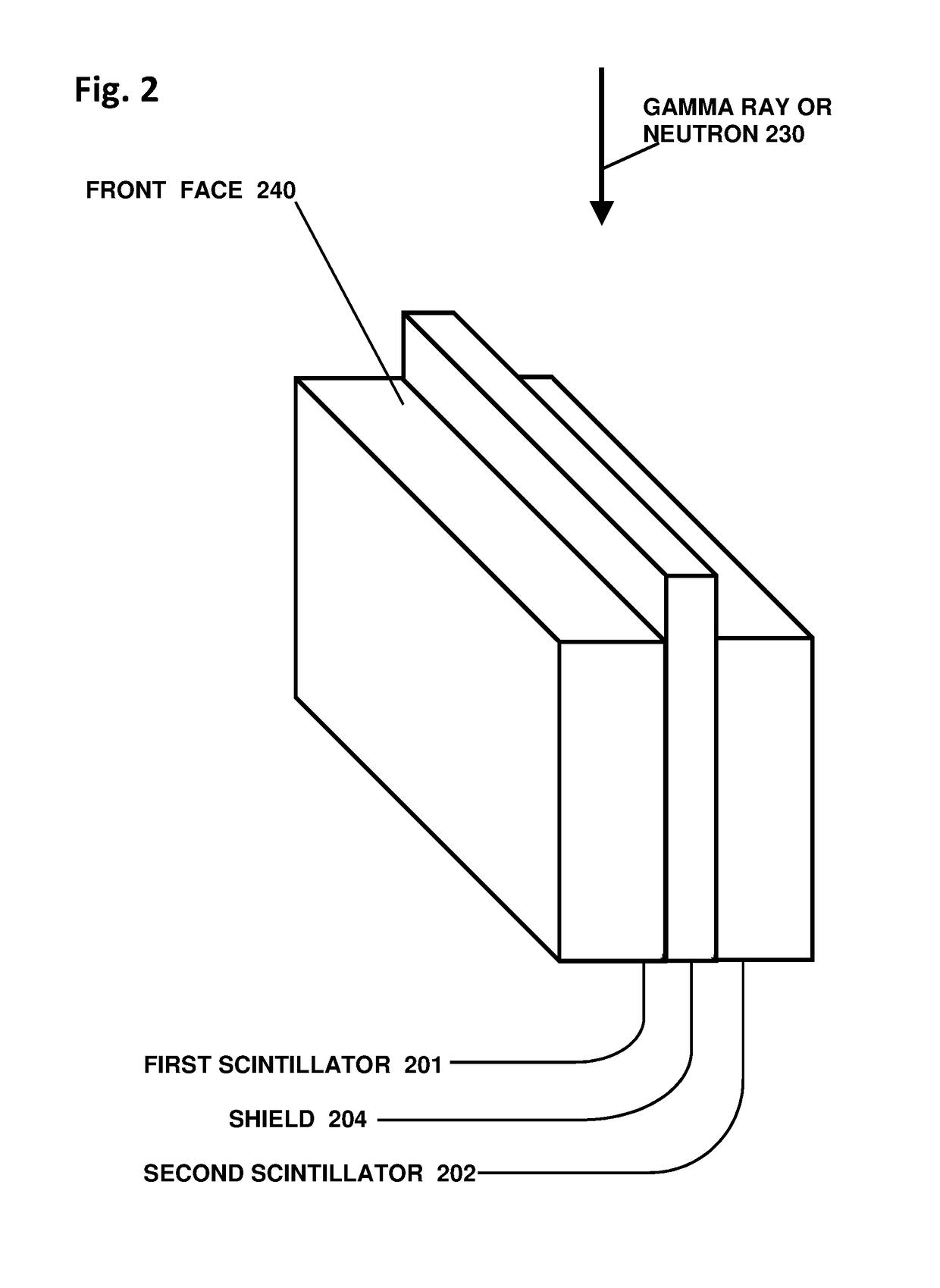
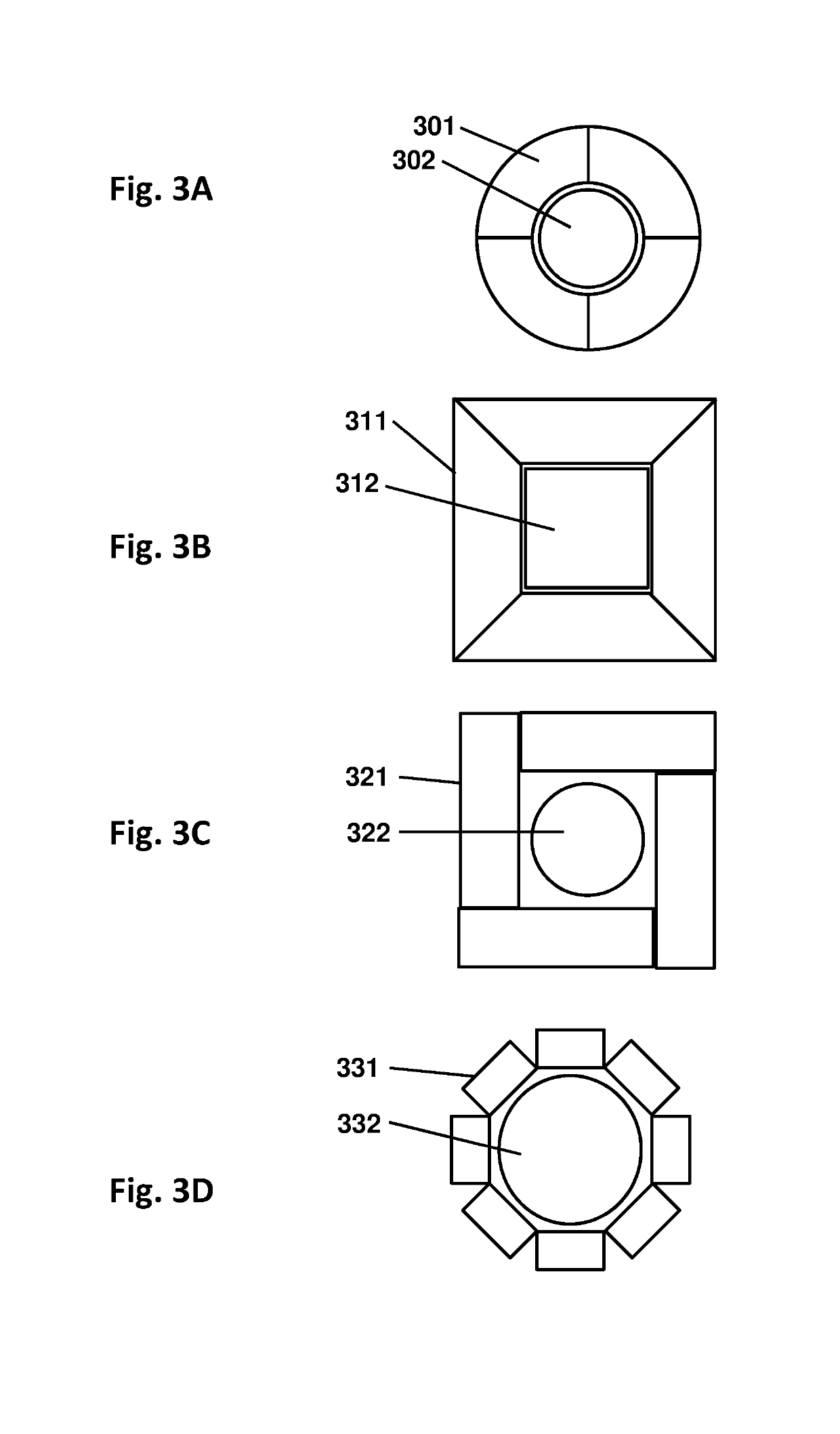
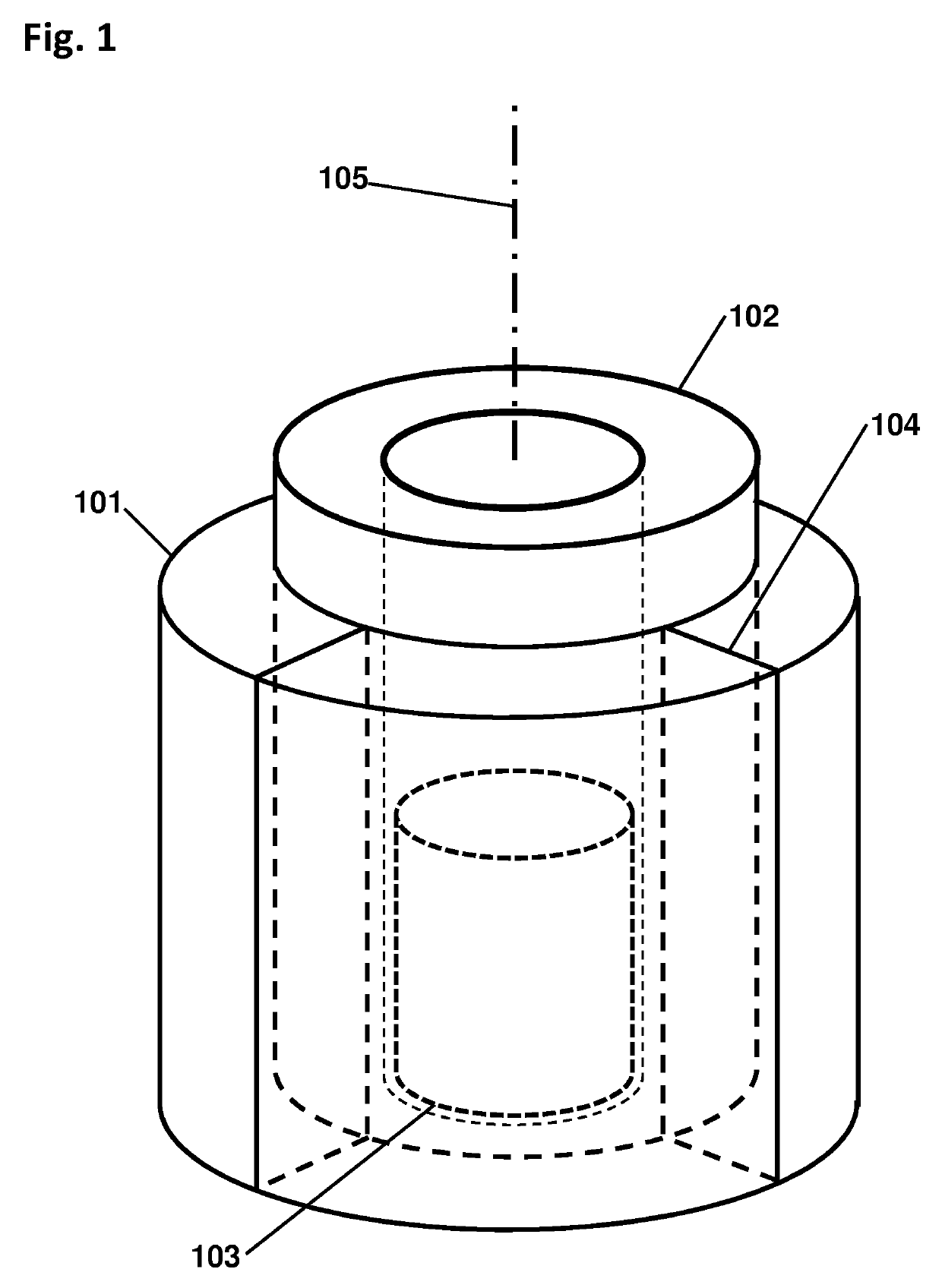
Directional particle detector with shield and scintillators
ActiveUS9864074B1Increase contrastSolve the low detection efficiencyMeasurement with scintillation detectorsRadiation intensity measurementCounting rateGamma ray
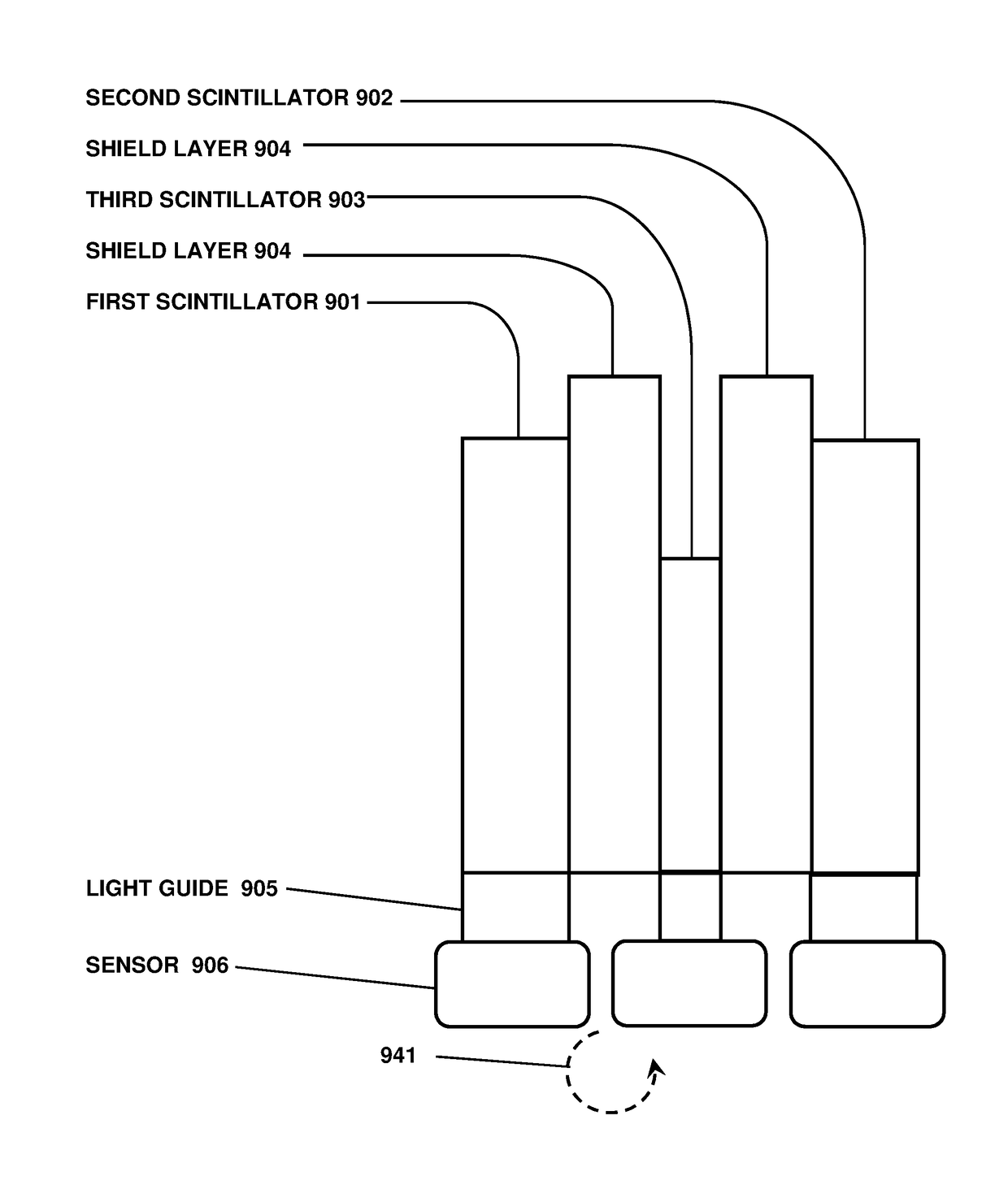
A device that detects gamma rays or neutrons, and determines their source location, comprises two scintillator panels separated by a shield barrier. Particles incident from one side can fully strike the first scintillator, but are blocked by the shield from reaching the second scintillator. Particles from the other side can reach only the second scintillator. Thus the detector indicates the left-right direction for the source location quickly, and then with further data localizes the source precisely by analysis of the two opposite scintillator count rates versus angle, using methods disclosed. The detector enables rapid inspections of vehicles and cargo containers for clandestine radiological and nuclear weapons, and sensitive localization of radioactive material in a walk-through portal application. Detectors with such capabilities are essential for stopping nuclear and radiological terrorism.
Owner:NEWMAN DAVID EDWARD
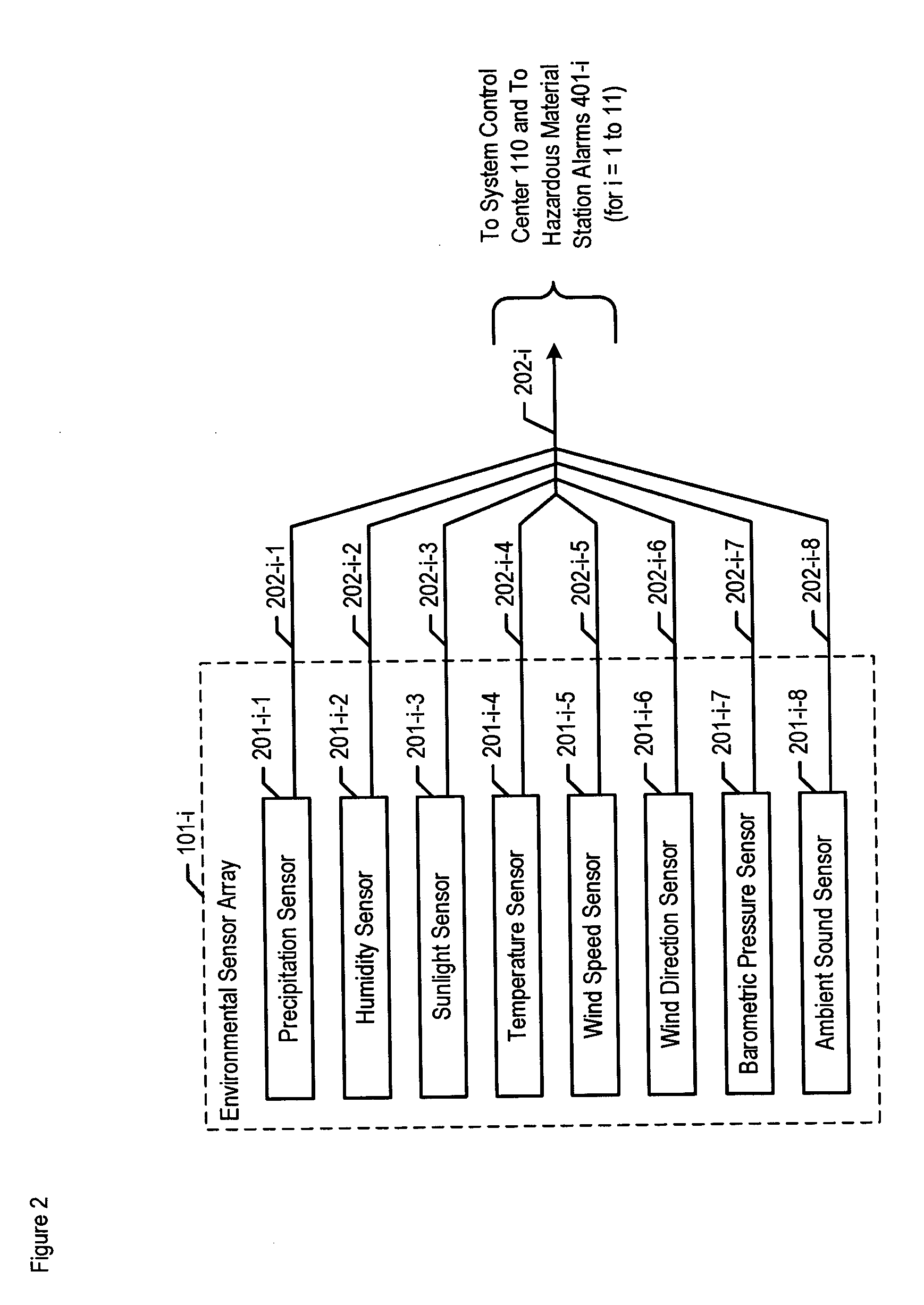
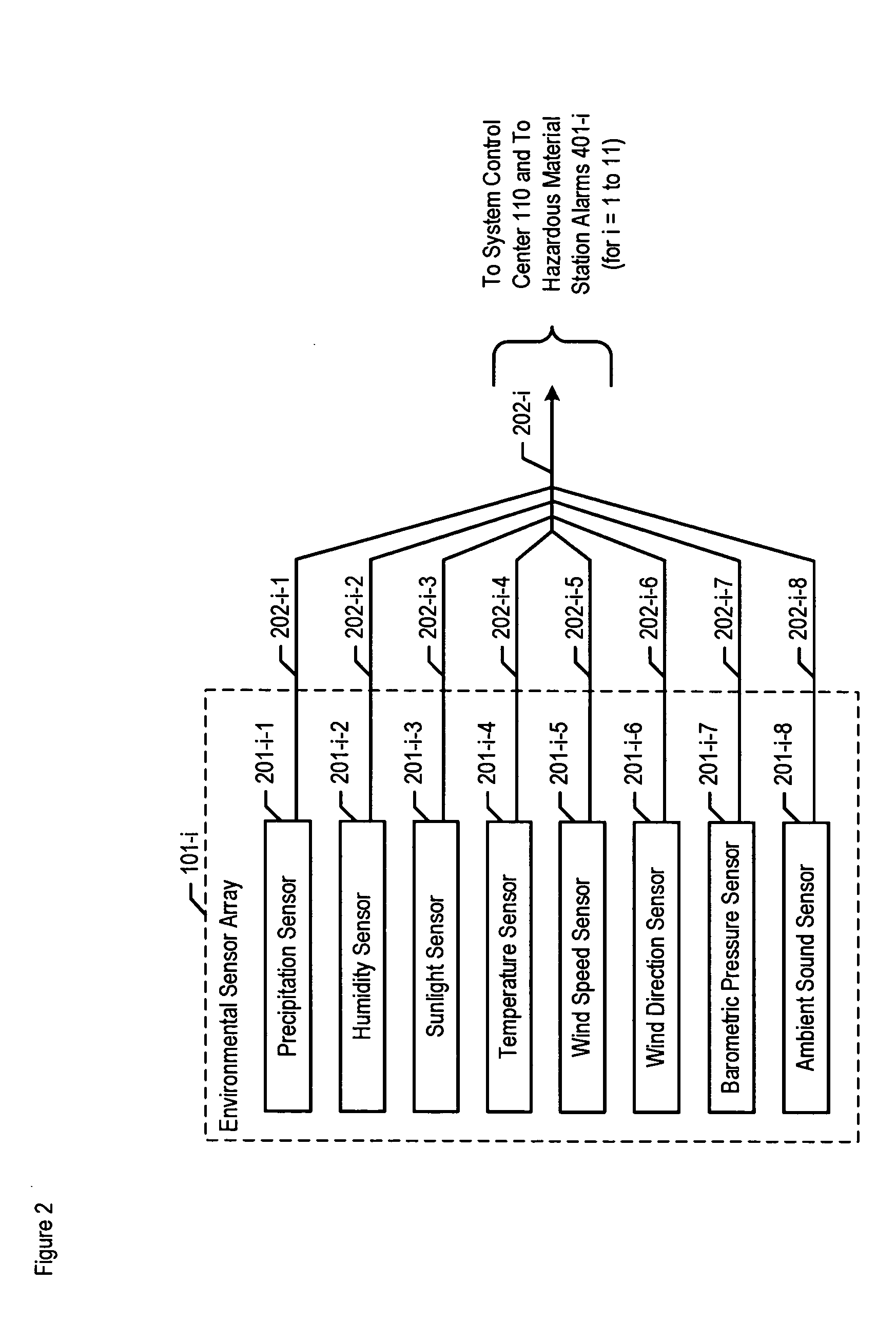
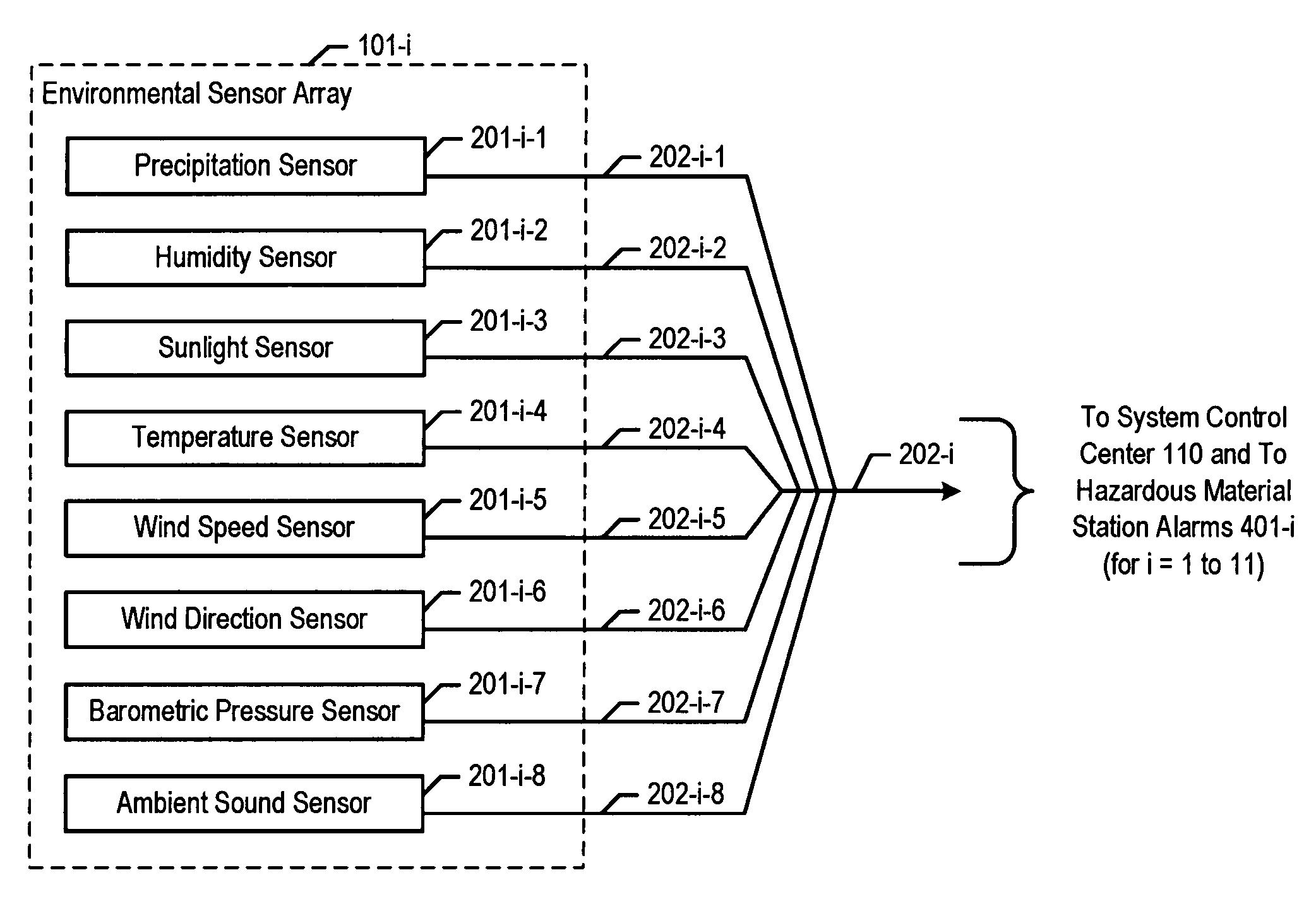
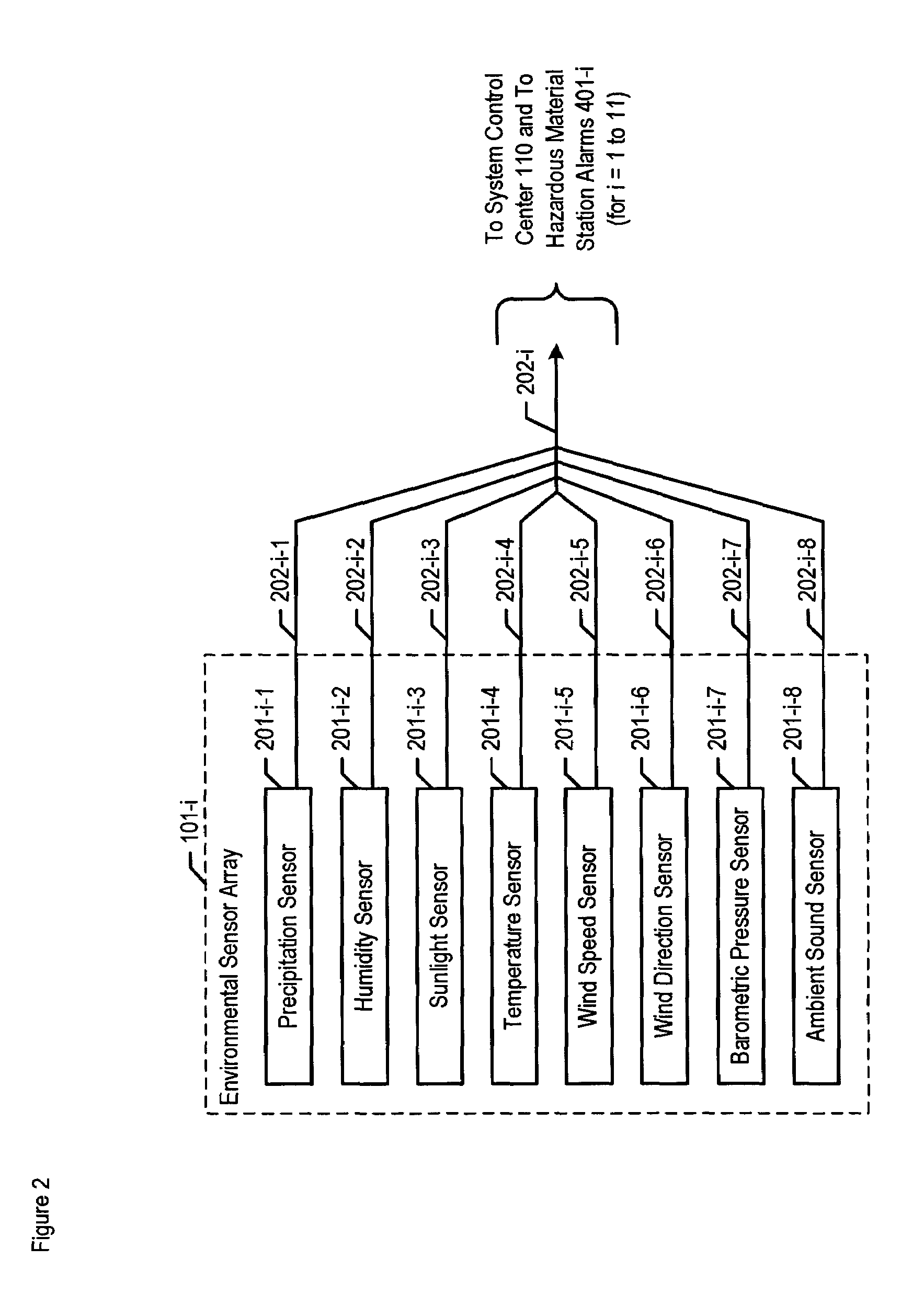
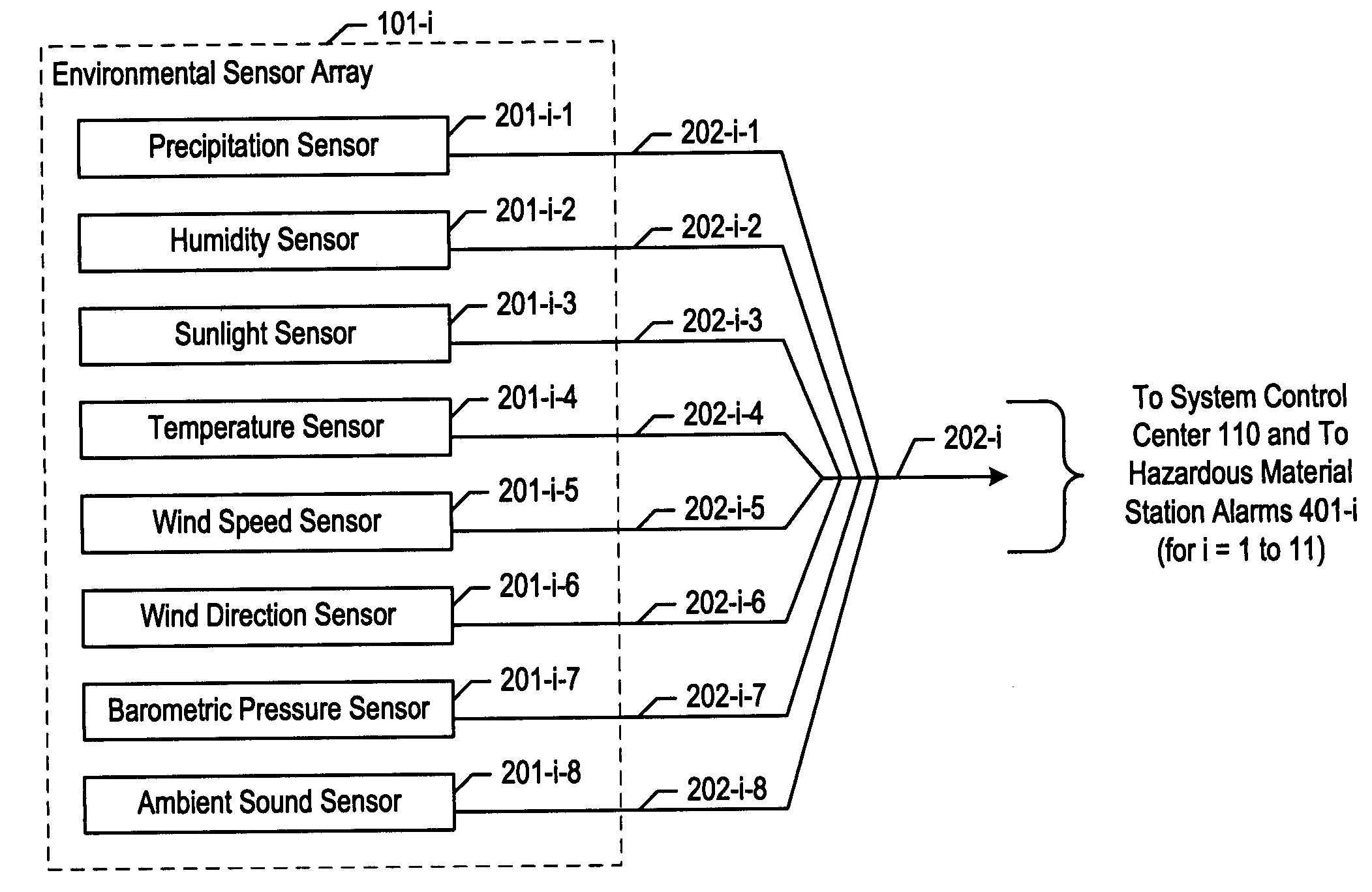
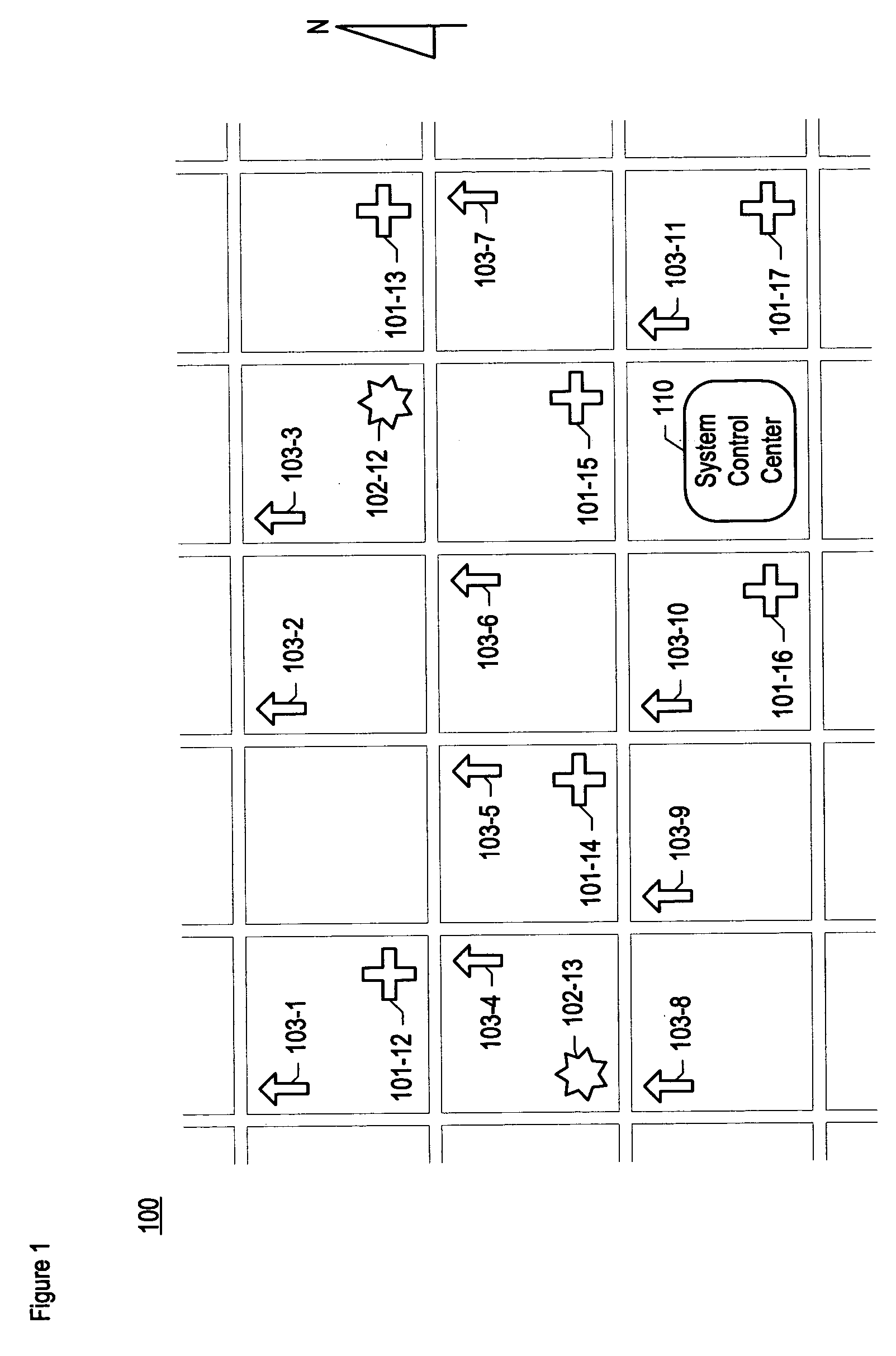
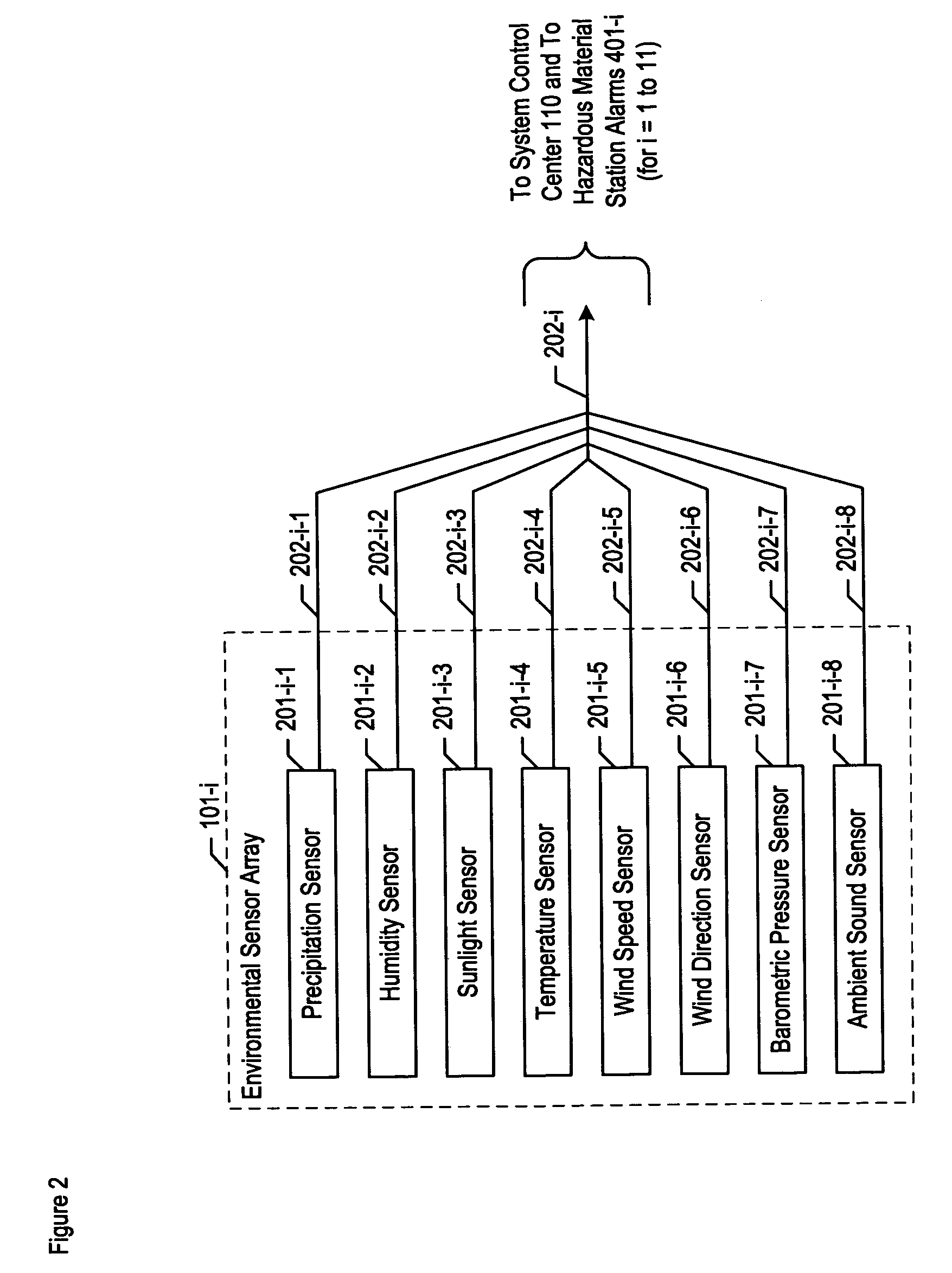
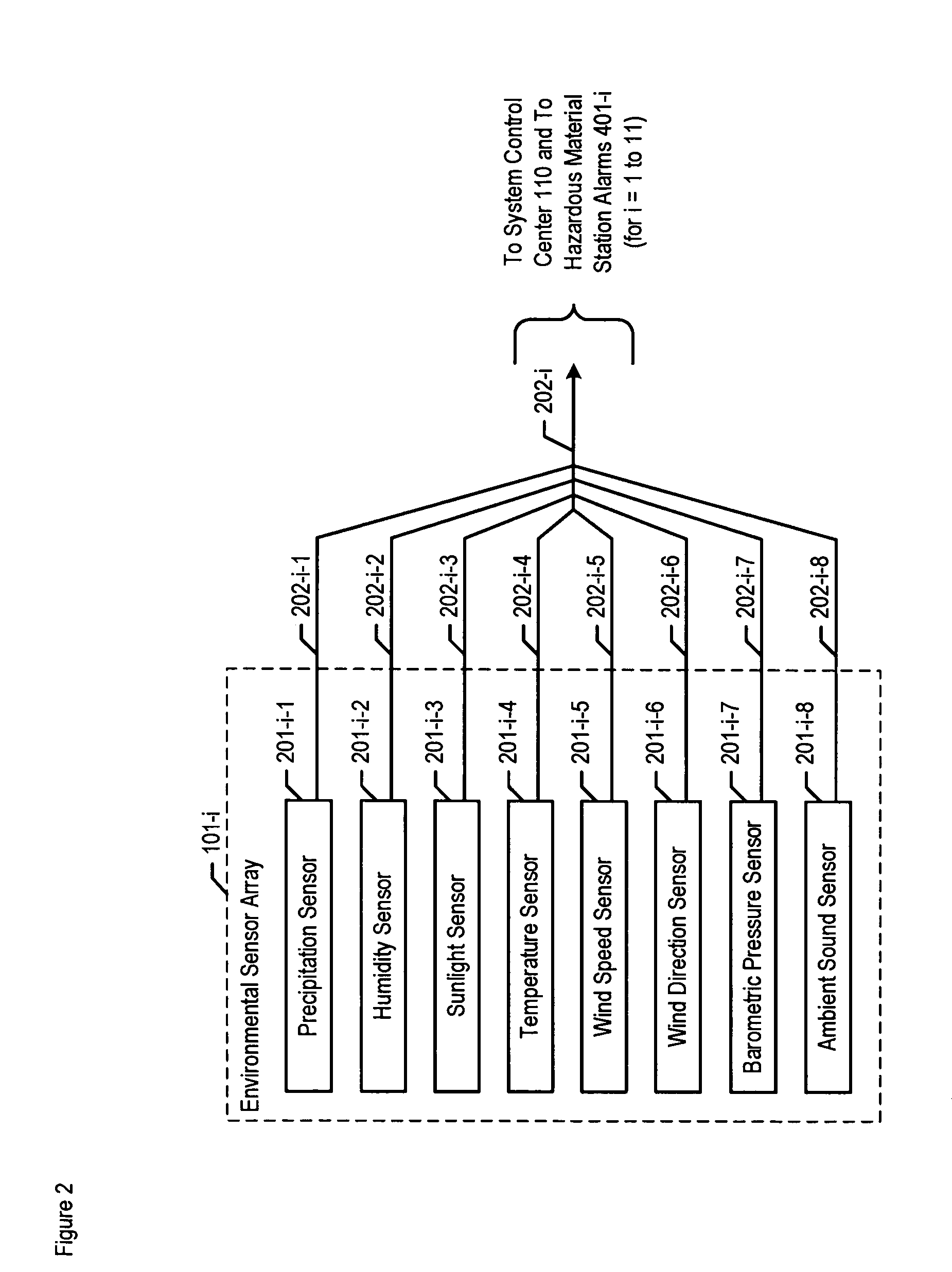
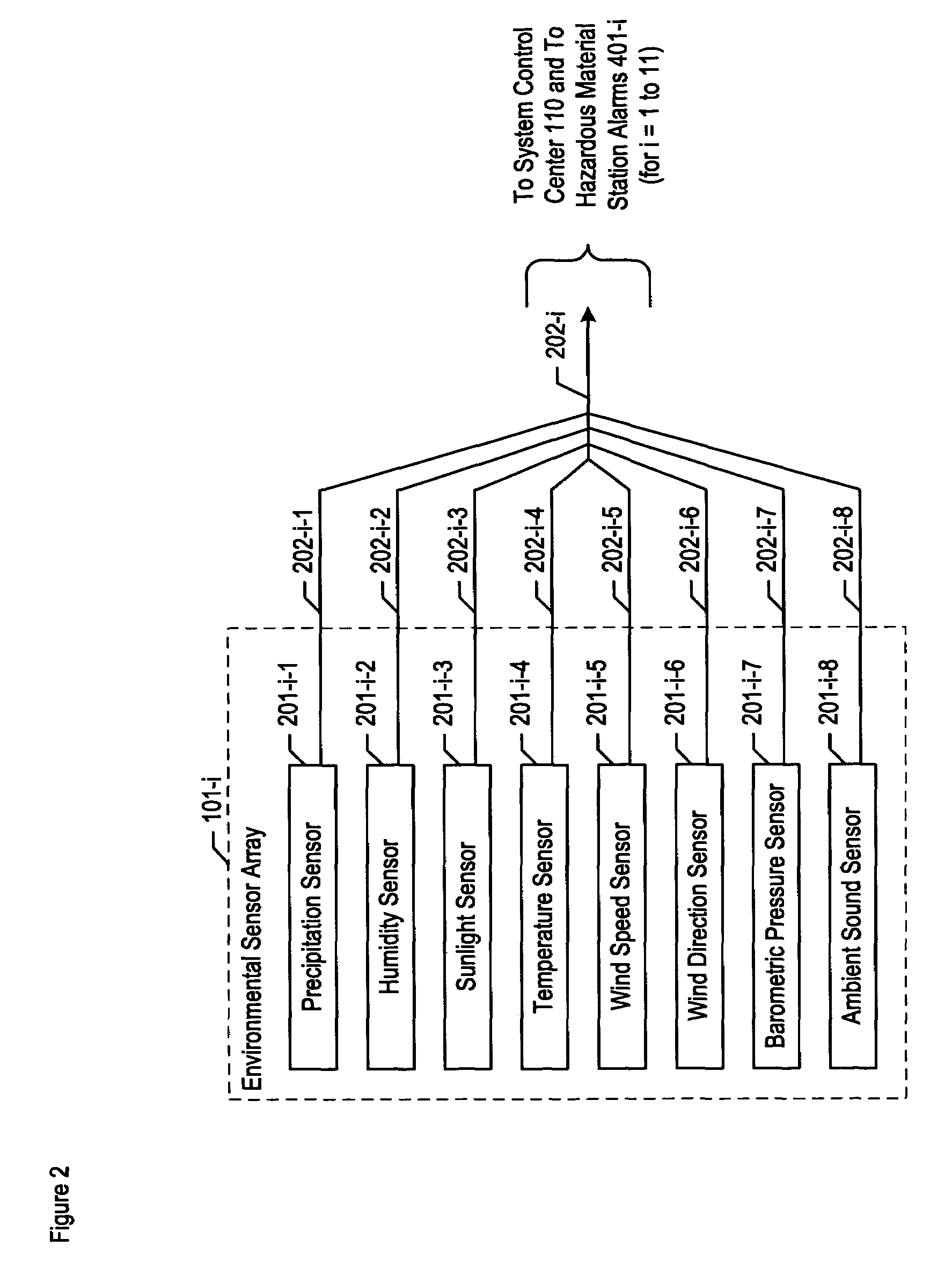
Chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear weapon detection system with environmental acuity
InactiveUS20070244653A1Quickly and accurately informingConfidenceBurglar alarm by openingAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceOrganismNuclear weapon
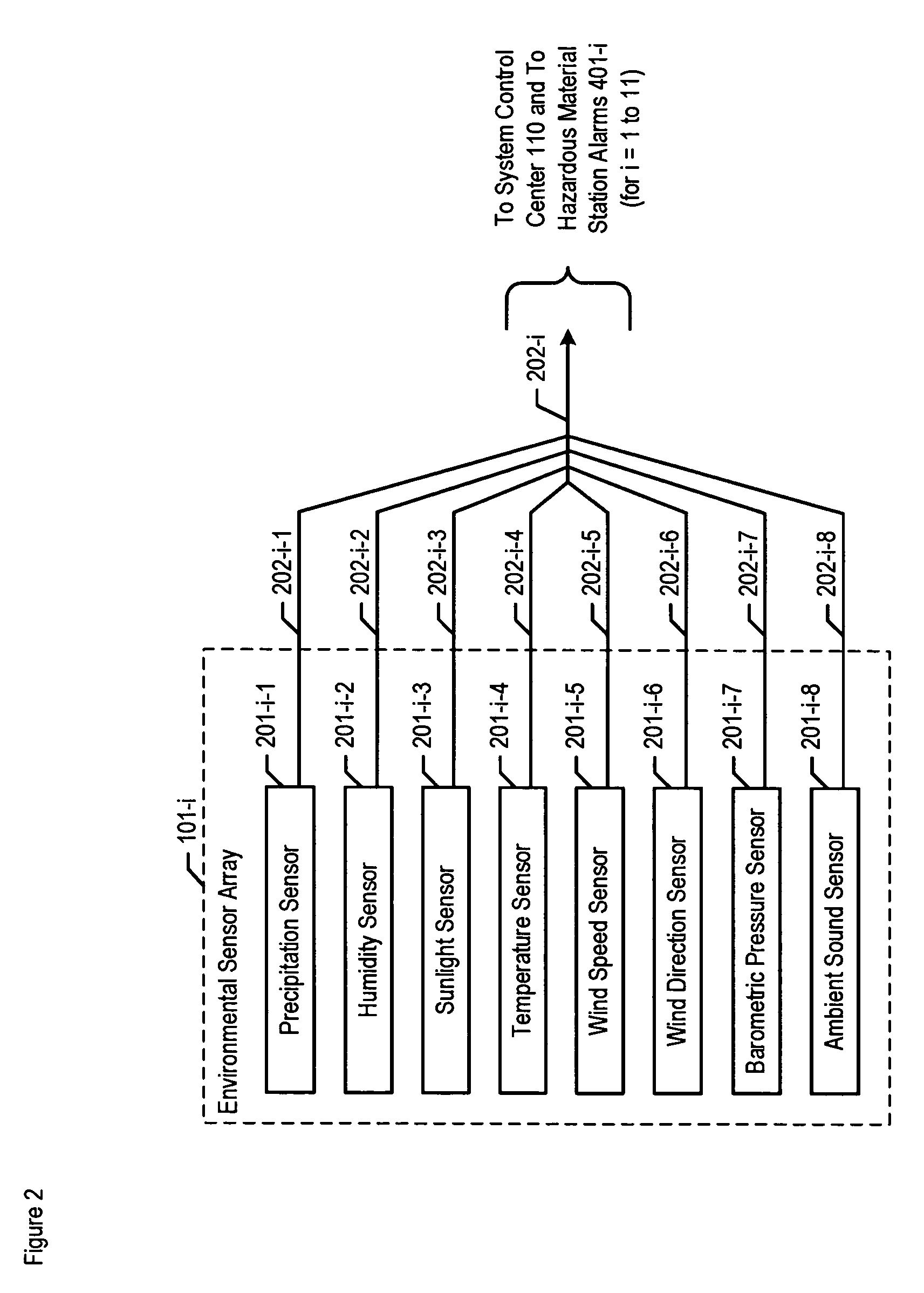
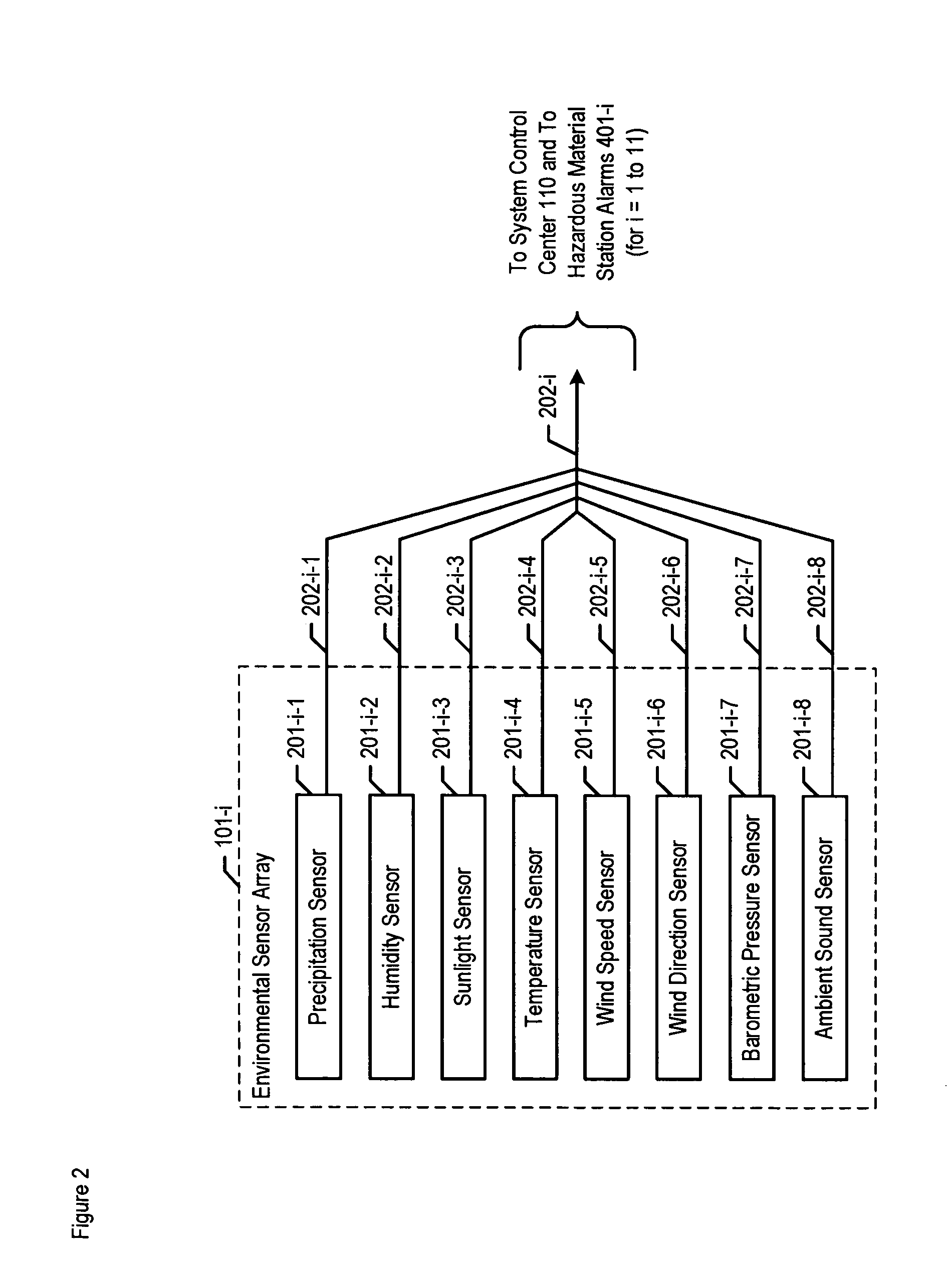
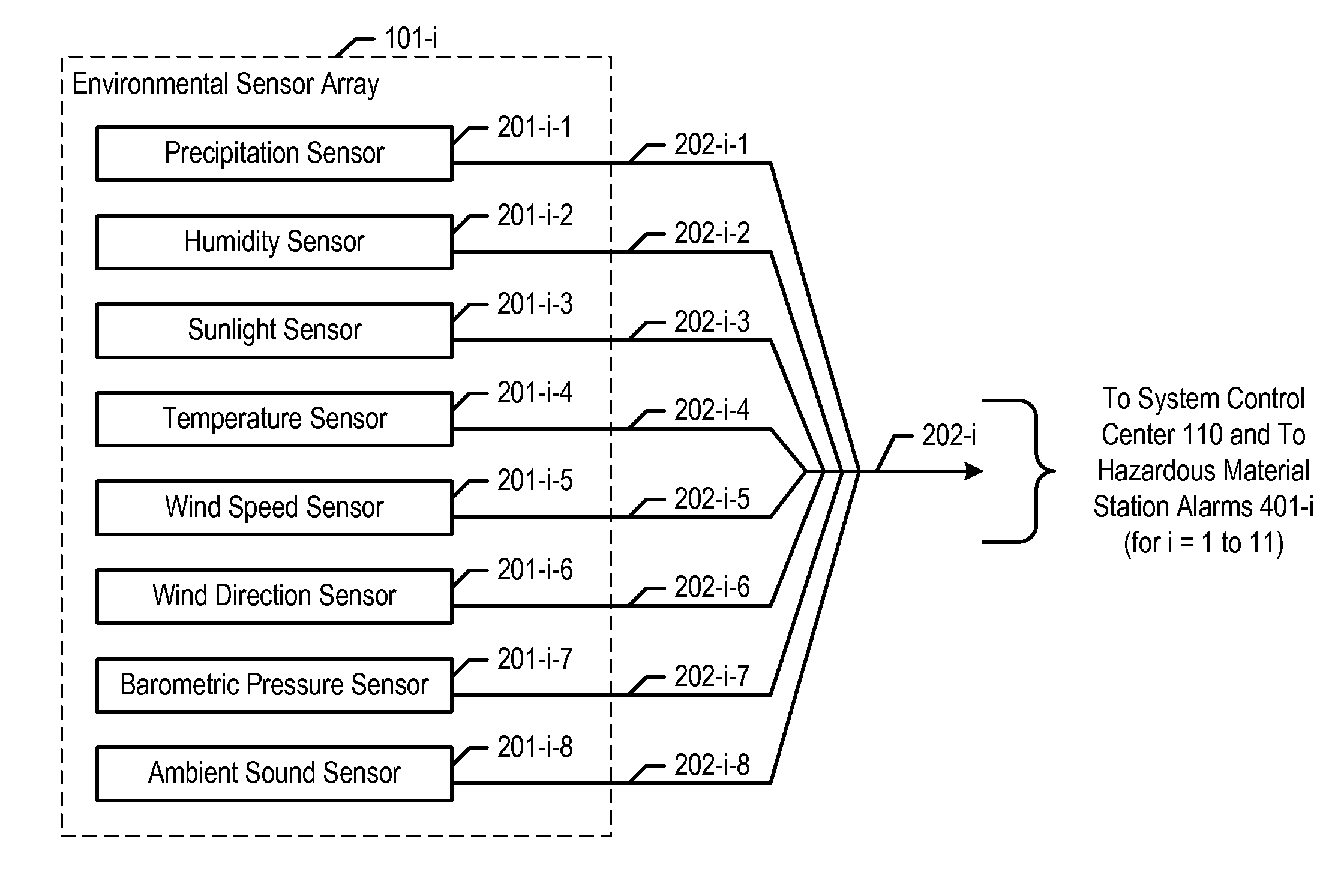
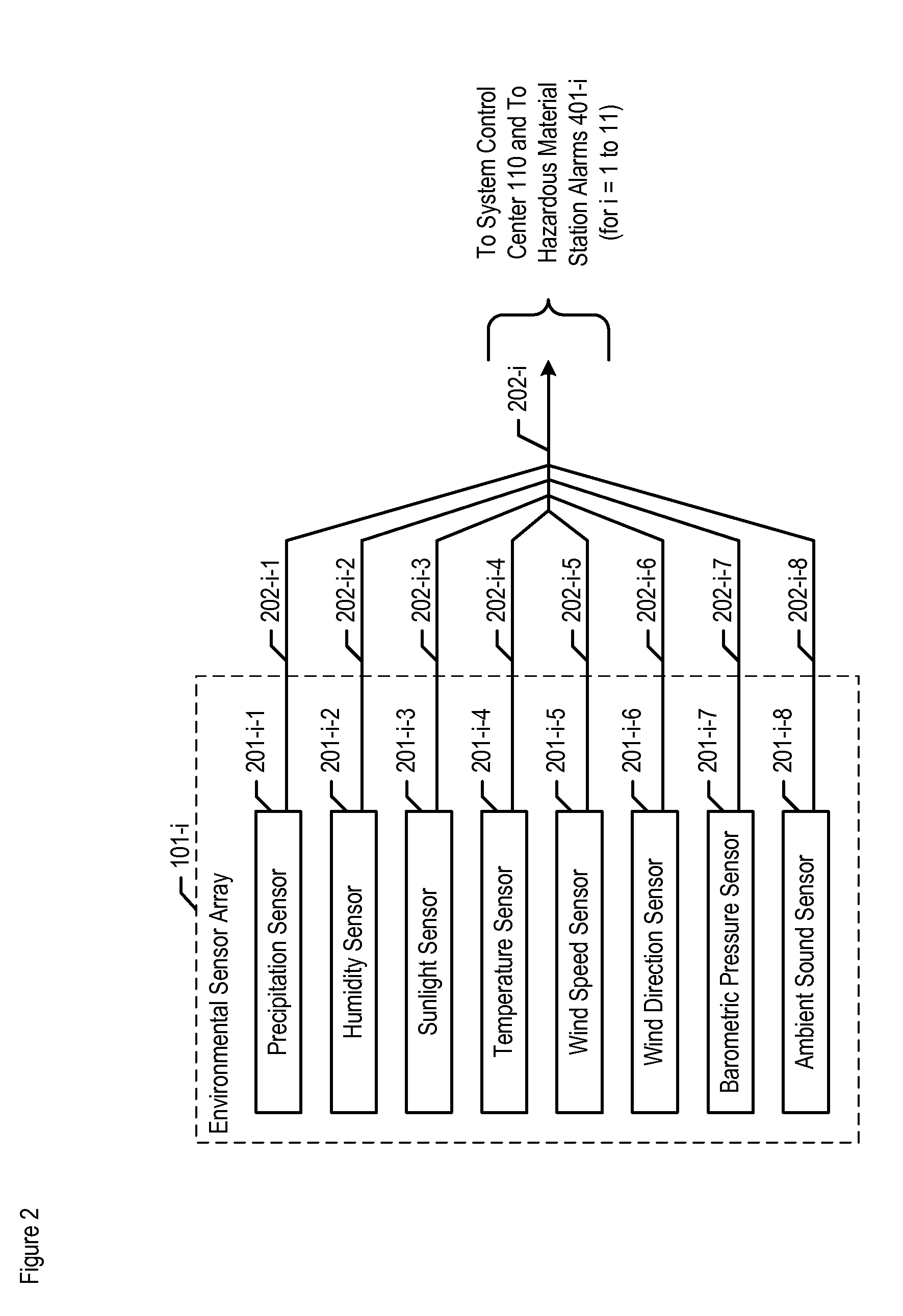
A chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear weapon detection system is disclosed that heightens its acuity and alertness when it senses that a chemical, biological, radiological, or nuclear weapon attack is more likely. For example, it is well understood that a chemical gas attack is likely to be less effective when it is raining than when it is clear because the rain will suppress and dilute the chemical agent. Therefore, the likelihood of a chemical gas attack is higher when it is clear. In light of this and similar knowledge, the illustrative embodiment checks for evidence of an attack more frequently and with great acuity than when the ambient environmental (e.g., meteorological, etc.) characteristics (e.g., whether is it precipitating or not, whether it is sunny or not, etc) suggest that an attack is more likely. This enables the embodiment to conserve consumables that are used in detecting attacks for when the attacks are more likely.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
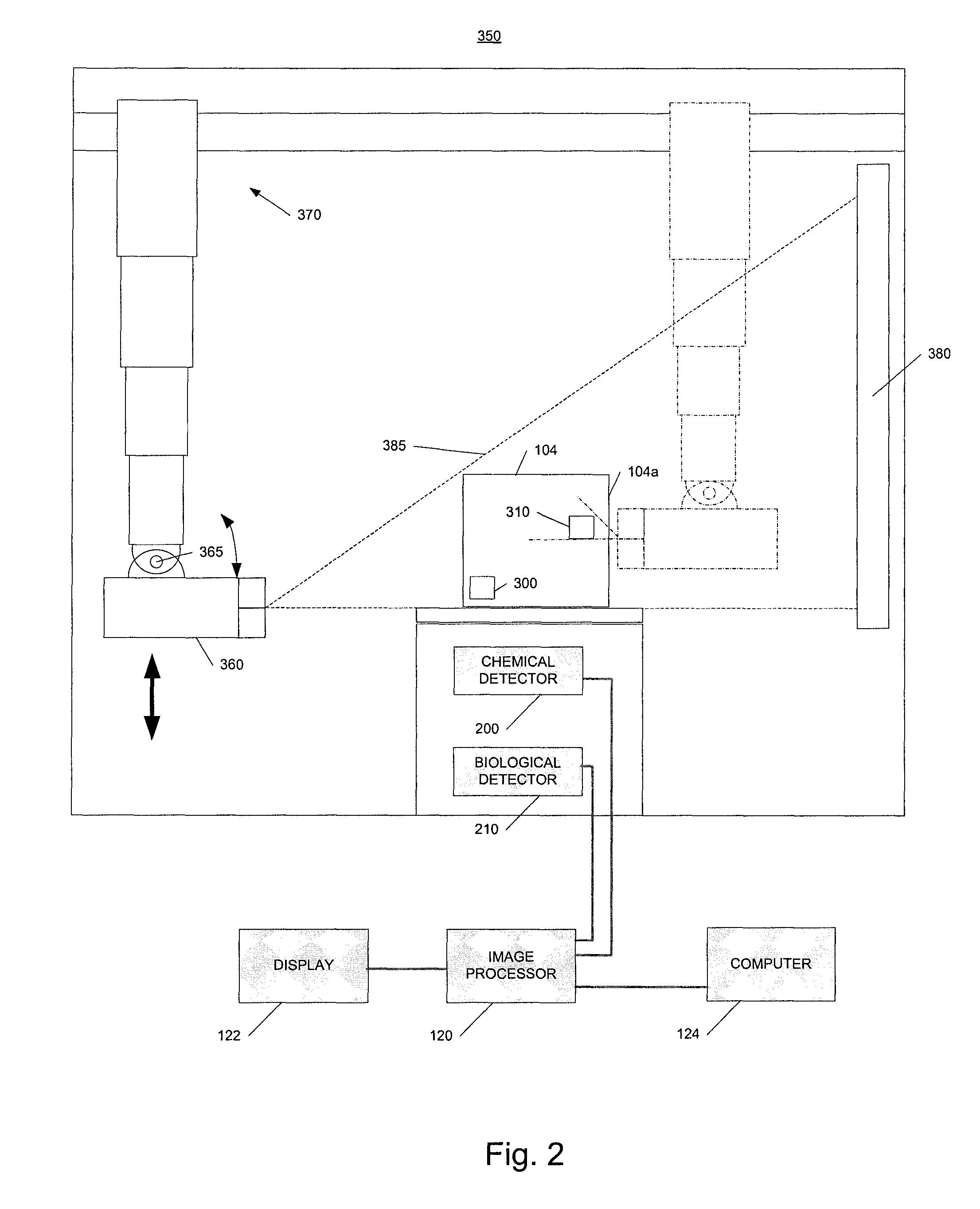
Radiation scanning and disabling of hazardous targets in containers
ActiveUS20120148019A1Stop sproutingIncrease storage spaceMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationIrradiation devicesNuclear weaponRadiation beam
In one example, a method of examining a container is disclosed comprising detecting a potential threat within contents of a container using radiation scanning and disabling the potential threat with radiation. In another example, a method of examining a container is disclosed comprising scanning at least a portion of the container with a first radiation beam, detecting radiation interacting with contents of the container, identifying a potential threat contained based, at least in part, on the detected radiation, and disabling the potential threat with a dose of radiation from a second radiation beam. The potential threat may be a nuclear, chemical, and / or biological weapon, for example. Chemical and / or biological detectors may also be provided. The threat and / or electronics associated with the threat, may be disabled. Systems are also disclosed.
Owner:VAREX IMAGING CORP
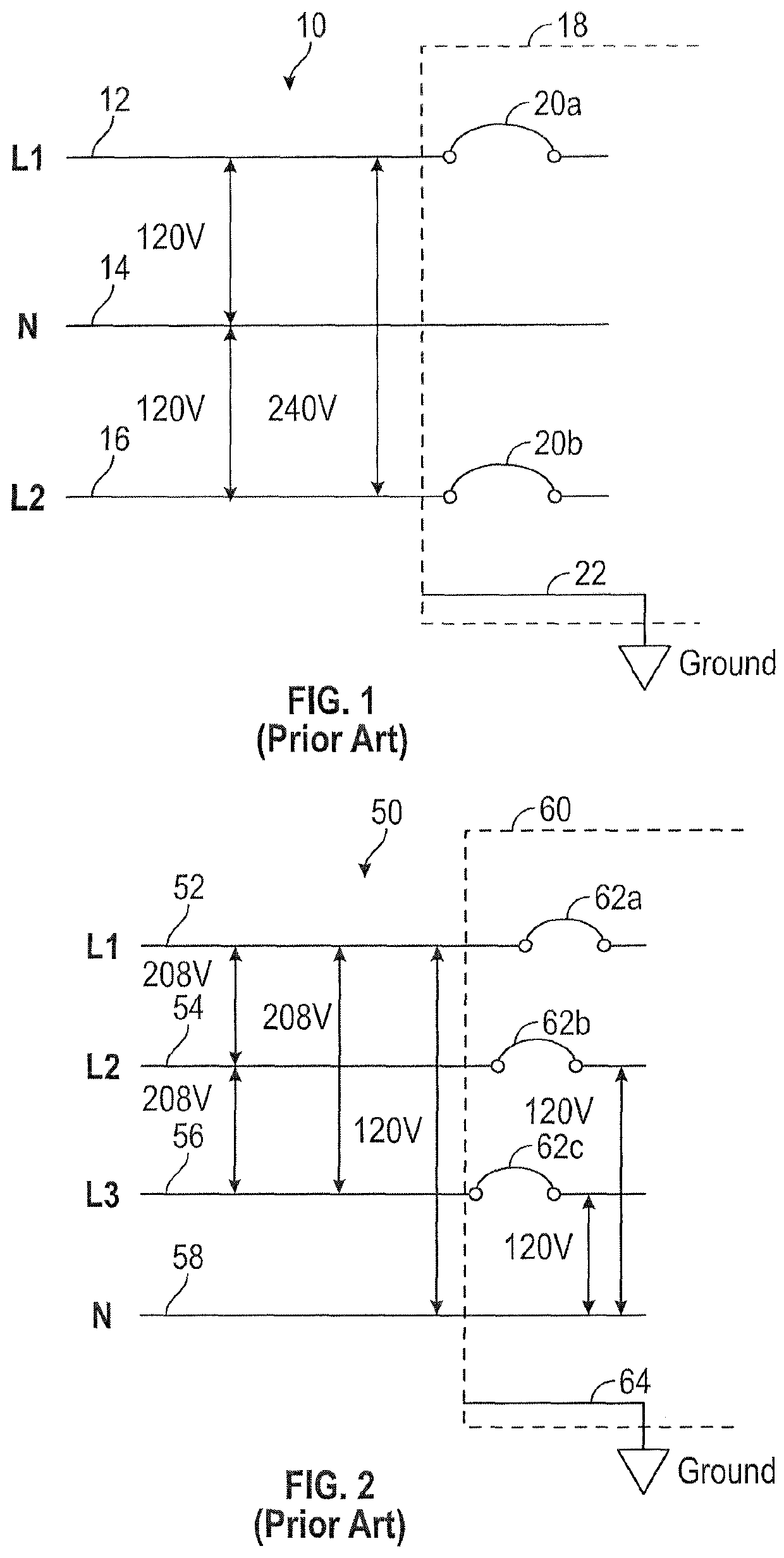
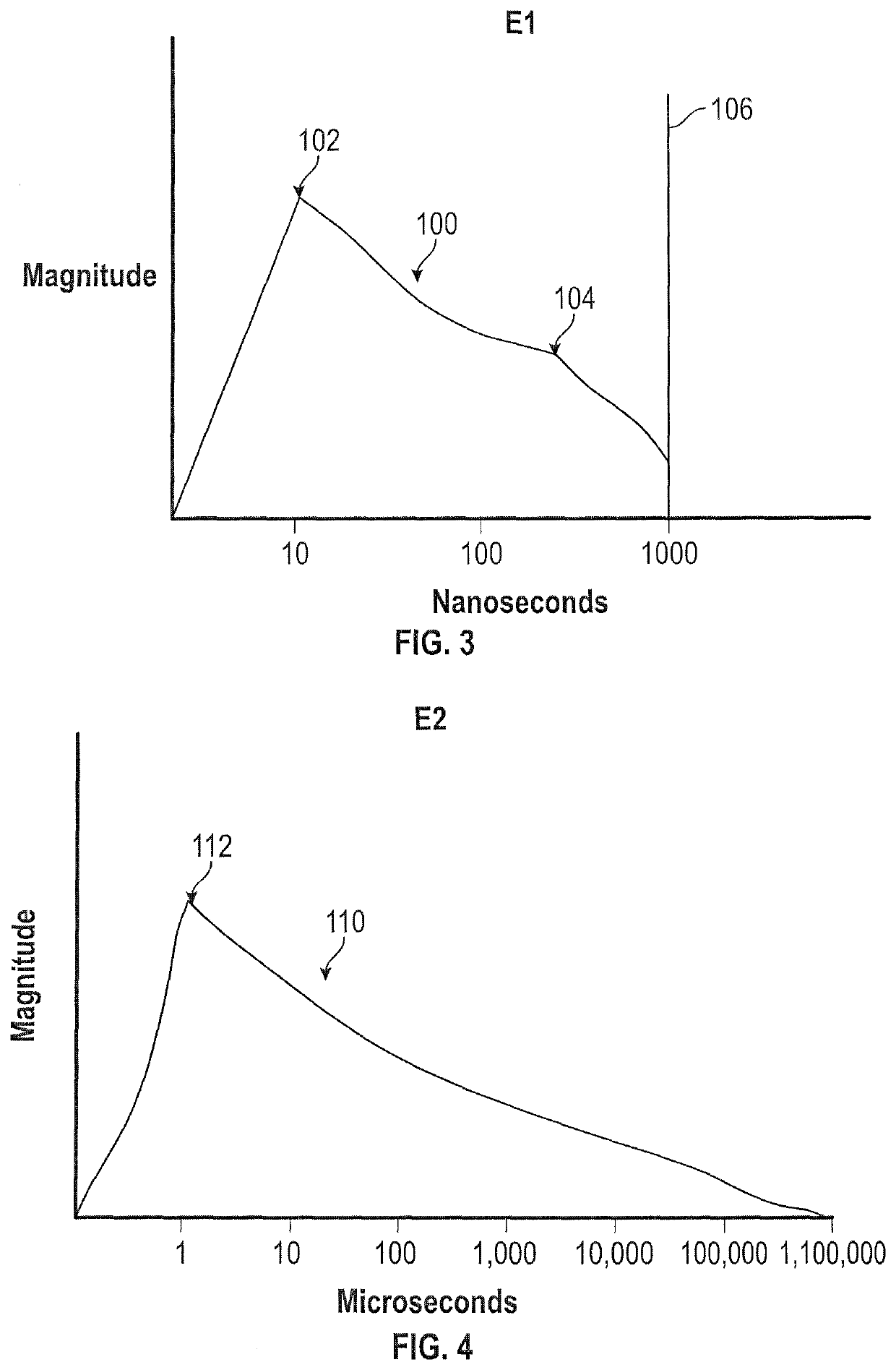
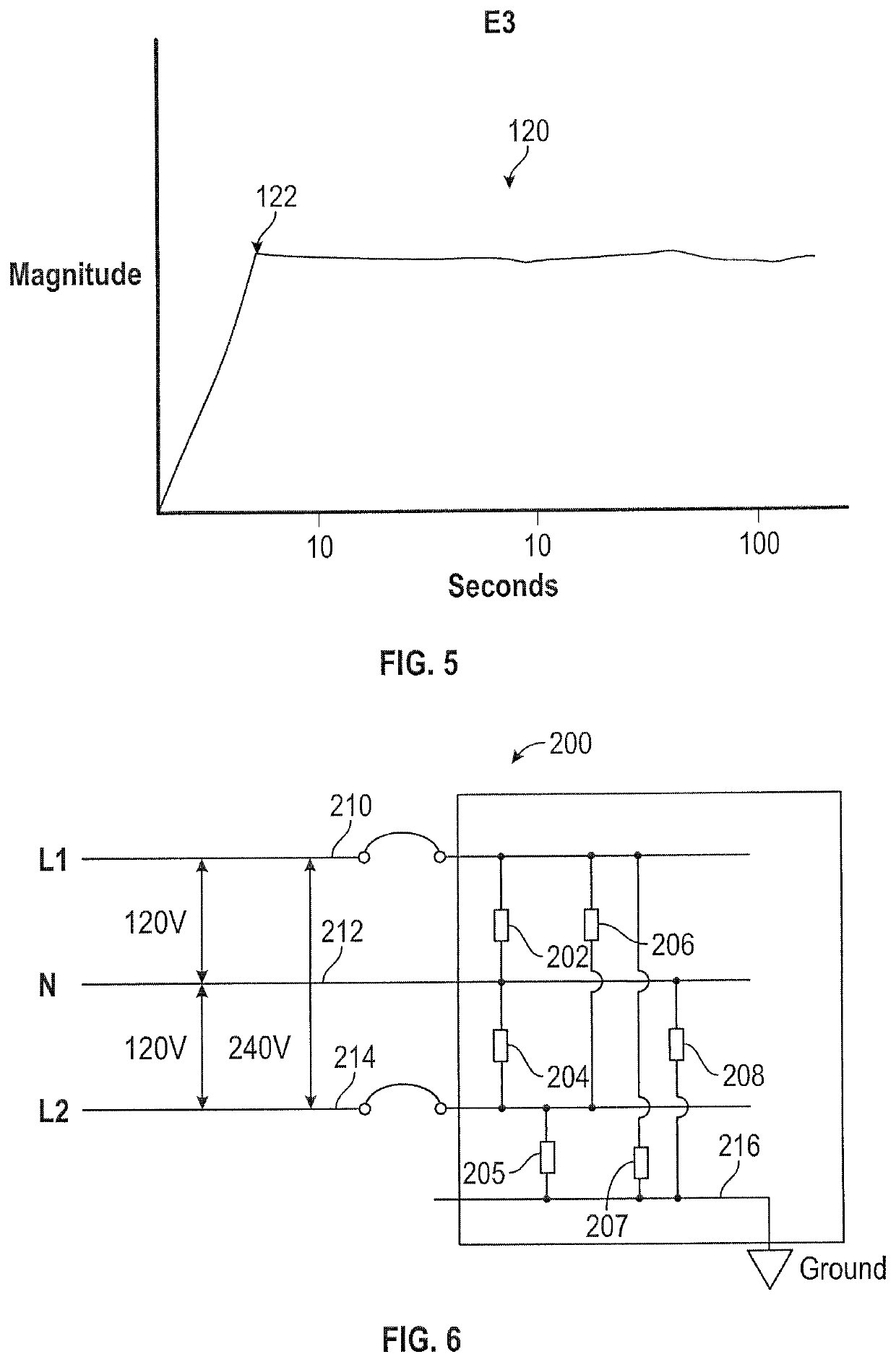
System and method for suppressing electromagnetic pulse-induced electrical system surges
ActiveUS20190214814A1Testing dielectric strengthArrangements responsive to excess currentElectricityOvervoltage
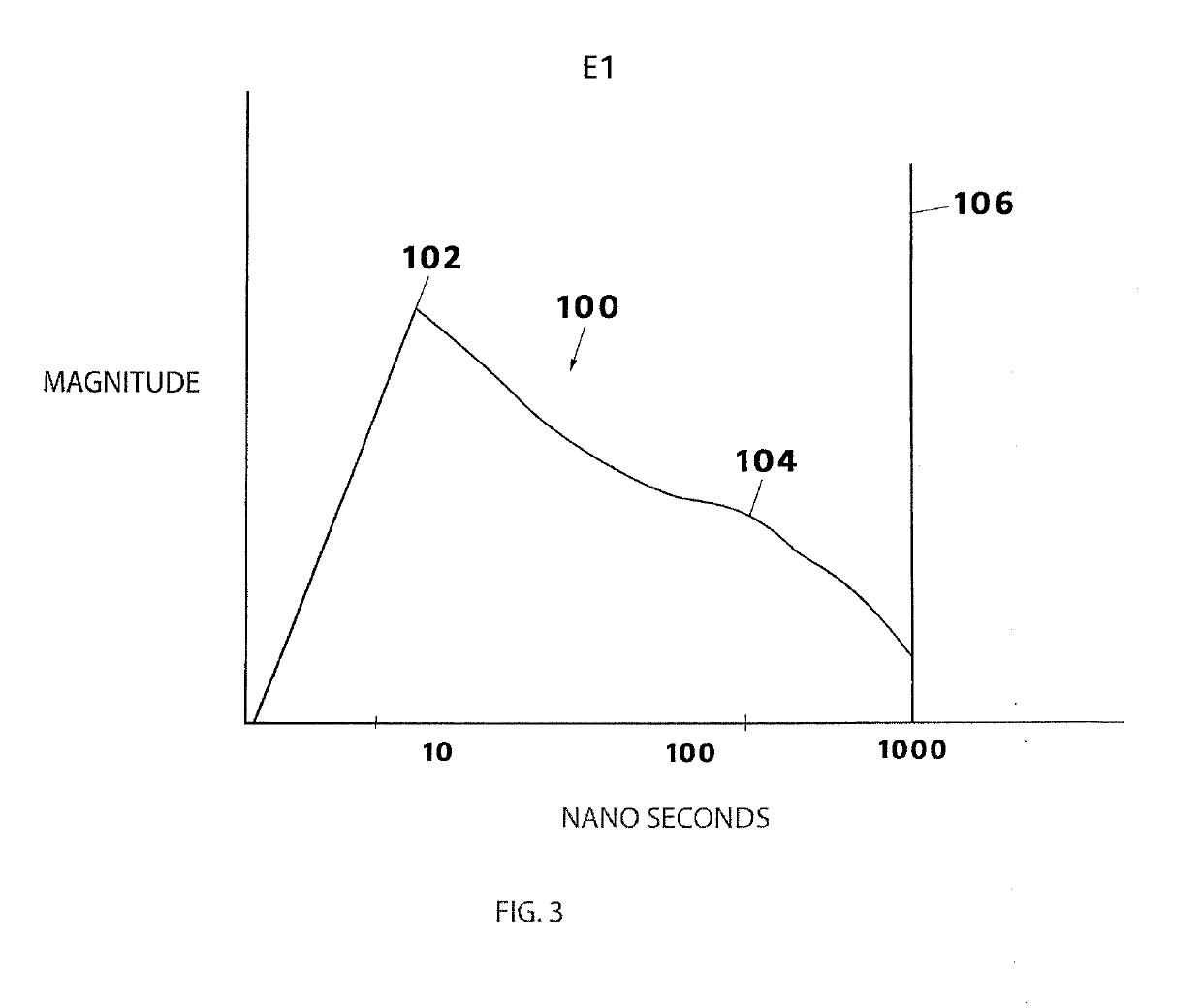
A system and method for suppressing EMP-induced electrical system voltage surges due to detonation of a nuclear weapon, the EMP comprising E1, E2, and E3 component pulses. A plurality of shunting assemblies, each including MOVs, gas discharge tubes, other mechanical, electrical and ionization discharge devices and combinations thereof, detect and react to the overvoltage according to timing parameters associated with each of the E1, E2, and E3 components and shunt the overvoltage to decrease to under a predetermined allowable level.
Owner:CARTY TIMOTHY A +1
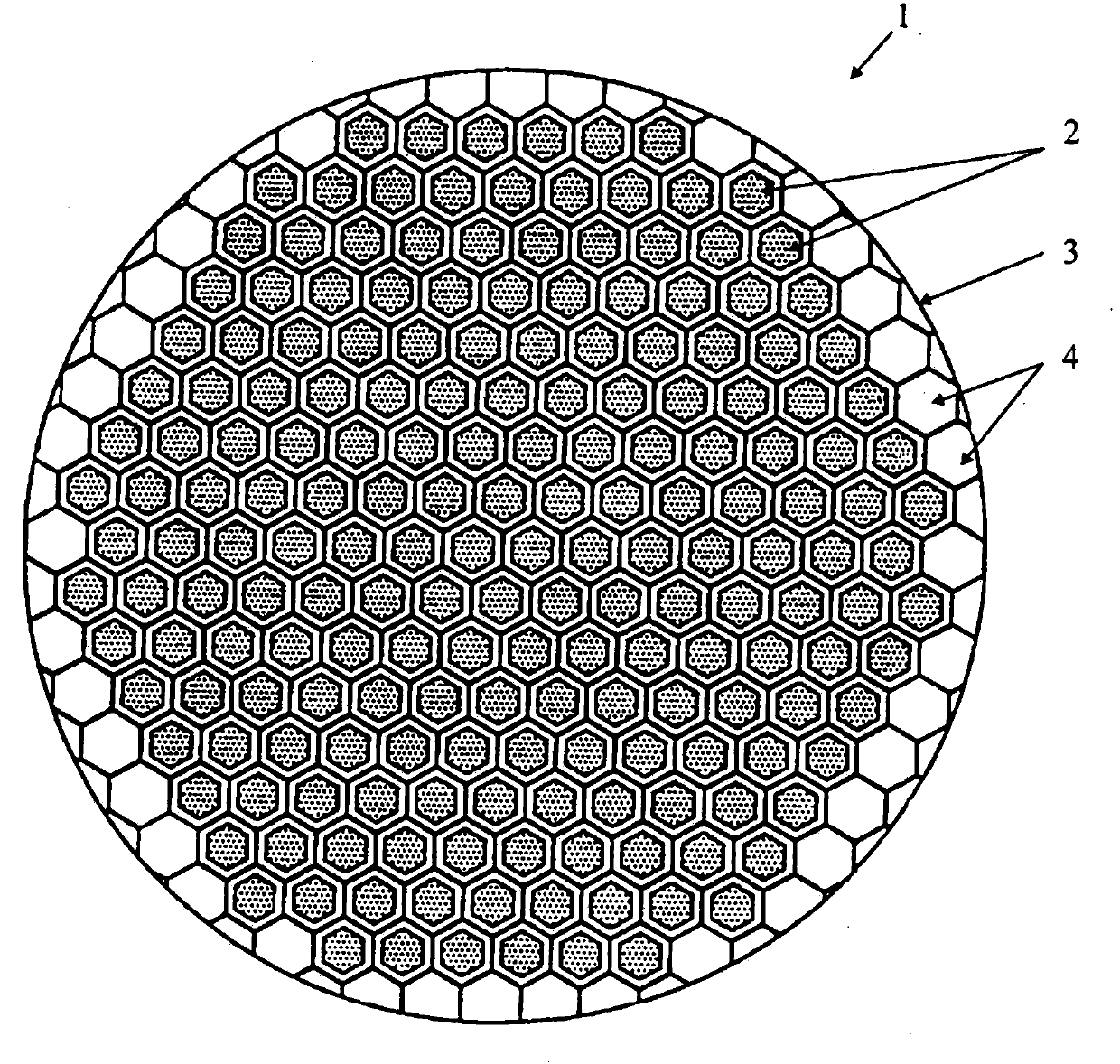
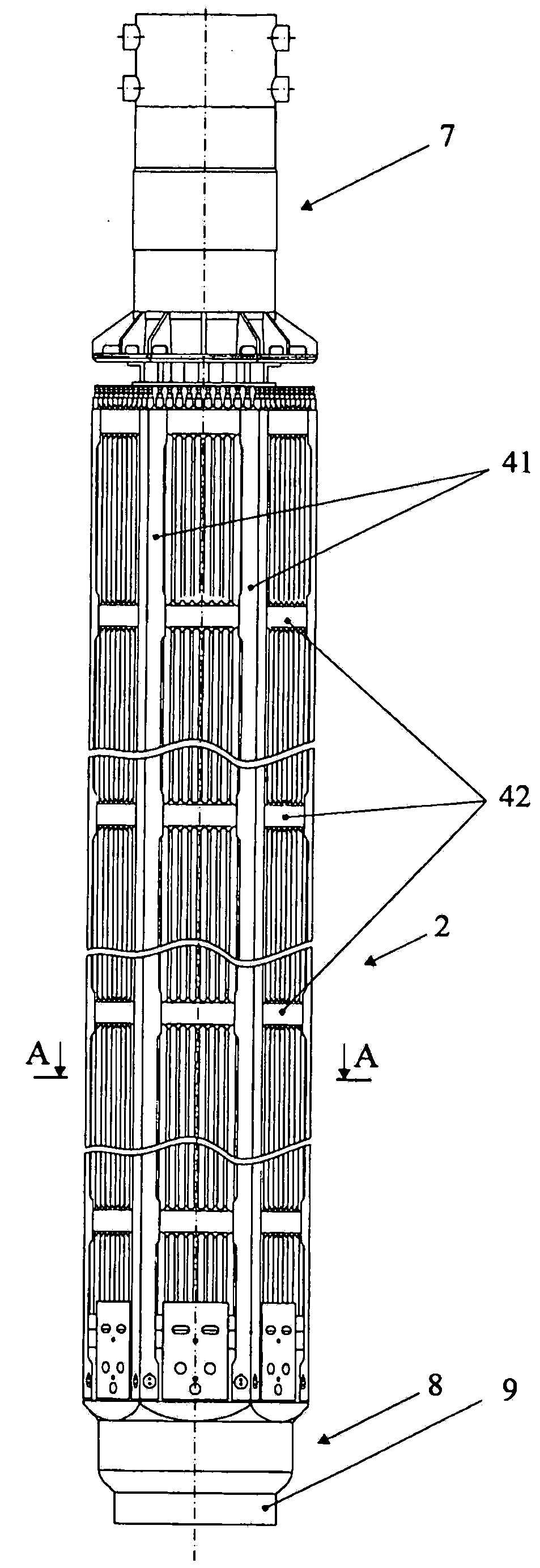
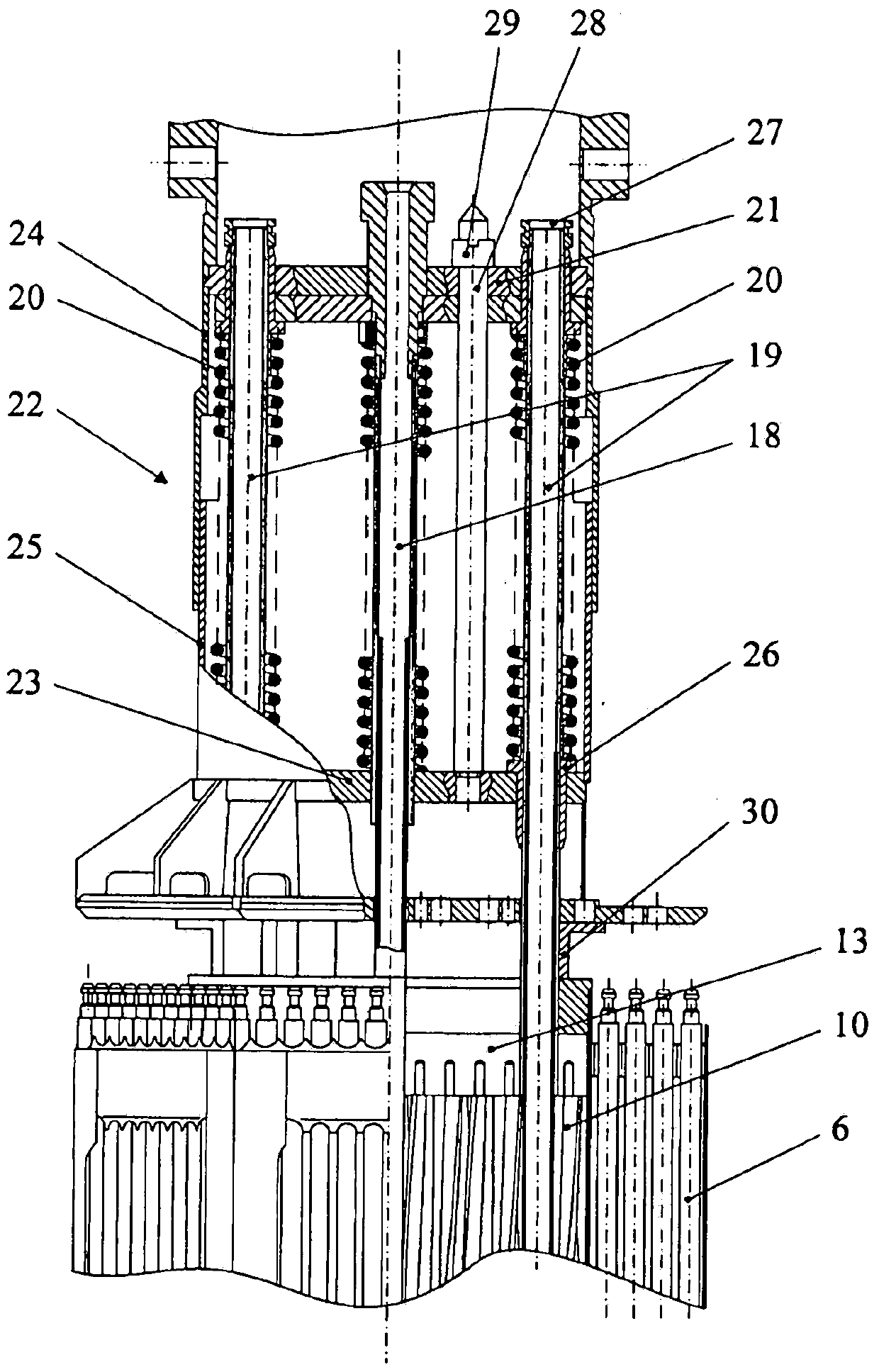
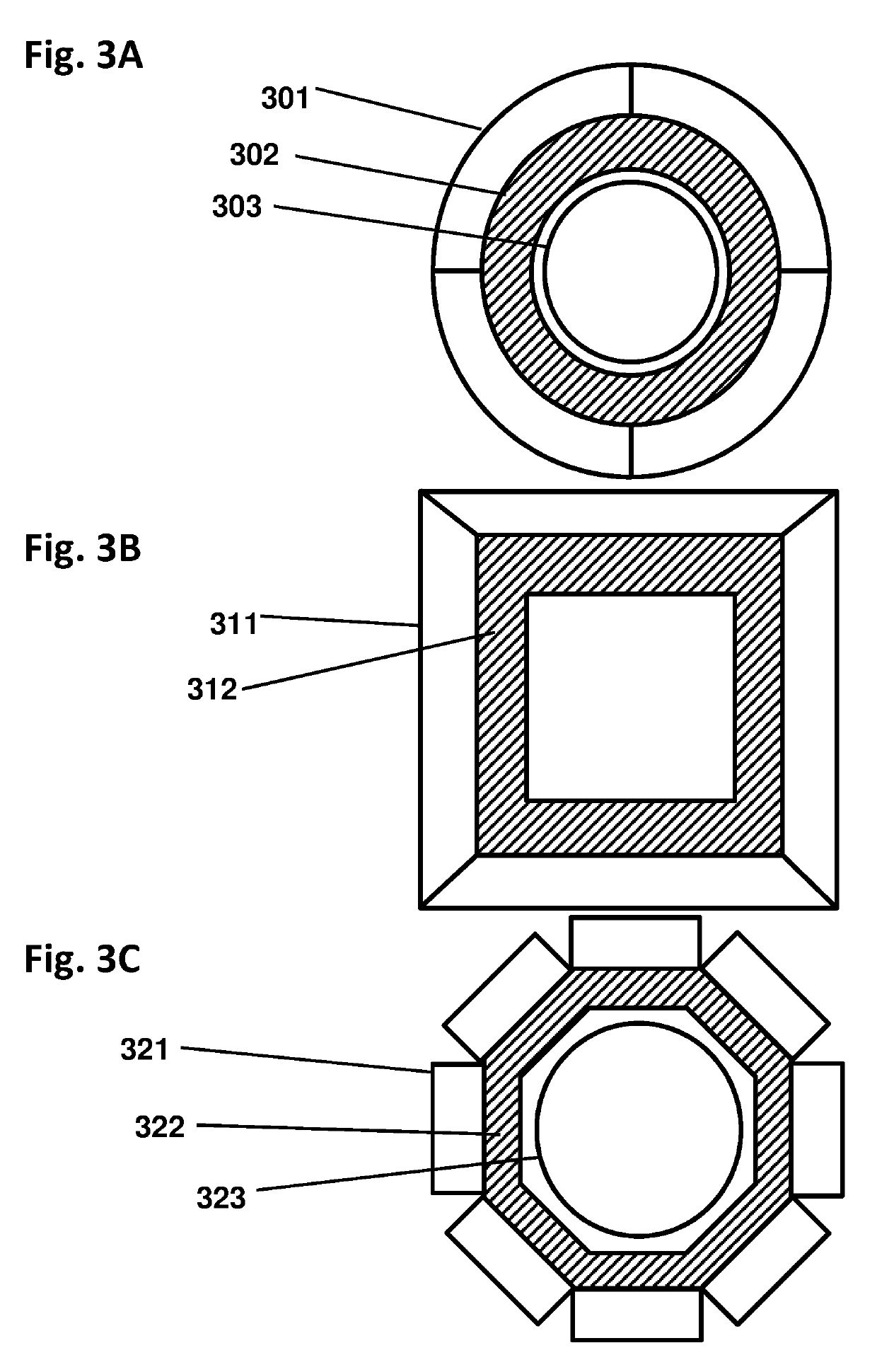
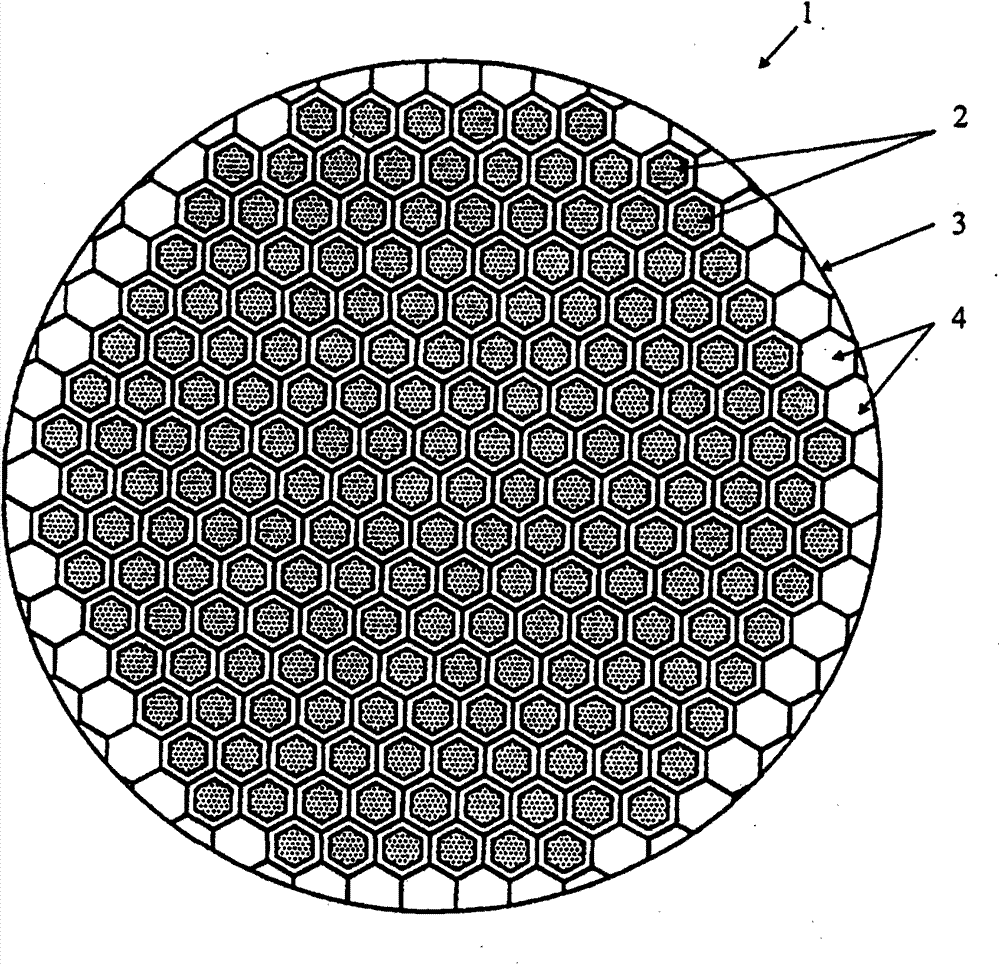
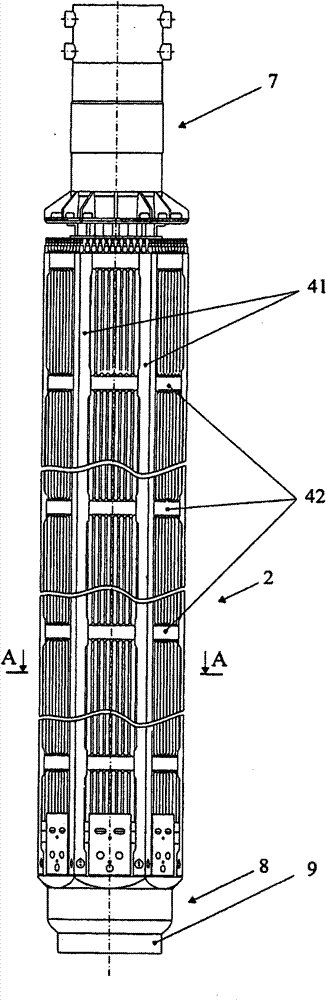
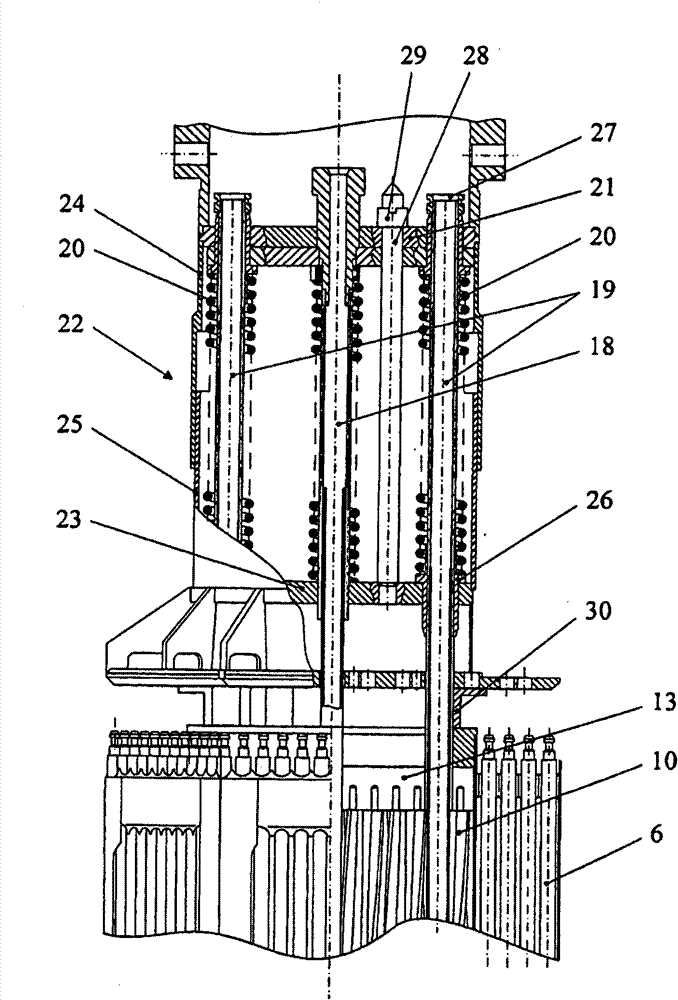
Nuclear reactor (variants), fuel assembly consisting of driver-breeding modules for a nuclear reactor (variants) and a fuel cell for a fuel assembly
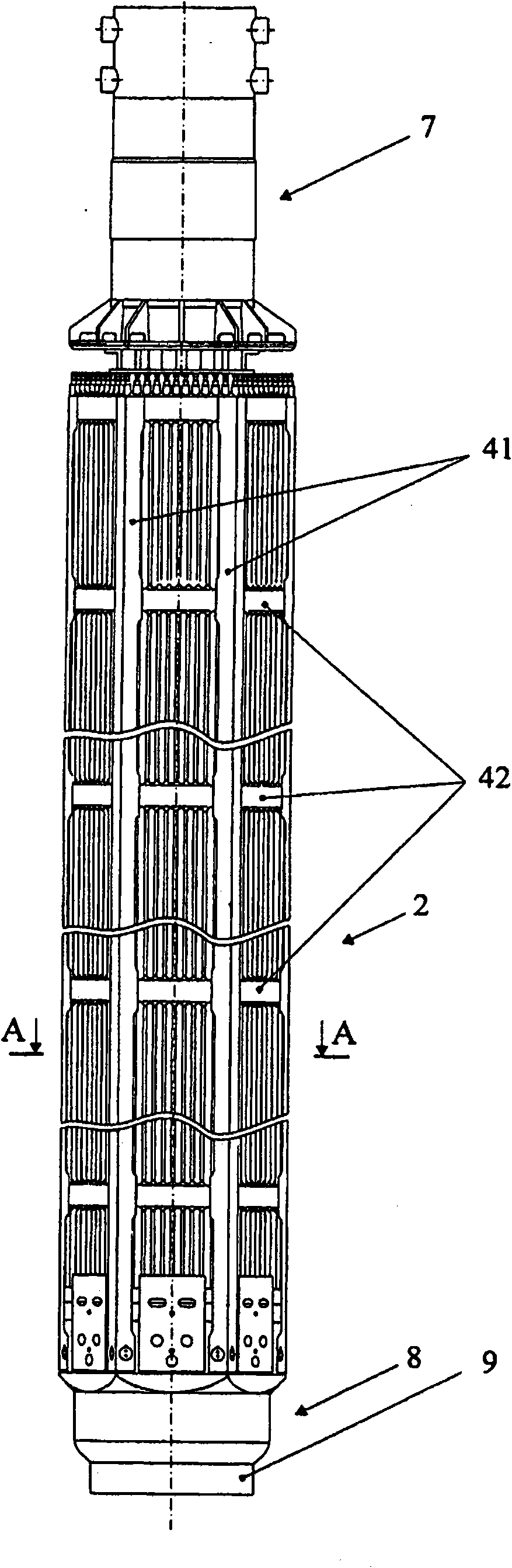
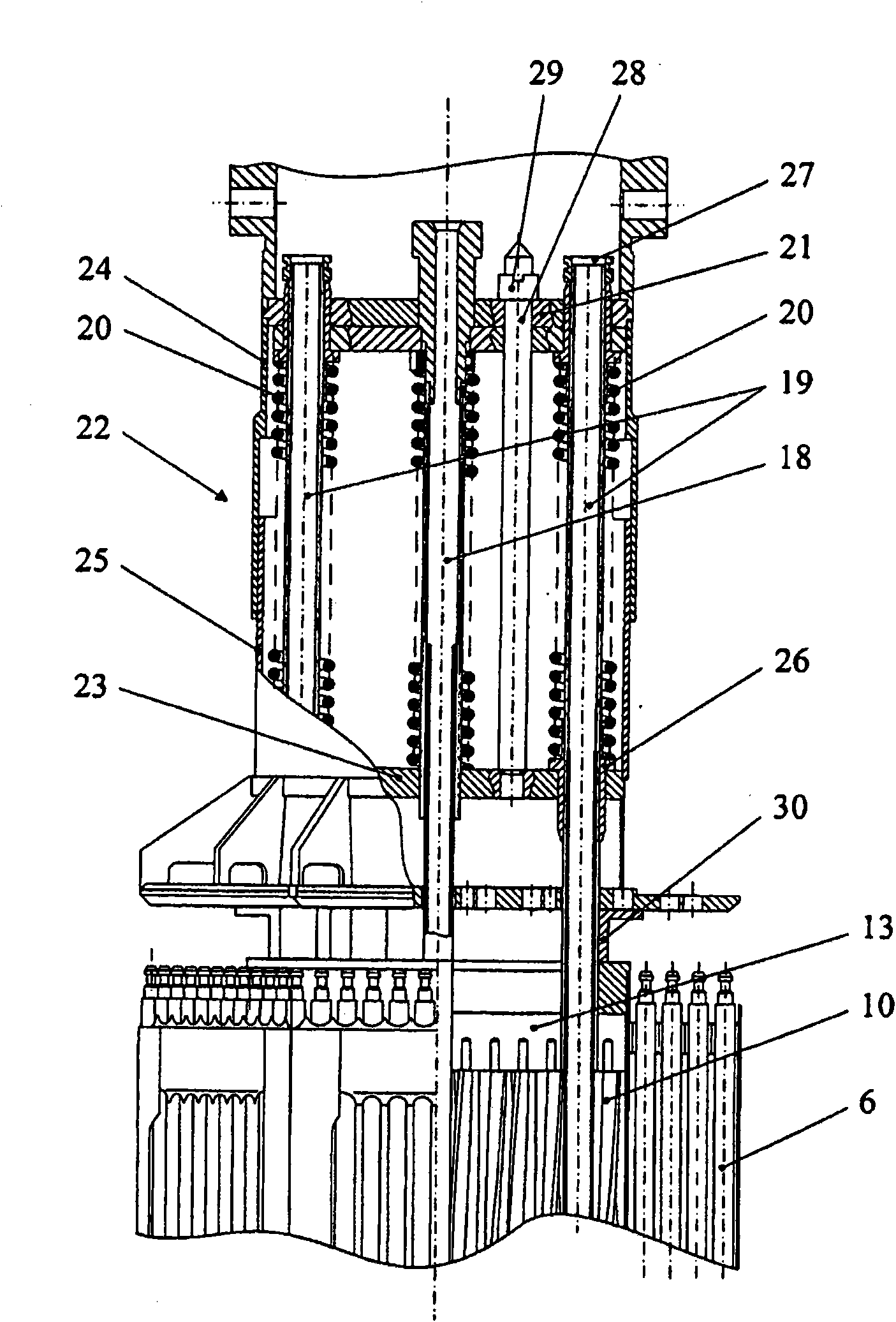
The invention relates to a structural design for light-water-moderated nuclear reactors using a thorium fuel, in particular to the structural design for caseless fuel assemblies constituting the cores of water moderated power-producing reactors, such as a WWER-1000 reactor. A thorium fuel in a breeding module together with a conventional reactor fuel containing unshaped enriched uranium or power producing plutonium in a driver module are burned in the core of a nuclear reactor which comprises a fuel assembly consisting of a driver and breeding modules. The driver module comprises a bundle of three leaf-shaped fuel cells forming screw spacer ribs. The driver and breeding modules can be coupled to each other by means of a spigot joint or be free of a rigid mechanical coupling. The inventive structural design of the fuel assembly provides the total compatibility thereof with existing fuel assemblies used in the WWER-1000 reactors. The fact that the two-section fuel assembly can be disassembled makes it possible to individually reload the driver module.
Owner:THORIUM POWER
Gamma ray detector with two-dimensional directionality
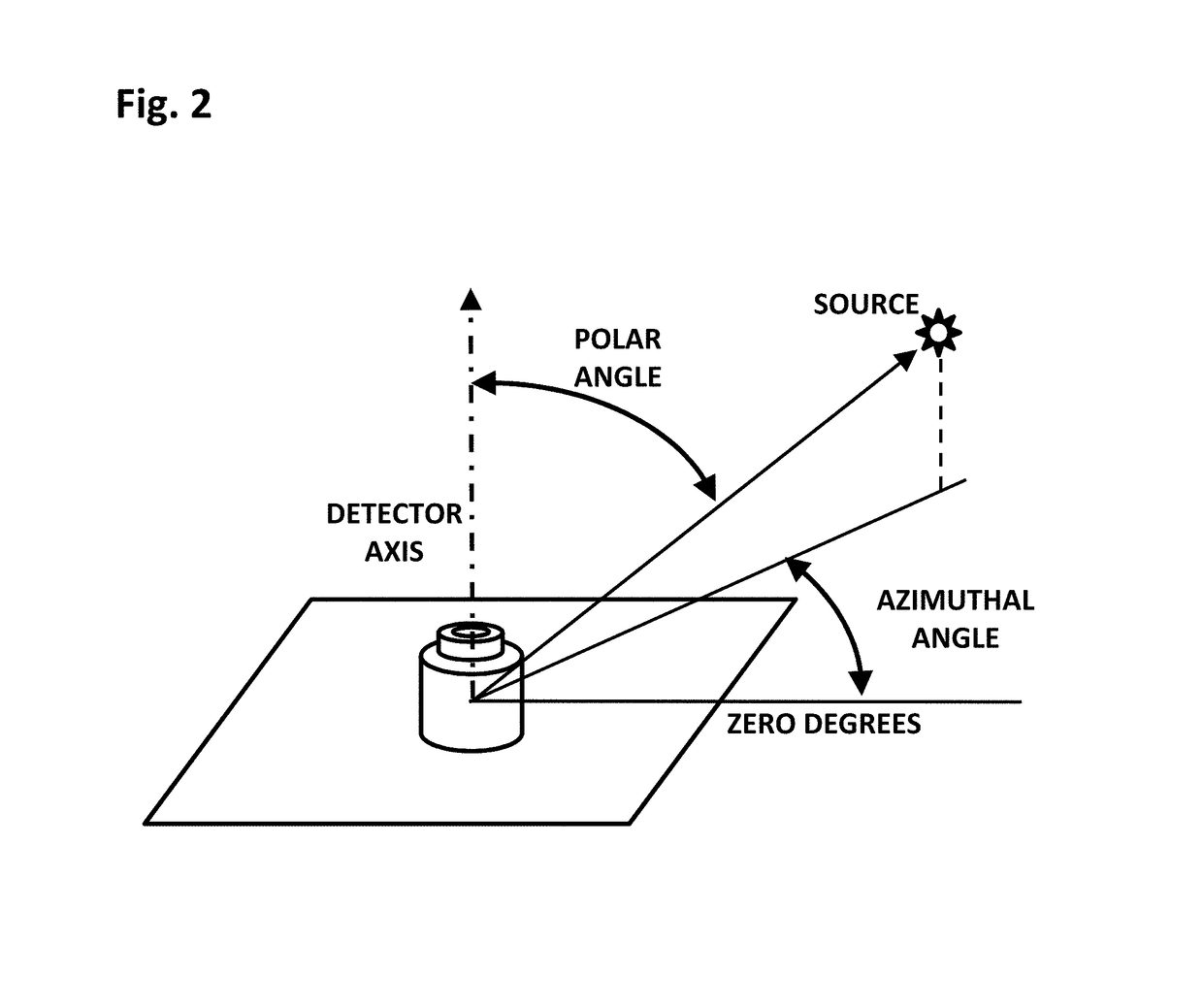
ActiveUS10024985B1High angular accuracyReduce weightMeasurement with scintillation detectorsMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationCounting rateRadiological weapon
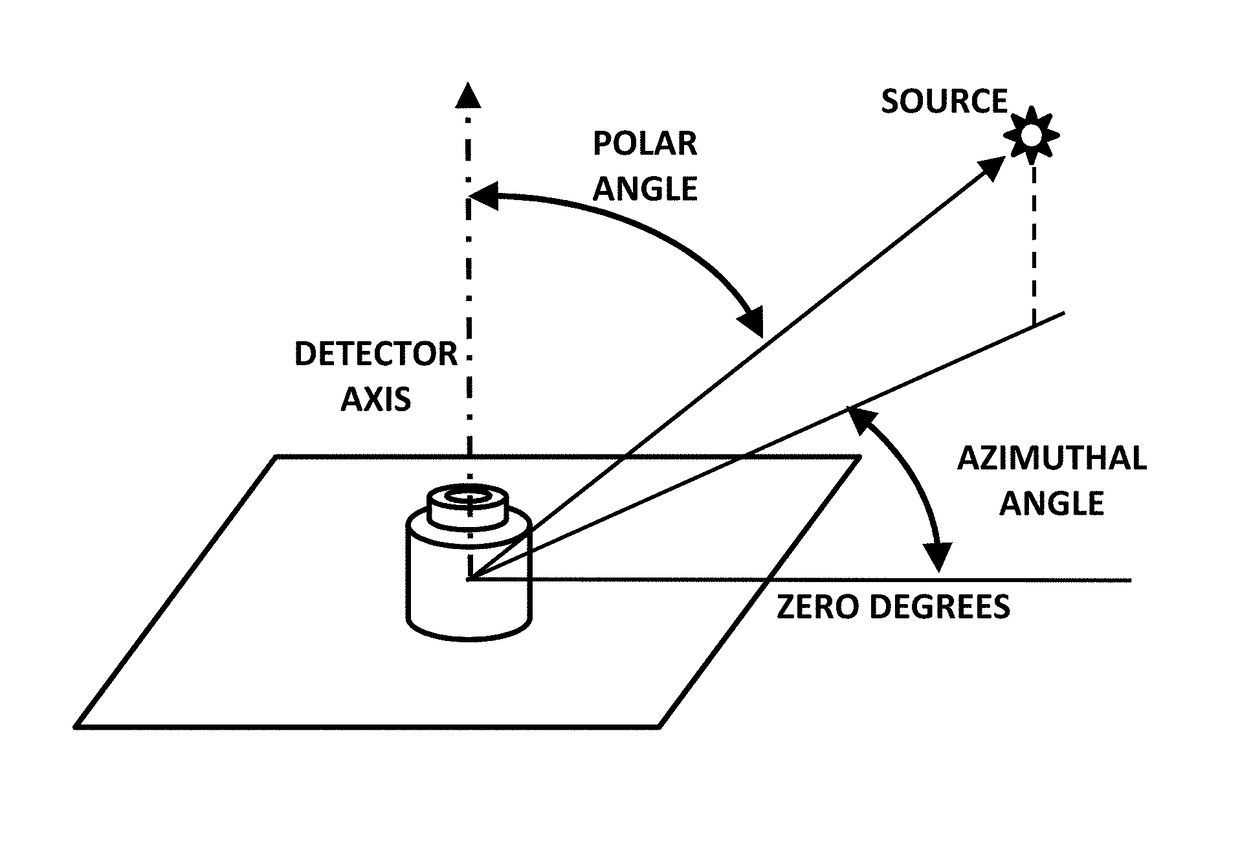
The invention is a gamma ray detector that locates a source, both horizontally and vertically. The detector comprises a tubular shield surrounded by scintillator panels. Gammas incident from one side can fully strike the scintillator facing the source, but are blocked from reaching the scintillators on the opposite side of the shield. The scintillator counting rates thus indicate the lateral direction of the source. By iteratively rotating toward the highest-counting scintillator, the detector converges to the source. An additional, central detector can be mounted within the tubular shield. When analyzed with the outer scintillators, the central detector determines the overall angular separation between the source and the detector axis, thereby locating the source in two dimensions automatically. The invention enables rapid detection and precise localization of clandestine nuclear and radiological weapons, despite shielding and clutter obfuscation, while quickly passing clean loads.
Owner:NEWMAN DAVID EDWARD
Nuclear reactor (optional), fuel assembly for seed-blanket subassembly of nuclear reactor (optional) as well as fuel element for fuel assembly
The invention relates to a fuel element for a fuel assembly of a nuclear reactor. The fuel element comprises a nucleus containinga fissionable material and cladding which seals the nucleus, wherein the fuel element is provided with a multifoil contour which forms spiral ribs; and the spiral ribs comprise the fissionable material and have axially torsional intervals, and the length of each interval is 5%-20% of that of the fuel element. According to embodiments of the invention, waste which can used for manufacturing nuclear weapons cannot be generated, a novel loading and unloading system is used for a first embodiment of the invention tomaximize recycling of fuel in a seed; and the system further guarantees that used nuclear fuel cannot be used for manufacturing nuclear weapons.
Owner:THORIUM POWER
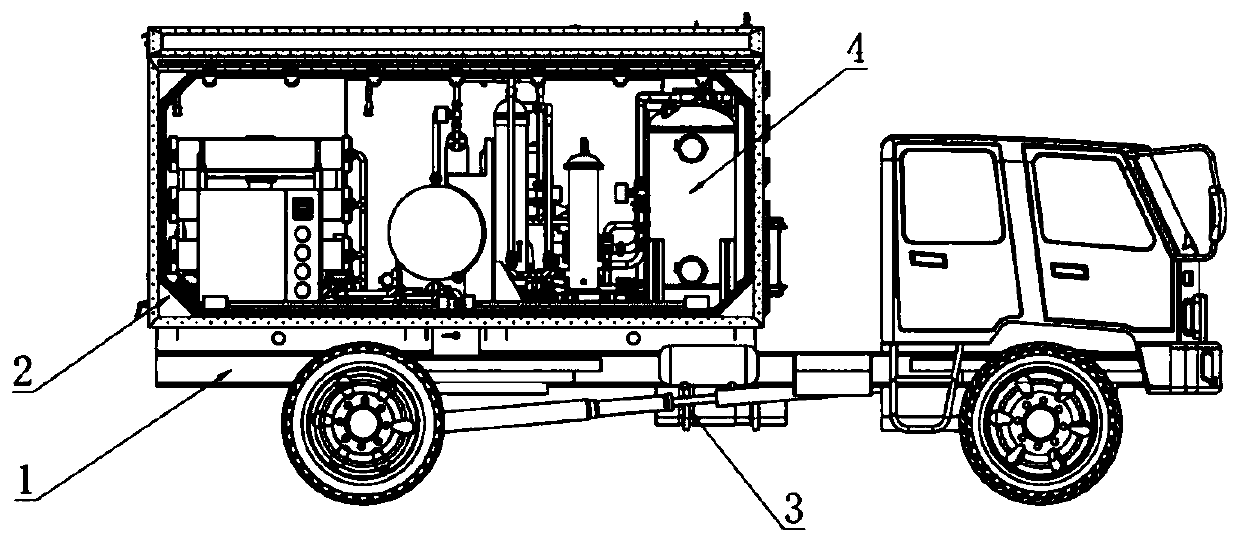
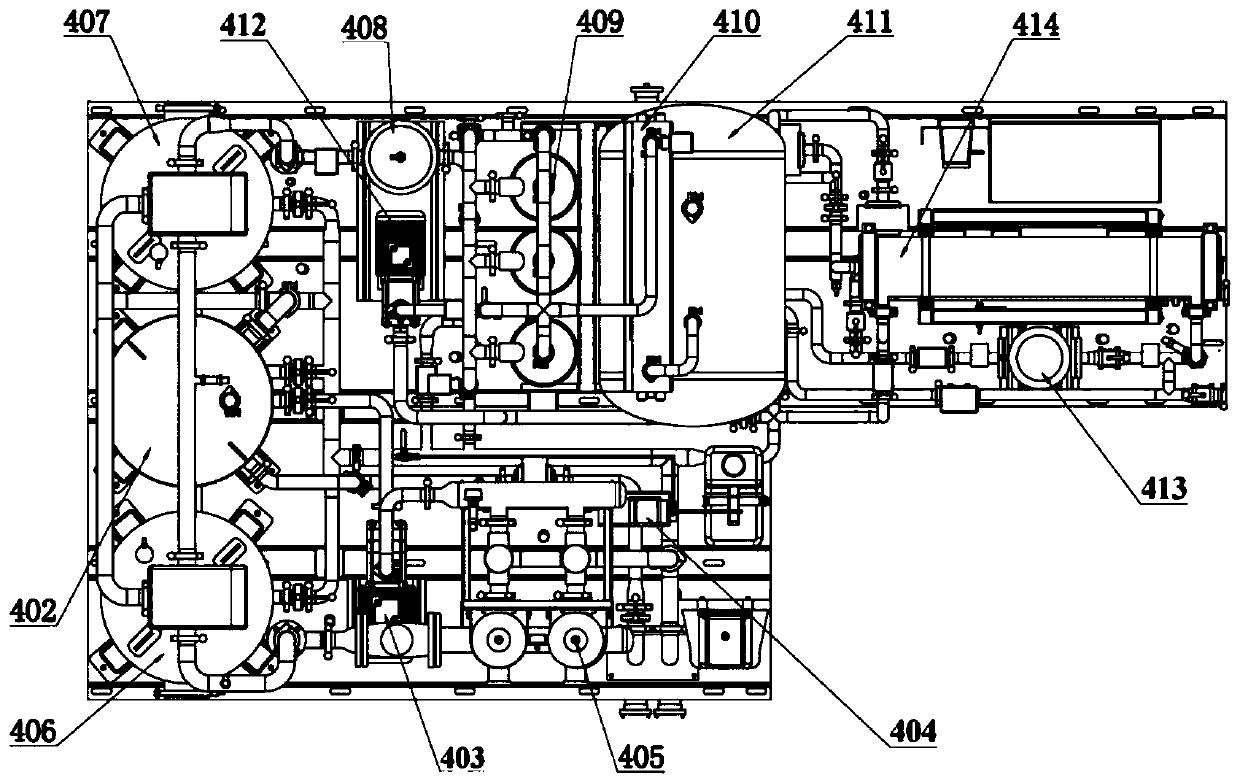
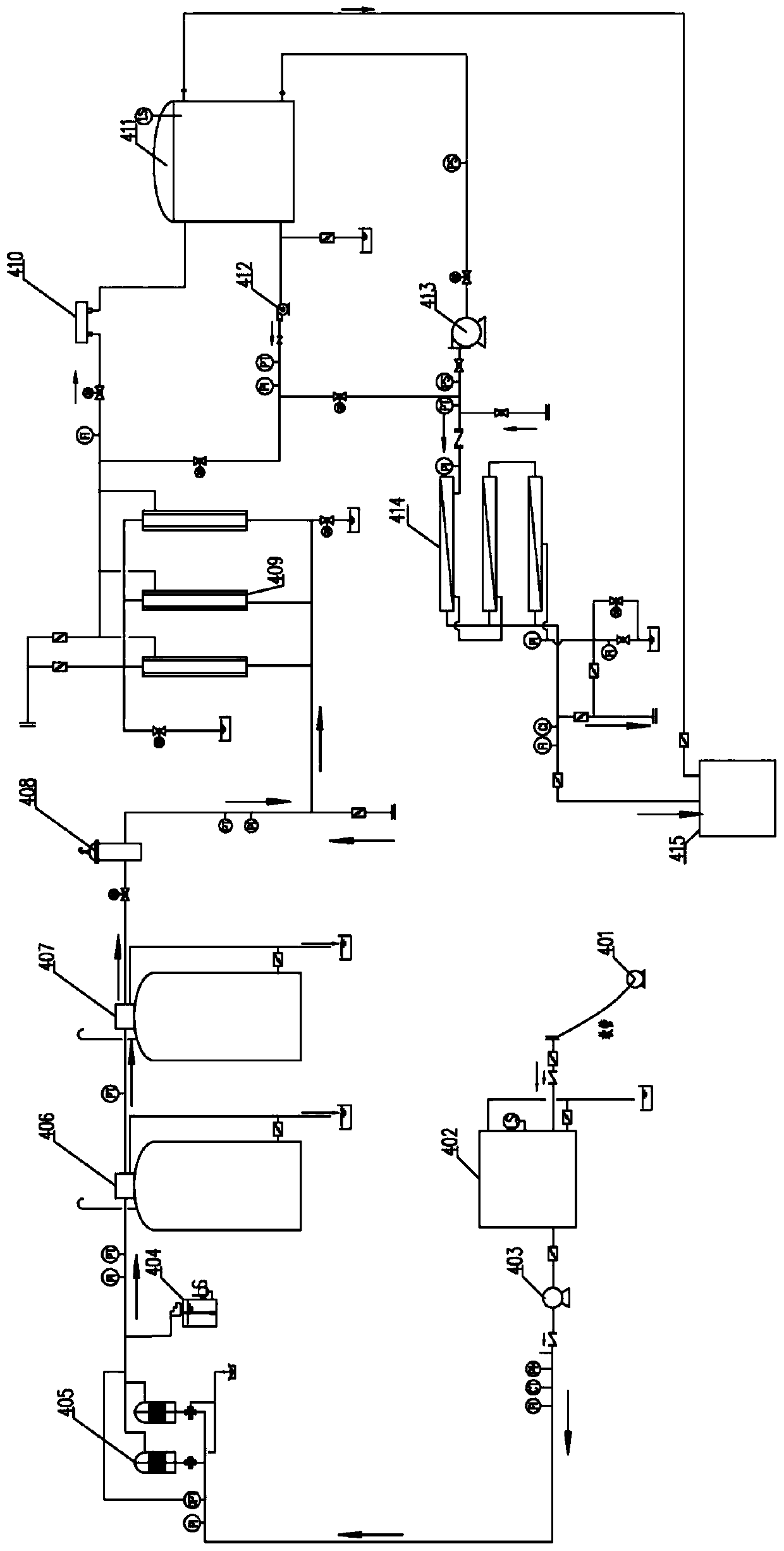
All-area water purifying vehicle
PendingCN109734227AApplicable to ensureAvoid damageMultistage water/sewage treatmentFiberCarbon fibers
The invention discloses an all-area water purifying vehicle which comprises a vehicle chassis with a heat-insulating square bin, a water purifying device arranged in the heat-insulating square bin anda tail gas heat exchange device. The water purifying device comprises a pretreatment component and a double-membrane treatment component, the pretreatment component comprises a pre-filter, a micro-flocculation filter, a precision filter and a security filter in sequential communication, the double-membrane treatment component comprises an ultrafiltration filter and a reverse osmosis filter in sequential communication, the pretreatment component is used for treating raw water, and the double-membrane treatment component is used for treating water after being treated by the pretreatment component; the tail gas heat exchange device utilizes tail gas of a vehicle chassis engine to heat the heat insulating square bin which is made of carbon fiber. The water purifying device in the all-area water purifying vehicle can purify high-turbidity, low-temperature and low-turbidity and organic pollution water sources and water sources polluted by chemical weapons, nuclear weapons and biological weapons to reach drinking water standards (GB5749-2006); the tail gas heat exchange device can heat the heat insulation square bin, so that the all-area water purifying vehicle is suitable for cold regions.
Owner:CHENGDU DUCHENG ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION CO LTD
Gamma Ray Detector with Two-Dimensional Directionality
InactiveUS20180321399A1High angular accuracyReduce weightMeasurement with scintillation detectorsMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationCounting rateRadiological weapon
The invention is a gamma ray detector that locates a source, both horizontally and vertically. The detector comprises a tubular shield surrounded by scintillator panels. Gammas incident from one side can fully strike the scintillator facing the source, but are blocked from reaching the scintillators on the opposite side of the shield. The scintillator counting rates thus indicate the lateral direction of the source. By iteratively rotating toward the highest-counting scintillator, the detector converges to the source. An additional, central detector can be mounted within the tubular shield. When analyzed with the outer scintillators, the central detector determines the overall angular separation between the source and the detector axis, thereby locating the source in two dimensions automatically. The invention enables rapid detection and precise localization of clandestine nuclear and radiological weapons, despite shielding and clutter obfuscation, while quickly passing clean loads.
Owner:NEWMAN DAVID EDWARD
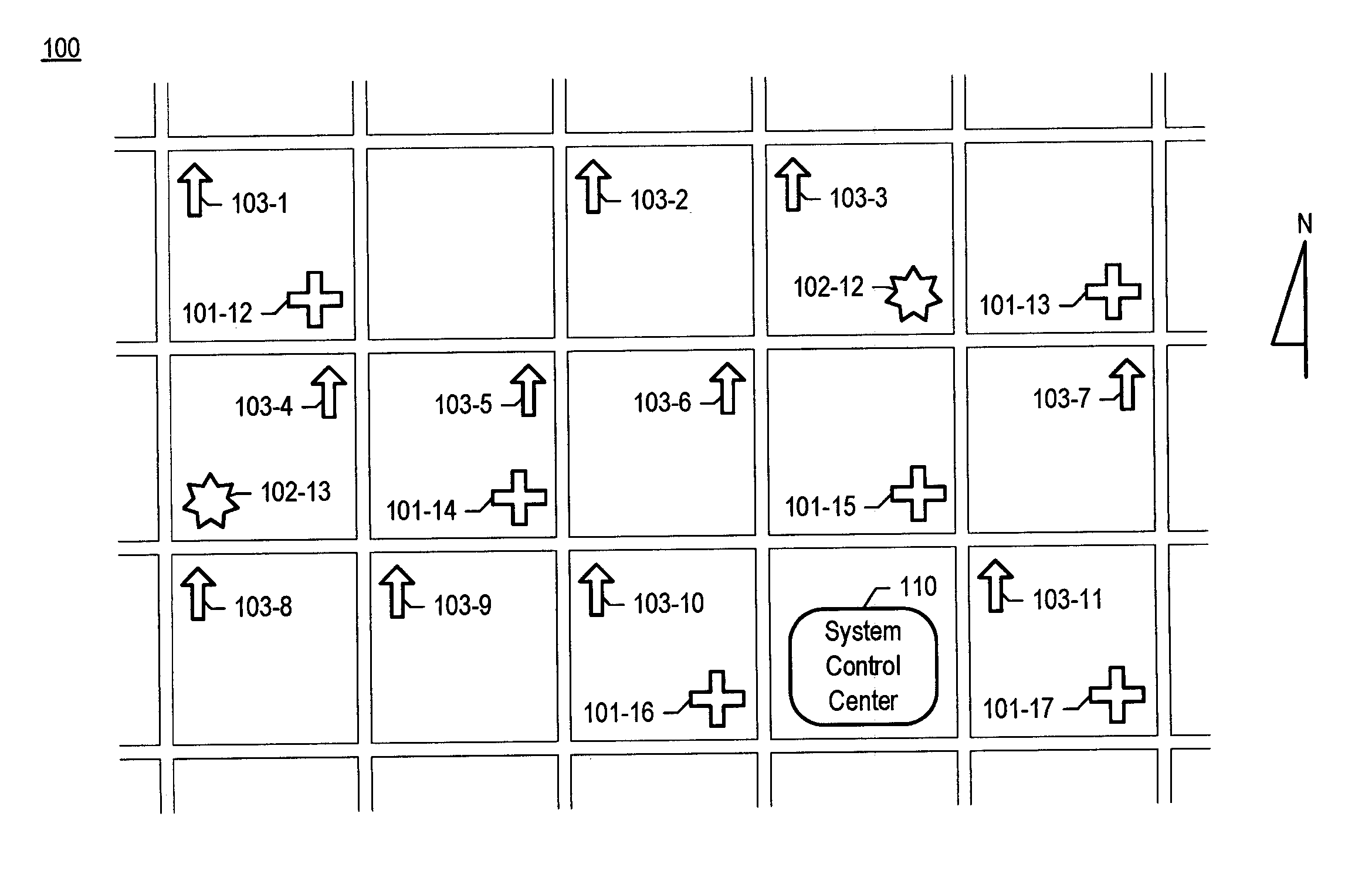
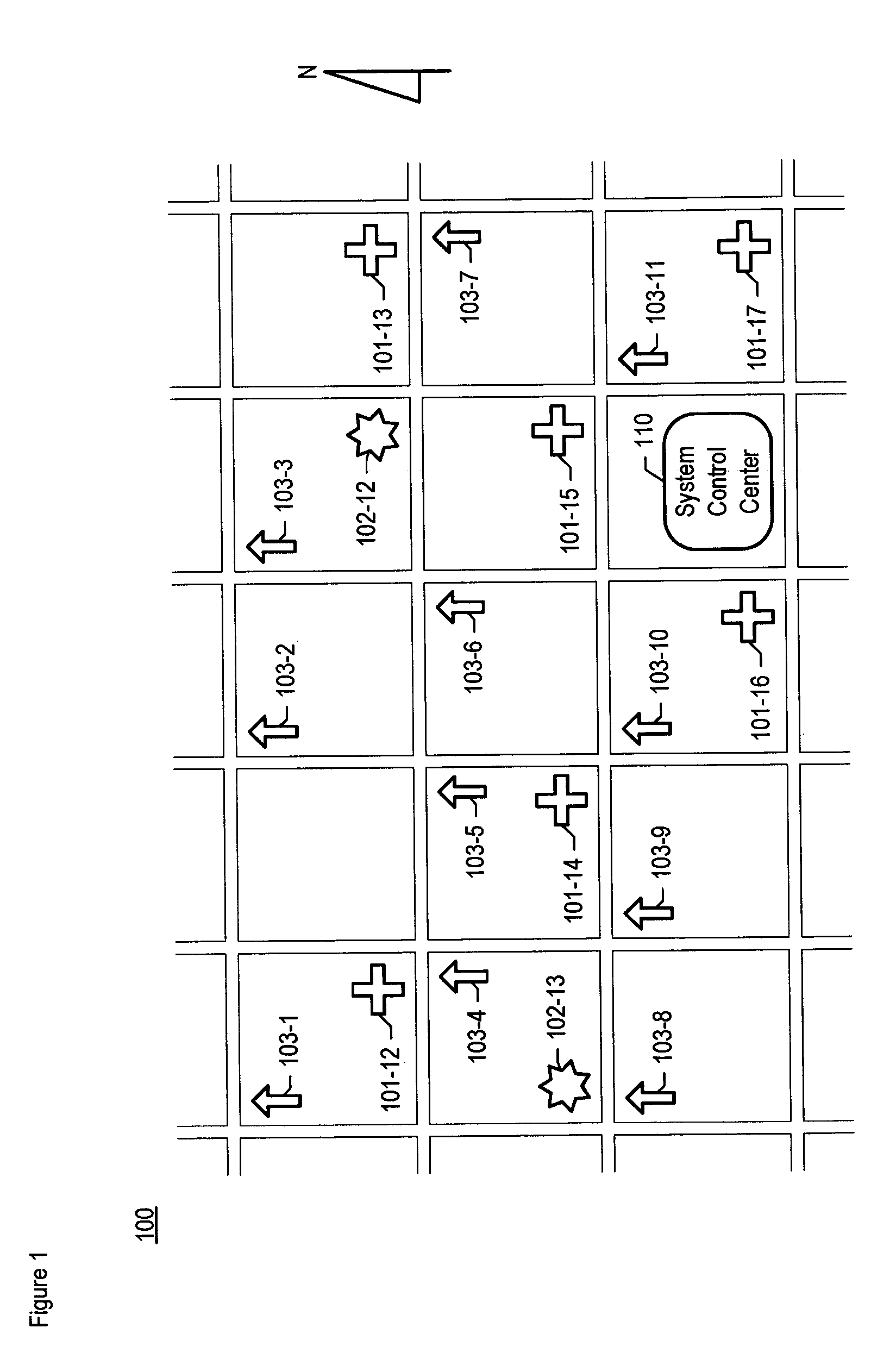
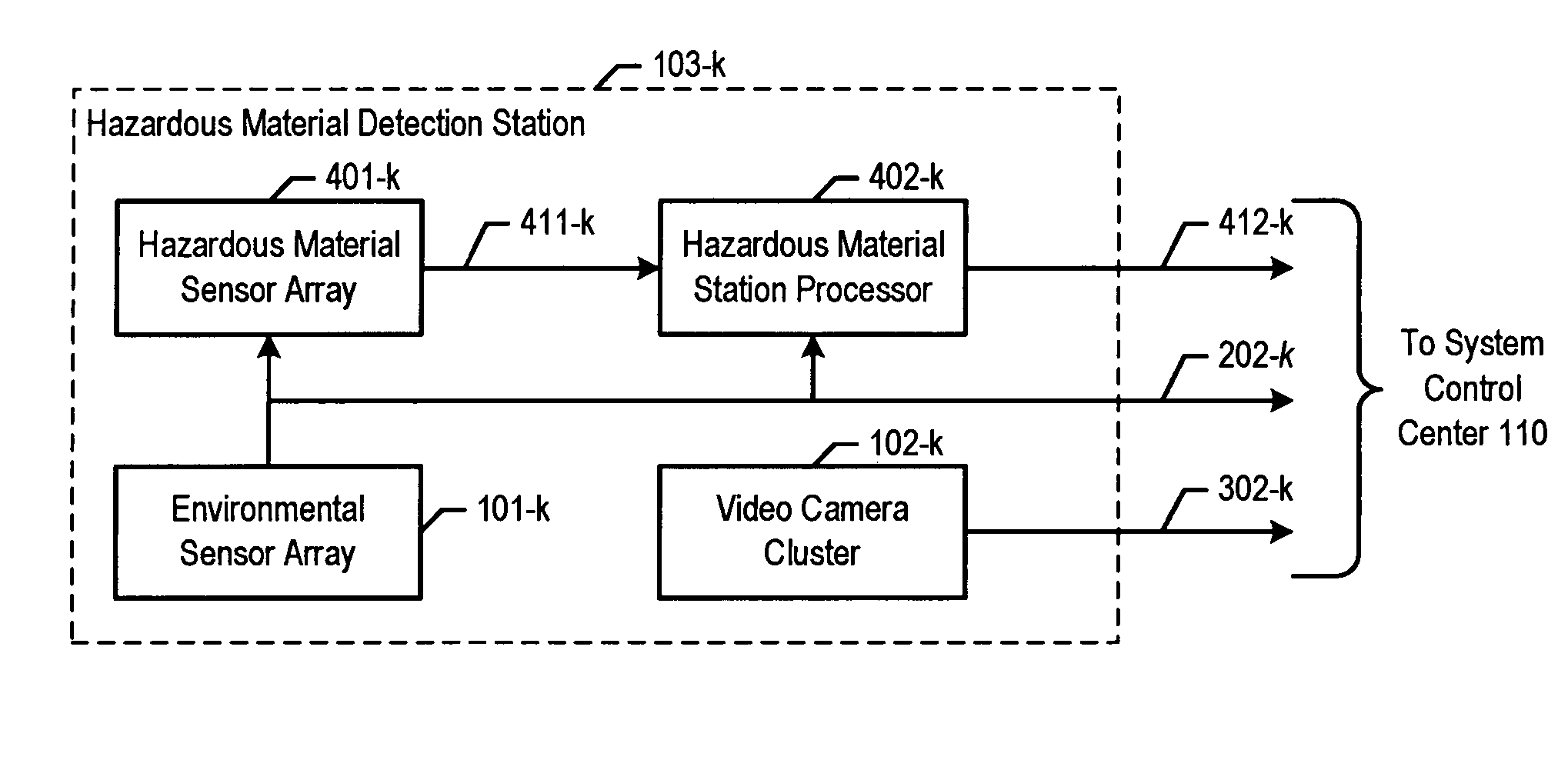
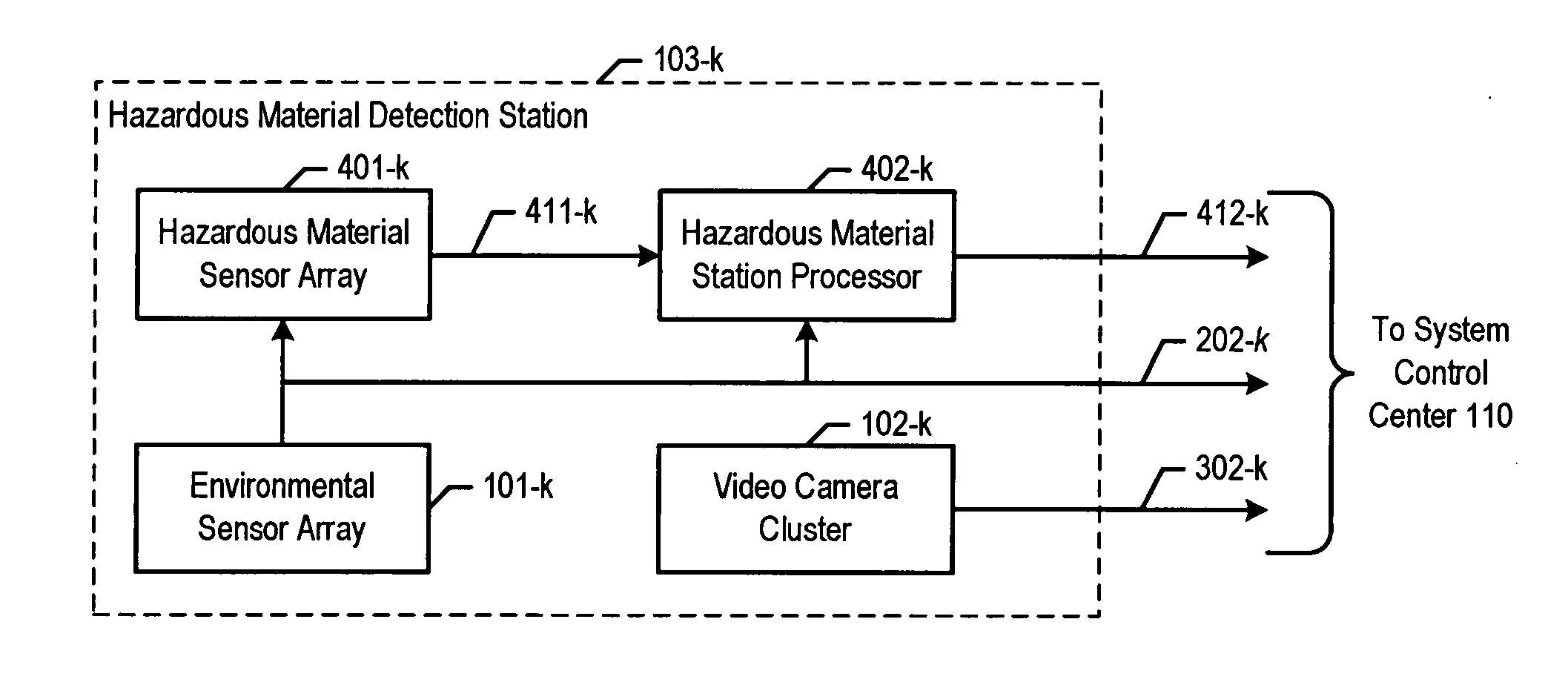
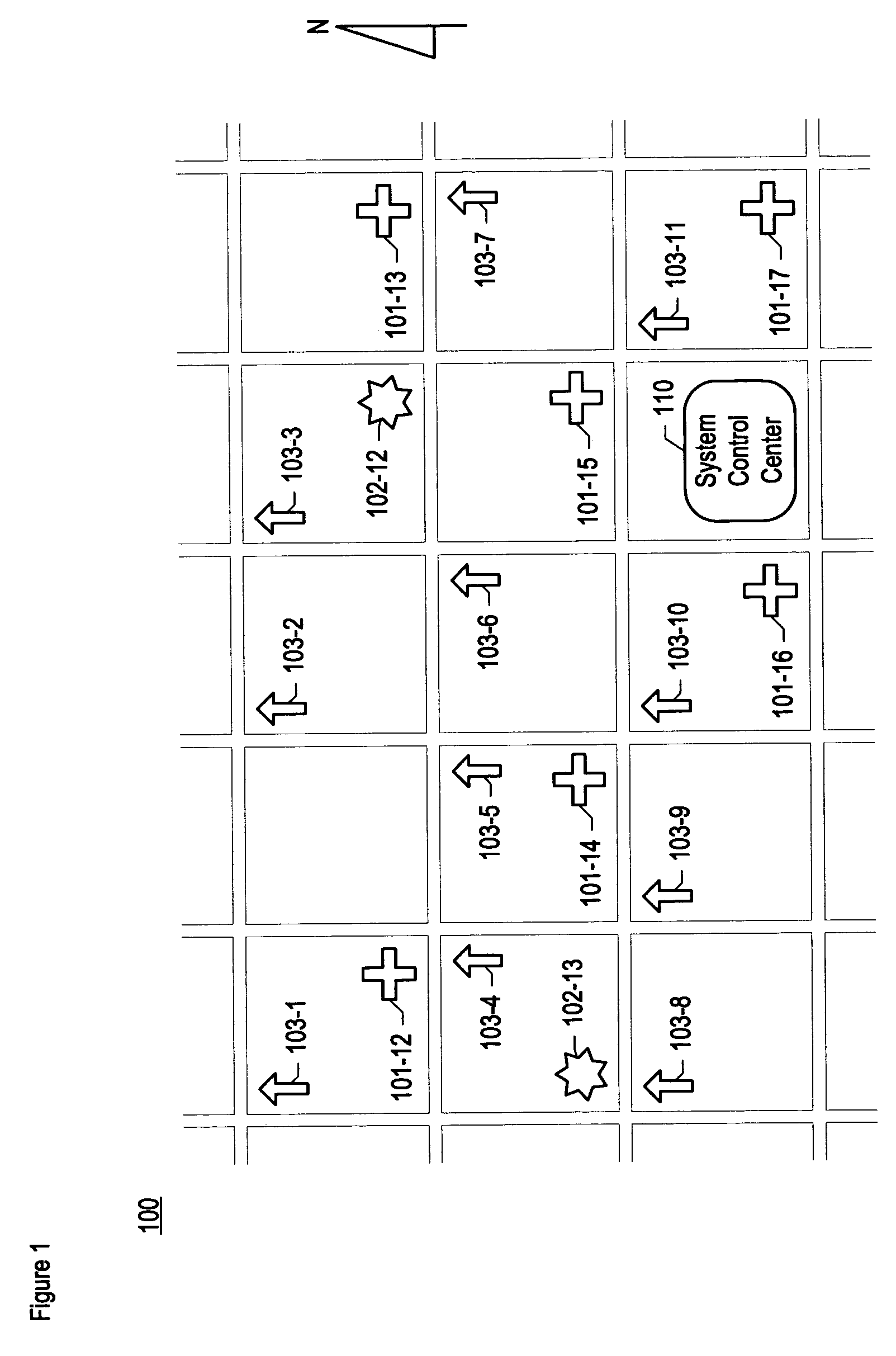
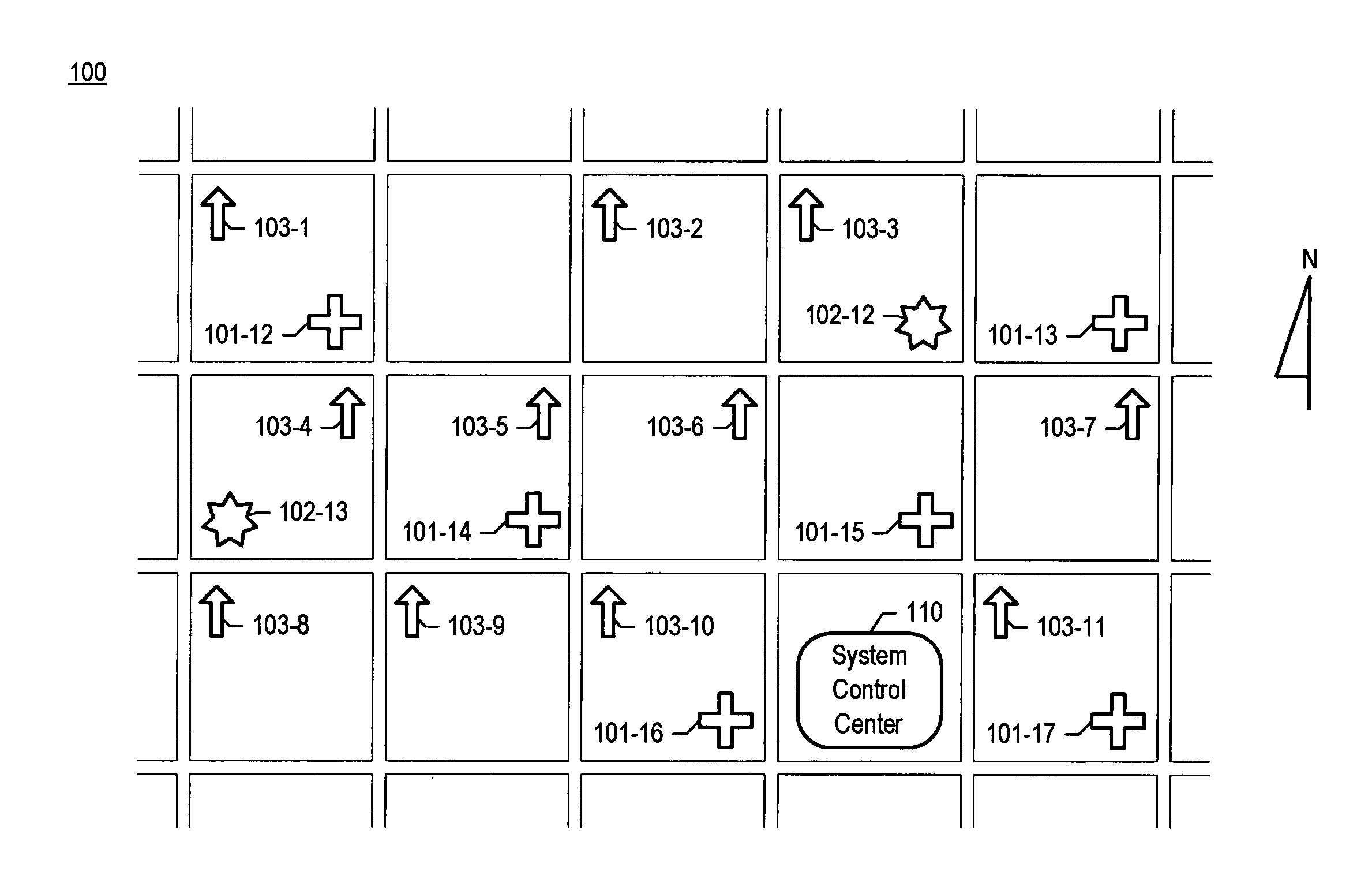
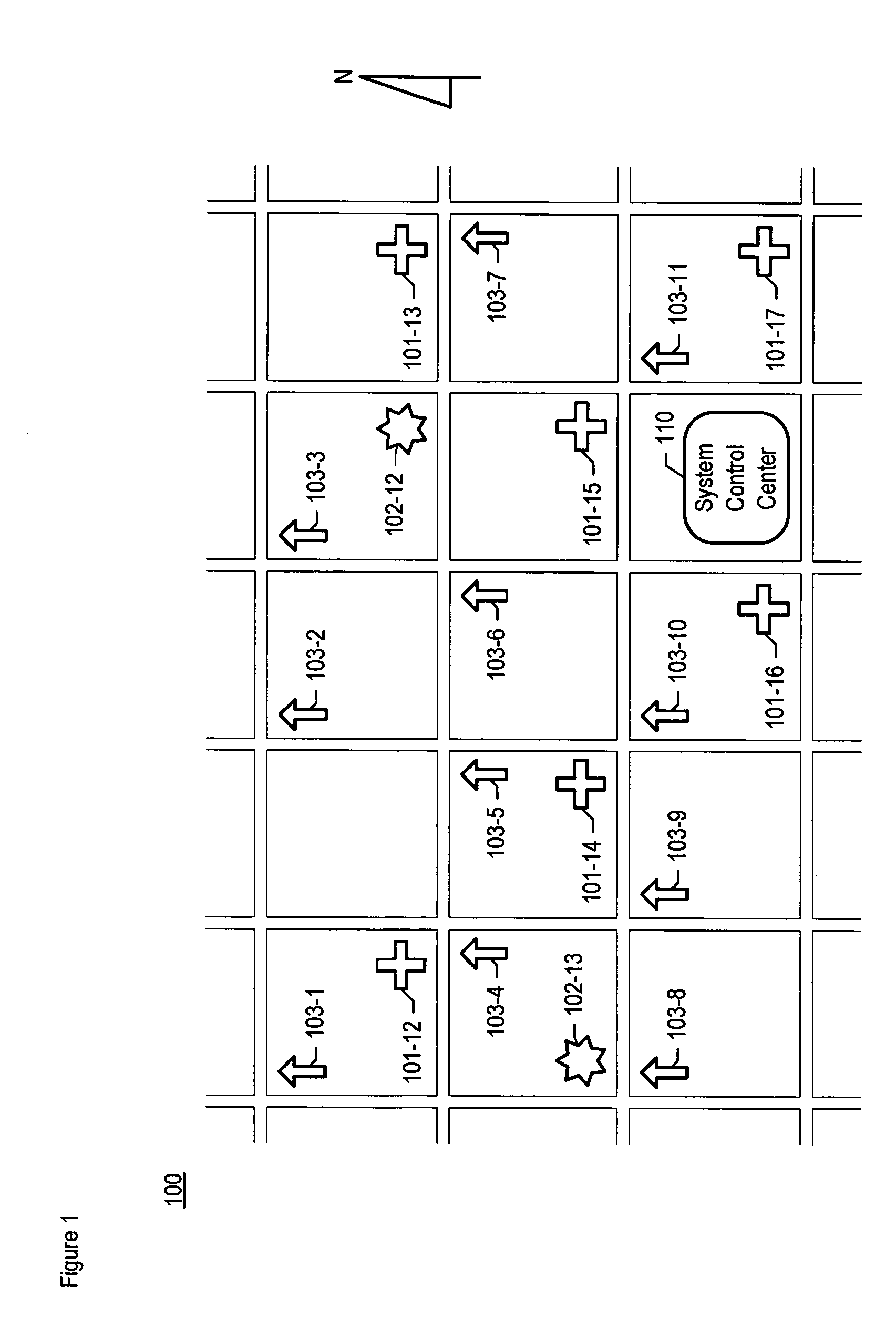
Chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear weapon detection system comprising array of spatially-disparate sensors and surveillance equipment
ActiveUS20060109344A1Quickly and accurately informingLose their confidenceComponent separationColor television detailsEngineeringNuclear weapon
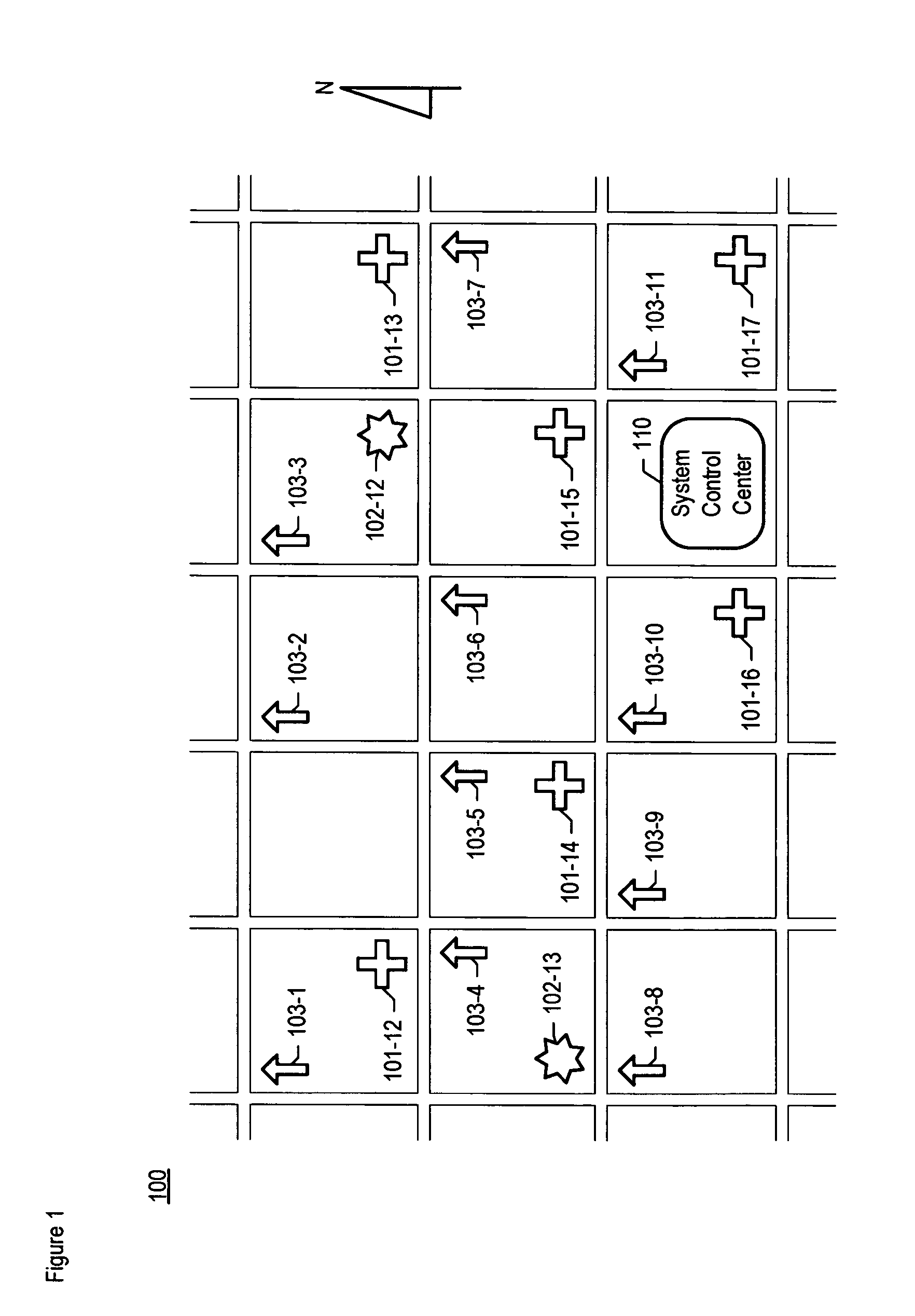
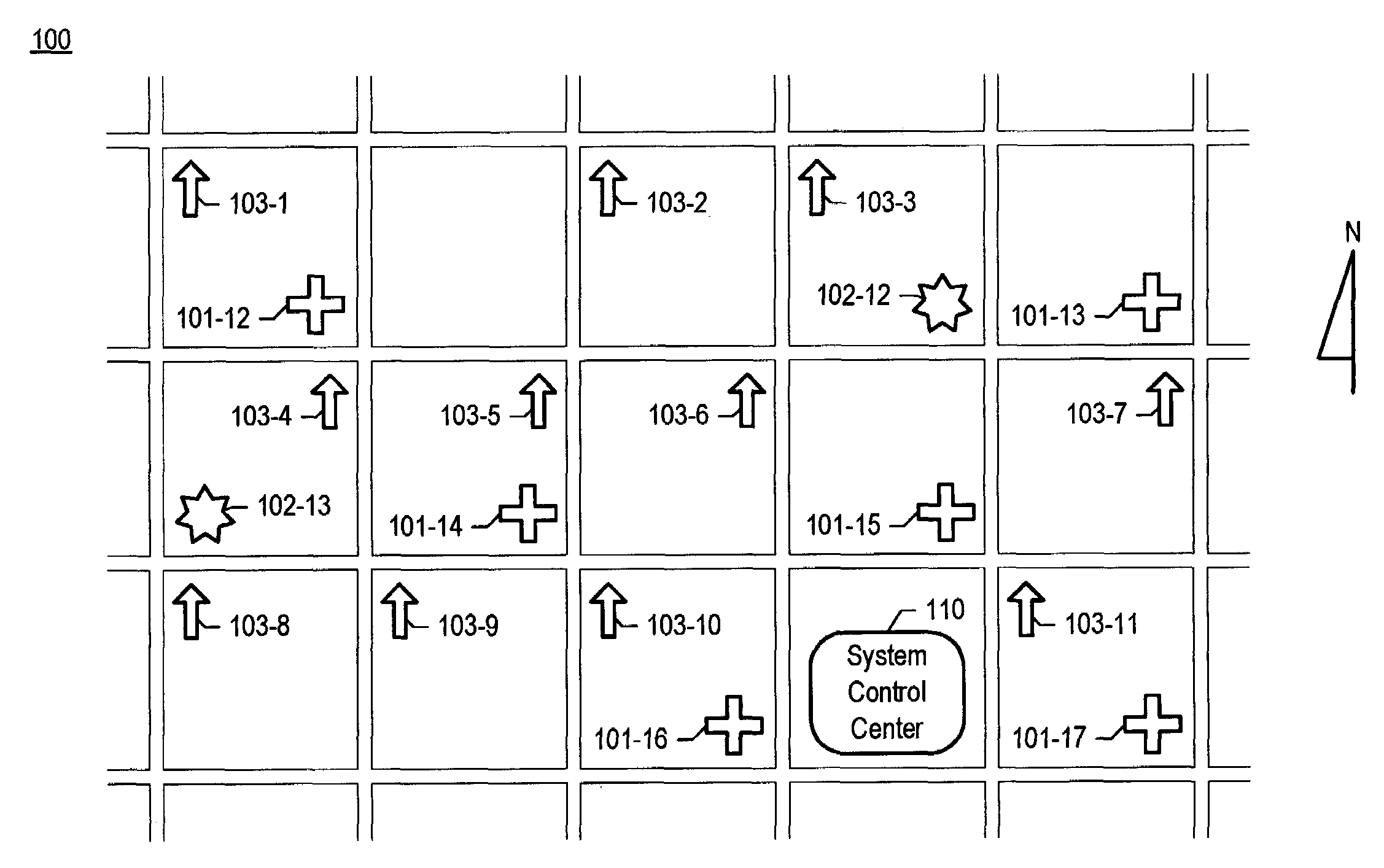
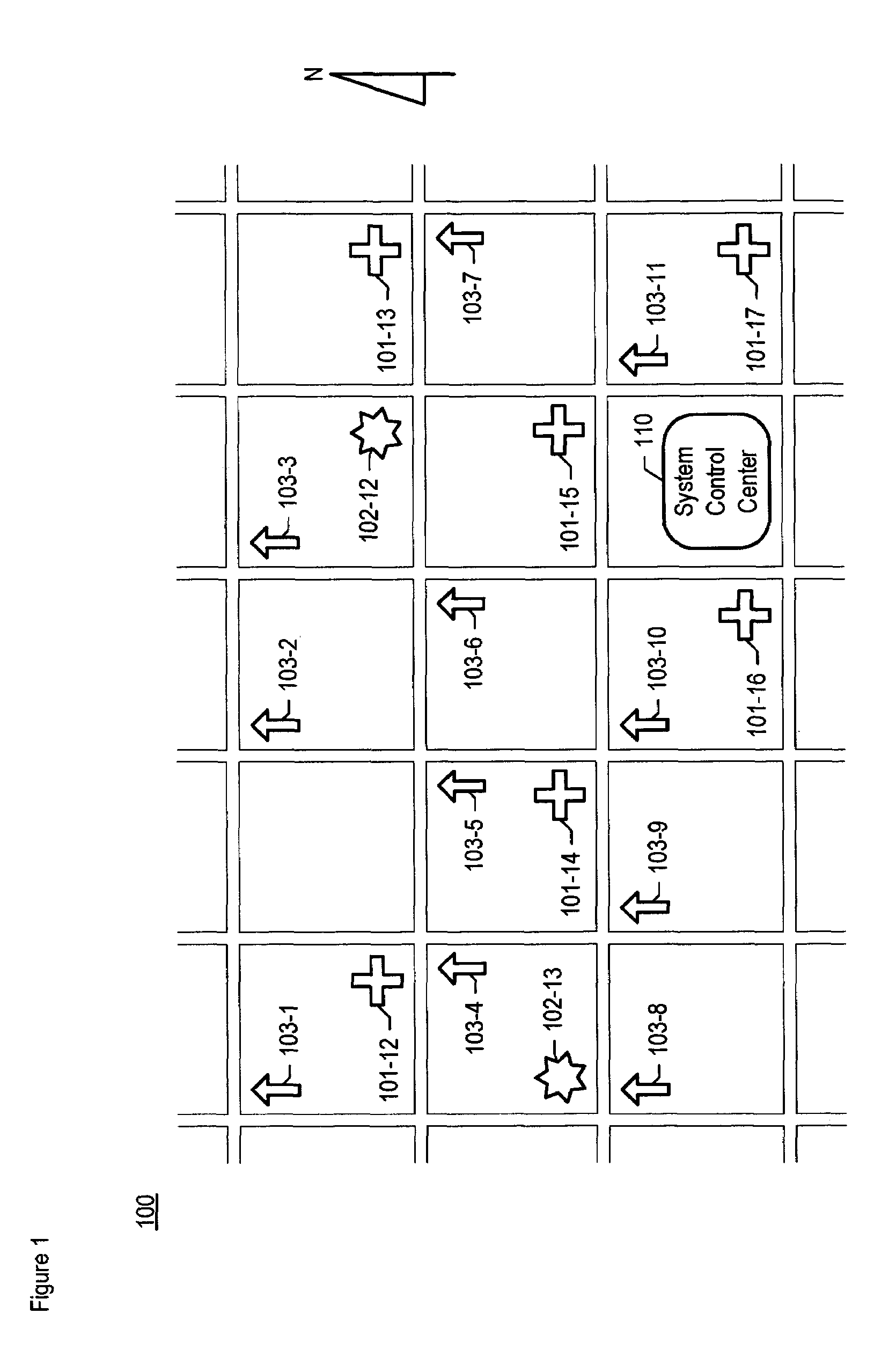
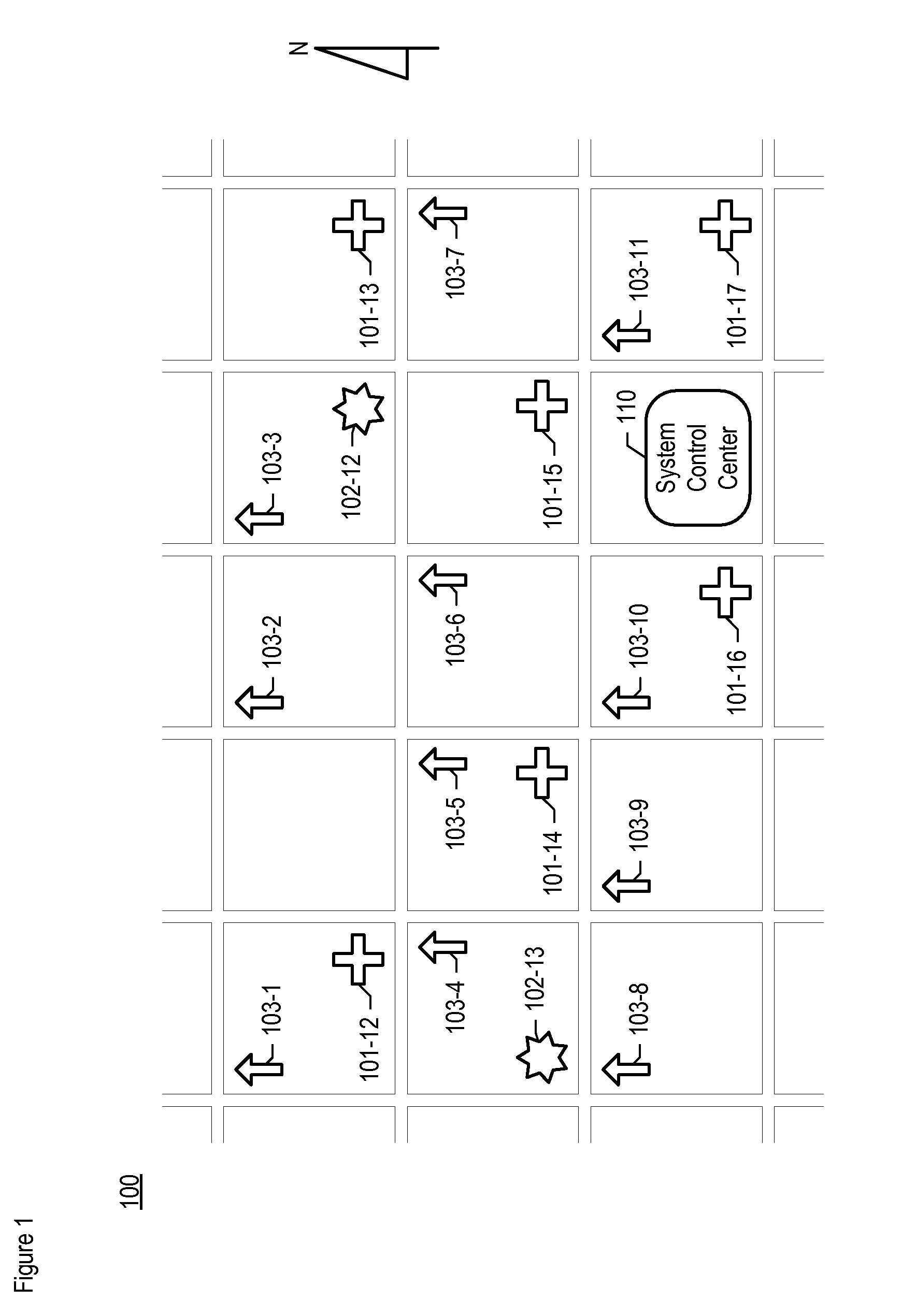
A chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear weapon detection system is disclosed that comprises an array of spatially-disparate hazardous material sensors and an array of spatially-disparate video cameras. The telemetry from the sensors and the video feed from the cameras are all fed back to a centralized system control center. When the illustrative embodiment suspects that an attack has occurred, it switches the feed from the video cameras in the vicinity of where the attack is believed to occur to a monitor. This enables the personnel who monitor the illustrative embodiment to further verify the attack.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Double-head automobile
At present, no double-head automobile is reported, the existing single-head automobile can not turn around conveniently; and when the existing single-head automobile goes wrong, the application thereof is influenced, especially for important passengers or materials, for example the transportation of a head of state, currency or nuclear weapons has quite high requirements on automobile service performance. The invention provides a double head automobile which is formed by carrying out back-forth two-way layout on two sets of various machine elements ensuring normal operation of an automobile; and if one set has technical problems or road condition problems or suffers surprise attack, the other set can substitute for operation immediately.
Owner:任立蓬
Chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear weapon detection system comprising array of spatially-disparate sensors and surveillance equipment
ActiveUS7061388B1Quickly and accurately informingConfidenceComponent separationColor television detailsEngineeringNuclear weapon
A chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear weapon detection system is disclosed that comprises an array of spatially-disparate hazardous material sensors and an array of spatially-disparate video cameras. The telemetry from the sensors and the video feed from the cameras are all fed back to a centralized system control center. When the illustrative embodiment suspects that an attack has occurred, it switches the feed from the video cameras in the vicinity of where the attack is believed to occur to a monitor. This enables the personnel who monitor the illustrative embodiment to further verify the attack.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear weapon detection system with environmental acuity
InactiveUS7362223B2Quickly and accurately informingConfidenceBurglar alarm by openingAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceNuclear weaponOrganism
A chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear weapon detection system is disclosed that heightens its acuity and alertness when it senses that a chemical, biological, radiological, or nuclear weapon attack is more likely. For example, it is well understood that a chemical gas attack is likely to be less effective when it is raining than when it is clear because the rain will suppress and dilute the chemical agent. Therefore, the likelihood of a chemical gas attack is higher when it is clear. In light of this and similar knowledge, the illustrative embodiment checks for evidence of an attack more frequently and with great acuity than when the ambient environmental (e.g., meteorological, etc.) characteristics (e.g., whether is it precipitating or not, whether it is sunny or not, etc) suggest that an attack is more likely. This enables the embodiment to conserve consumables that are used in detecting attacks for when the attacks are more likely.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
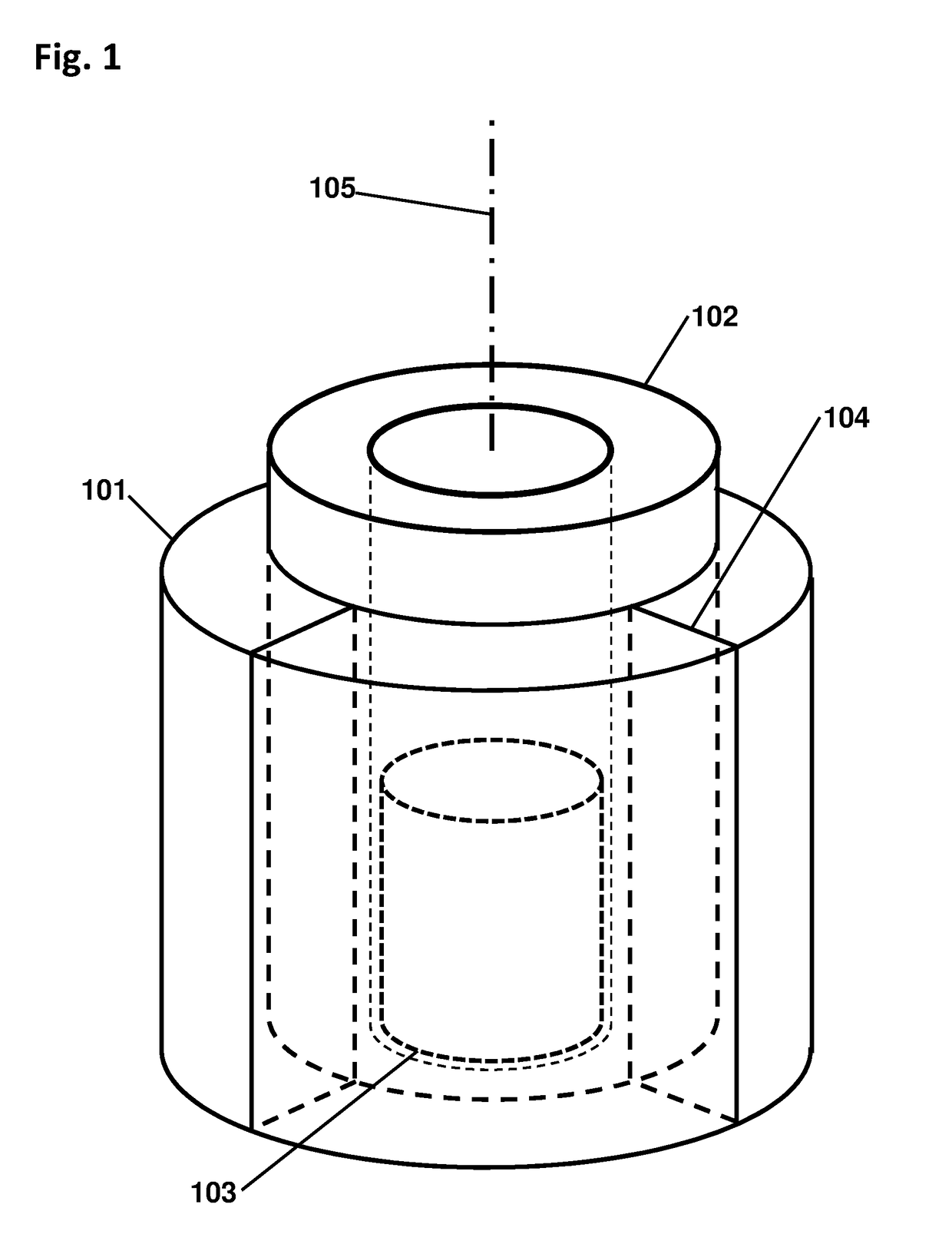
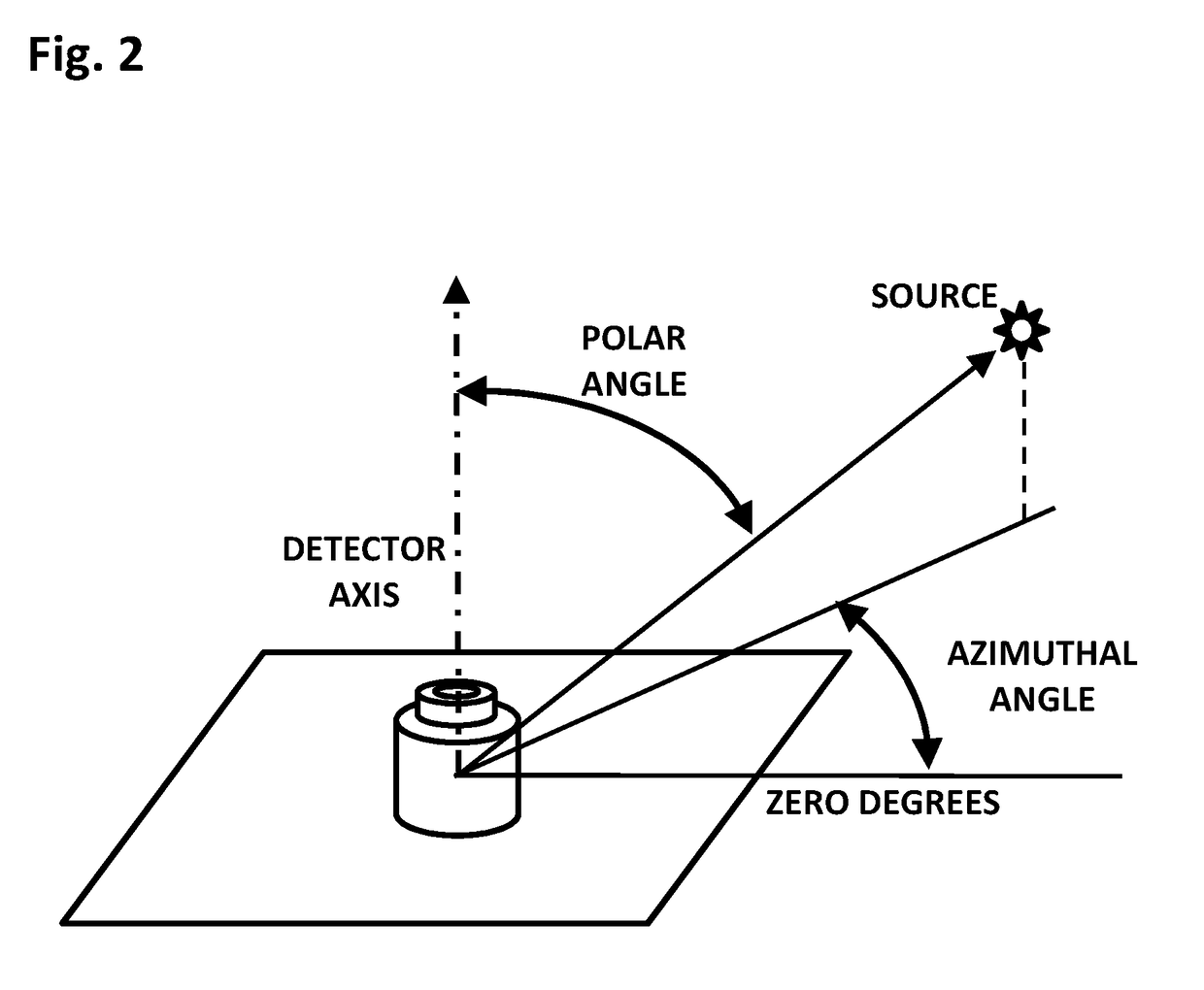
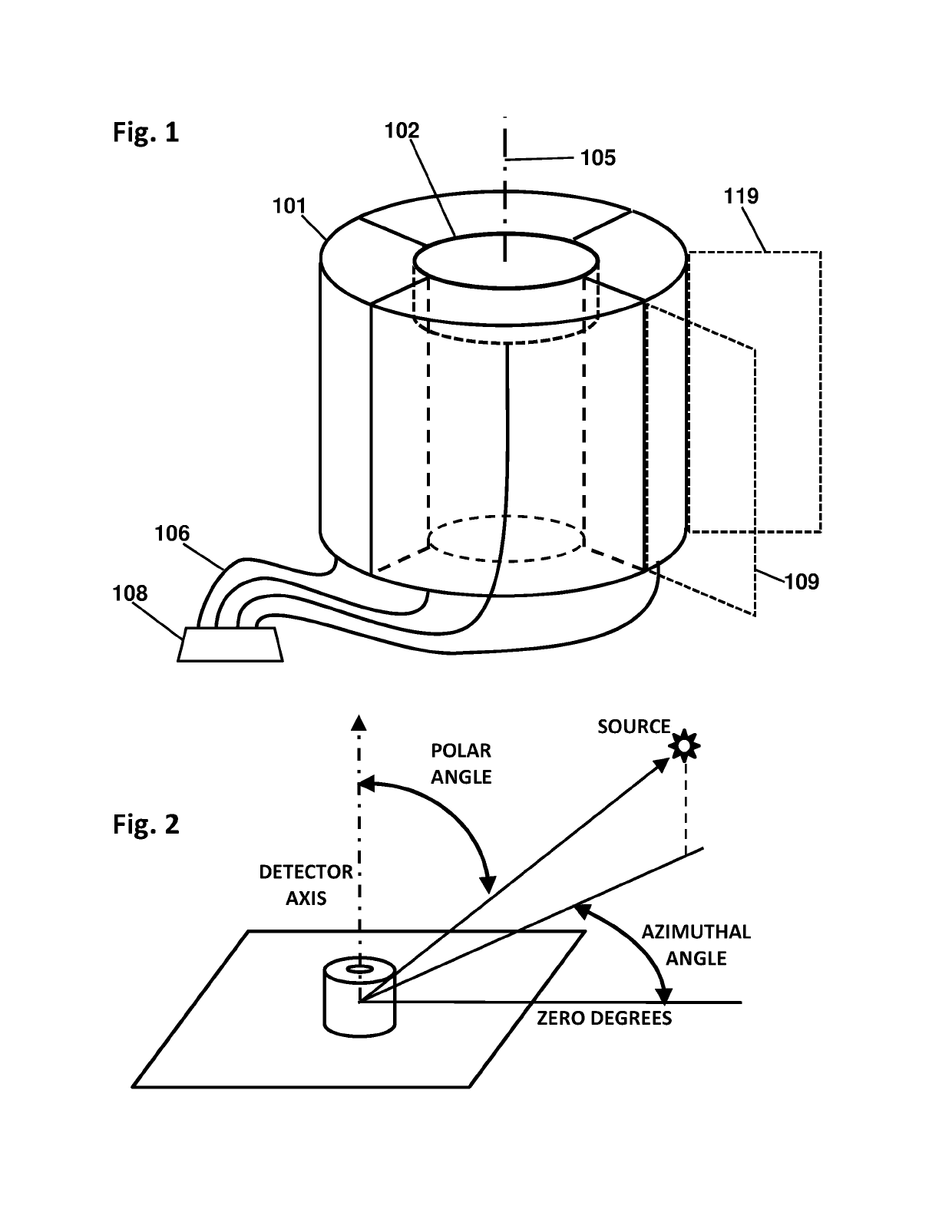
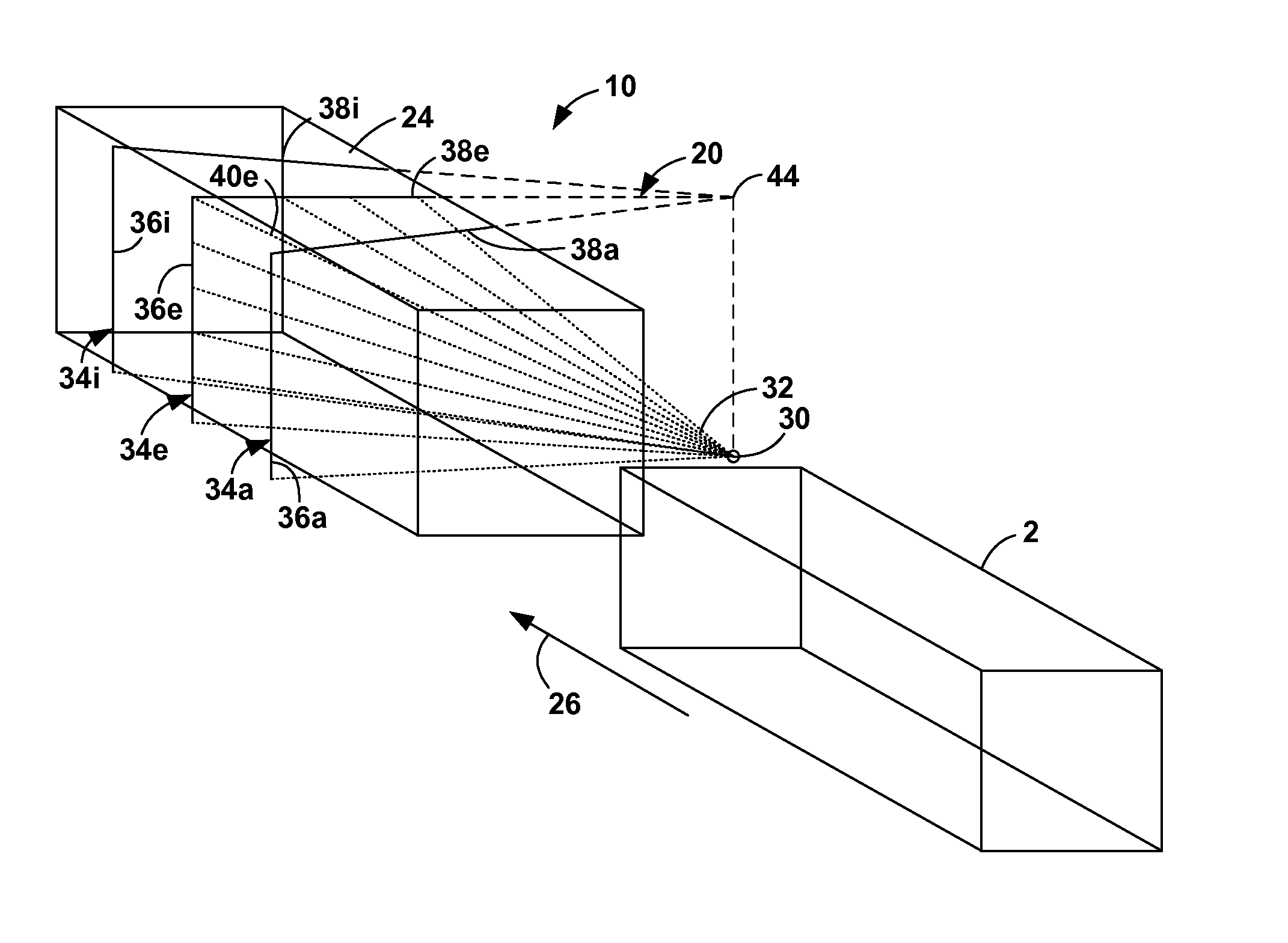
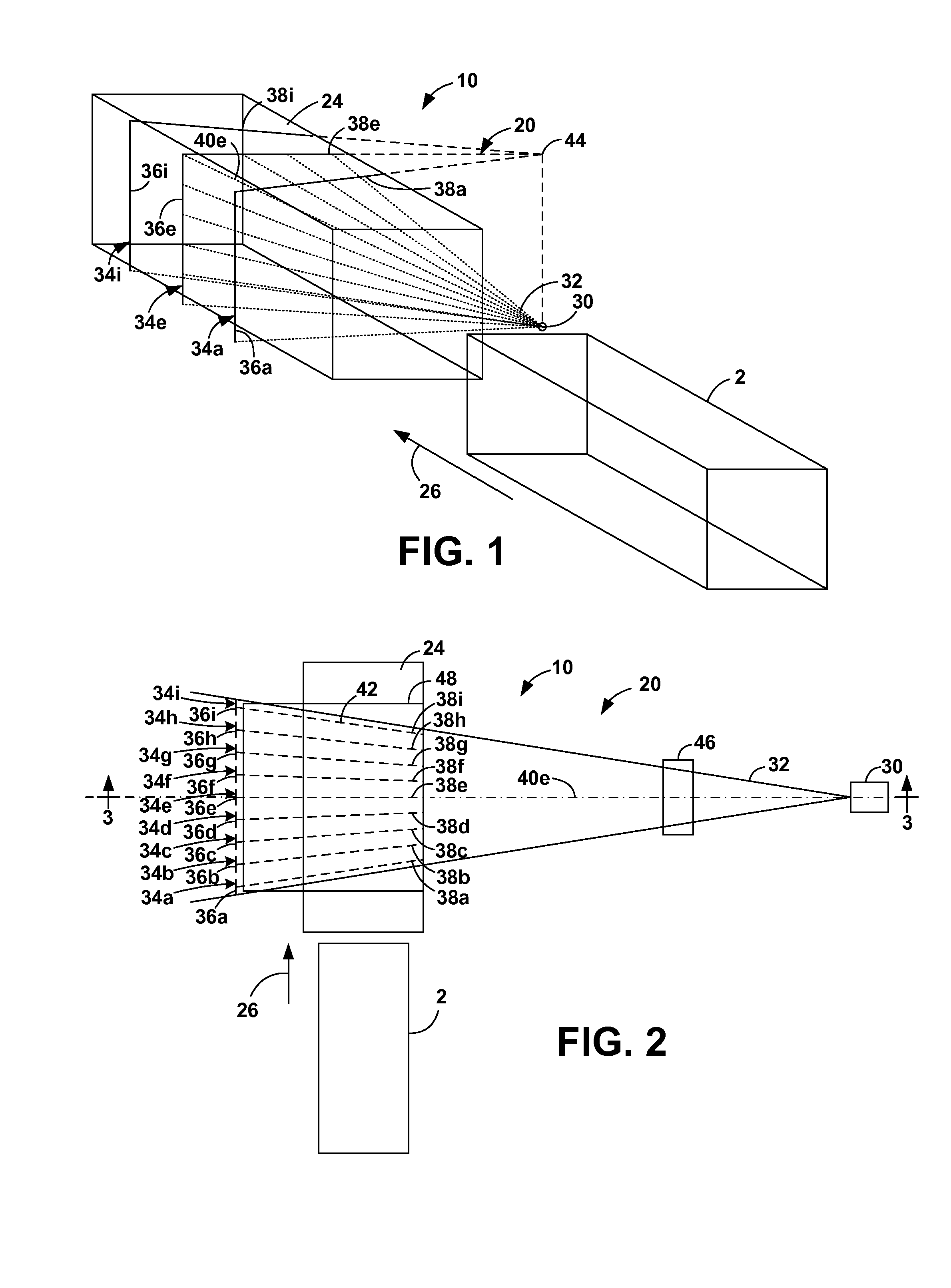
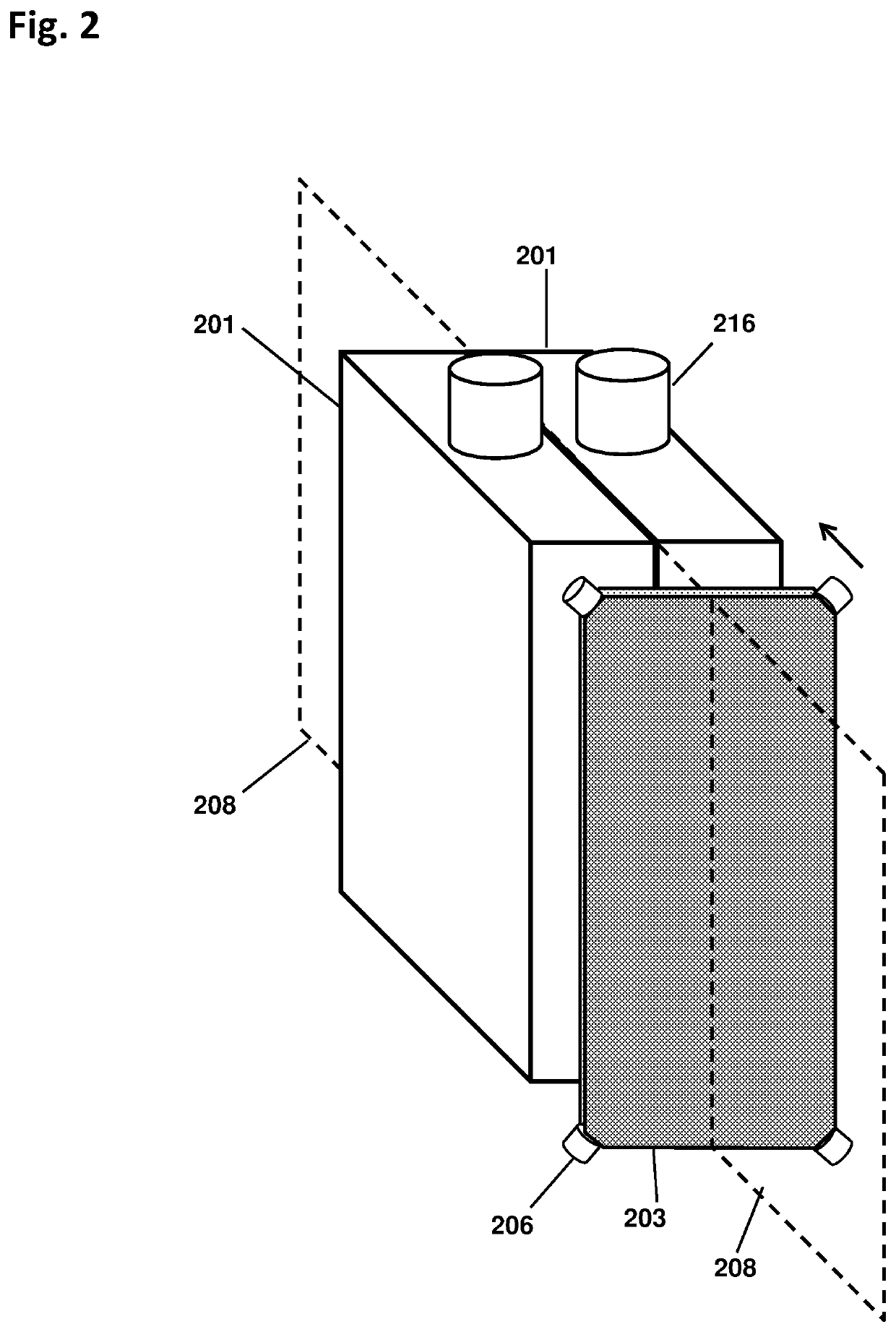
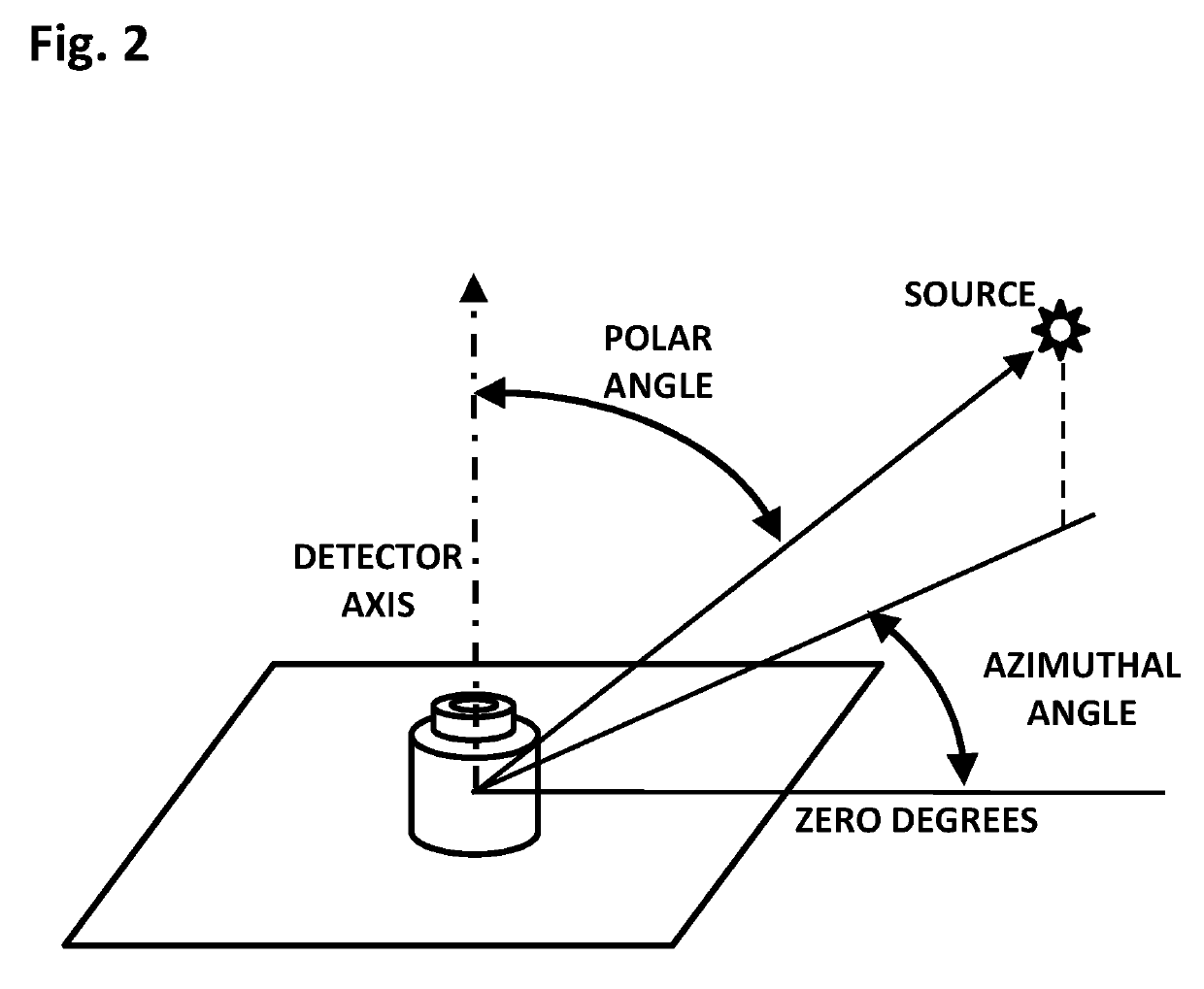
Cylindrical directional detector without collimator
ActiveUS10261200B1Measurement with semiconductor devicesMeasurement with scintillation detectorsCounting rateRadiological weapon
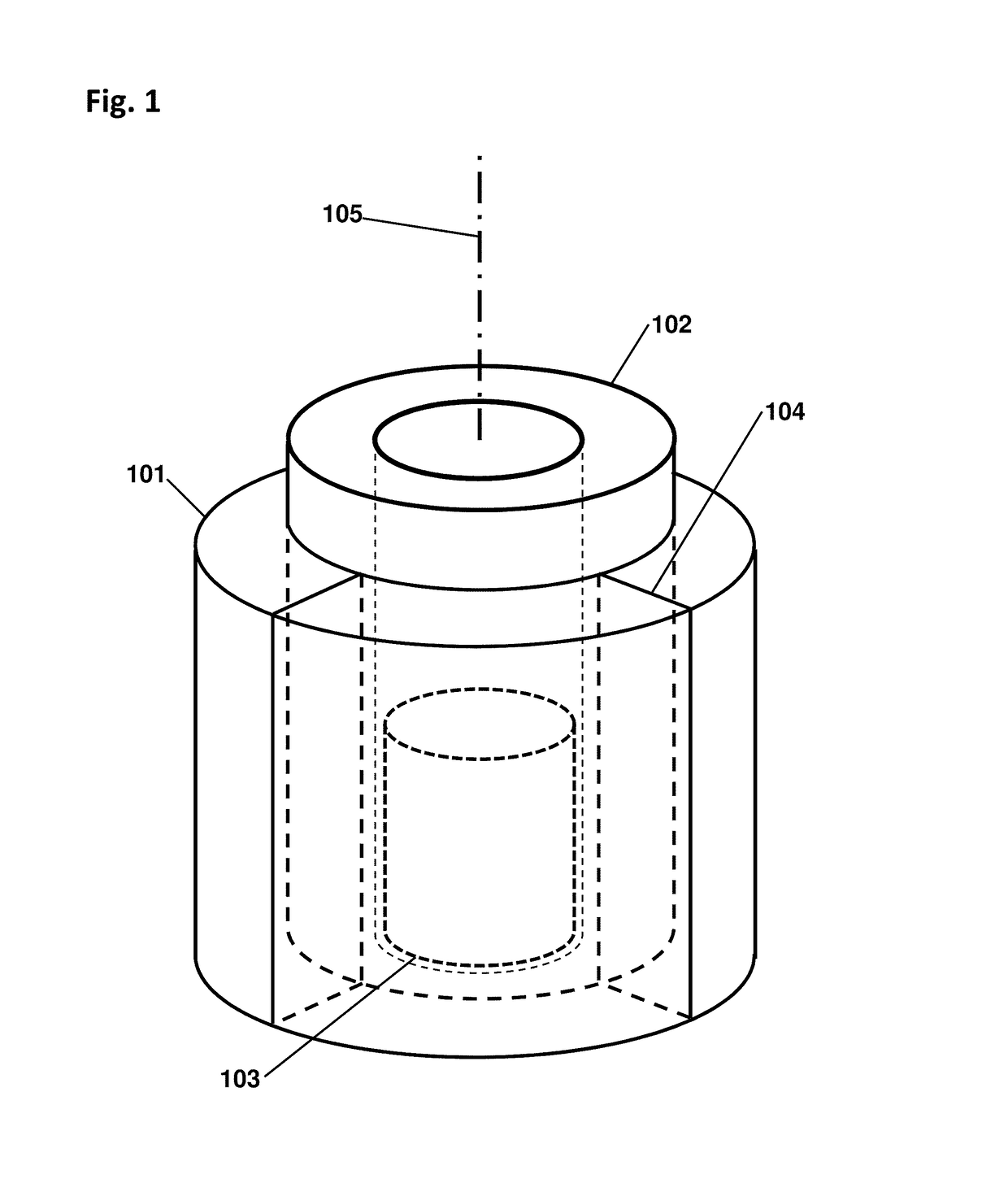
A device configured to detect particles from a radioactive source can localize the source in two dimension, such as the azimuthal and polar angles of the source. Embodiments of the device may comprise a hollow cylindrical or tubular array of “side” detector panels, plus a “central” detector positioned within the array, with no shield or collimator. The various side detector counting rates can indicate the azimuthal angle of the source, while the polar angle can be determined by a ratio of the side detector data divided by the central detector data. Embodiments of the directional detector device can provide greatly improved inspections, thereby detecting clandestine nuclear and radiological weapons, or other sources that are to be localized, rapidly and precisely.
Owner:NEWMAN DAVID EDWARD
Radiation scanning and disabling of hazardous targets in containers
ActiveUS20130001441A1Radiation therapyChemical conversion by chemical reactionNuclear weaponElectron
In one example, a method of examining a container is disclosed comprising detecting a potential threat within contents of a container using radiation scanning and disabling the potential threat with radiation. In another example, a method of examining a container is disclosed comprising scanning at least a portion of the container with a first radiation beam, detecting radiation interacting with contents of the container, identifying a potential threat contained based, at least in part, on the detected radiation, and disabling the potential threat with a dose of radiation from a second radiation beam. The potential threat may be a nuclear, chemical, and / or biological weapon, for example. Chemical and / or biological detectors may also be provided. The threat and / or electronics associated with the threat, may be disabled. Systems are also disclosed.
Owner:VAREX IMAGING CORP
Chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear weapon detection system with alarm thresholds based on environmental factors
ActiveUS20060001536A1Quickly and accurately informingLose their confidenceEpidemiological alert systemsAnalogue computers for chemical processesEngineeringOrganism
A chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear weapon detection system is disclosed that incorporates a mechanism to reduce the probability that a false alarm will be issued. In particular, the mechanism causes an alarm to be triggered when the amount of a hazardous material reaches a threshold, but changes the threshold based, at least in part, on environmental (e.g., meteorological, etc.) characteristics (e.g., whether is it precipitating or not, whether it is sunny or not, etc) that effect the efficacy of a chemical, biological, radiological, or nuclear weapon. Given that there are environmental factors that make an attack less effective, and given that terrorists are aware of this, the illustrative embodiment is less likely to issue an alarm when the environmental factors suggest that an attack is less effective, and, therefore, less likely. The illustrative embodiment accomplishes this by changing the threshold needed to issue an alarm based on one or more the environmental factors.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Method for detecting a nuclear weapon in a shipping container or other vehicle using x-rays
InactiveUS8660238B1Good conditionMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationNuclear radiation detectionHigh absorptionX-ray
A method of improving the detection of nuclear weapons in cargo containers. The container moves through an imaging region. An x-ray source emits a cone beam through the imaging region and to two or more detector columns, each detector column defining a fan beam. This hardware combines (1) the use of at least two detector assemblies, (2) use of both the current method and the photon counting method to determine x-ray intensities, and (3) use of large detector elements to increase the measured x-ray intensity by a typical factor of 270. The x-ray intensity for a pixel is read by each detector assembly at the appropriate time and the resulting x-ray intensities from each detector assembly are summed. A method of detecting a nuclear weapon includes identifying the nuclear device as the area of the image wherein a high absorption area is surrounded by a lower absorption area.
Owner:MARTIN ANNIS PATENT TRUST - 2009
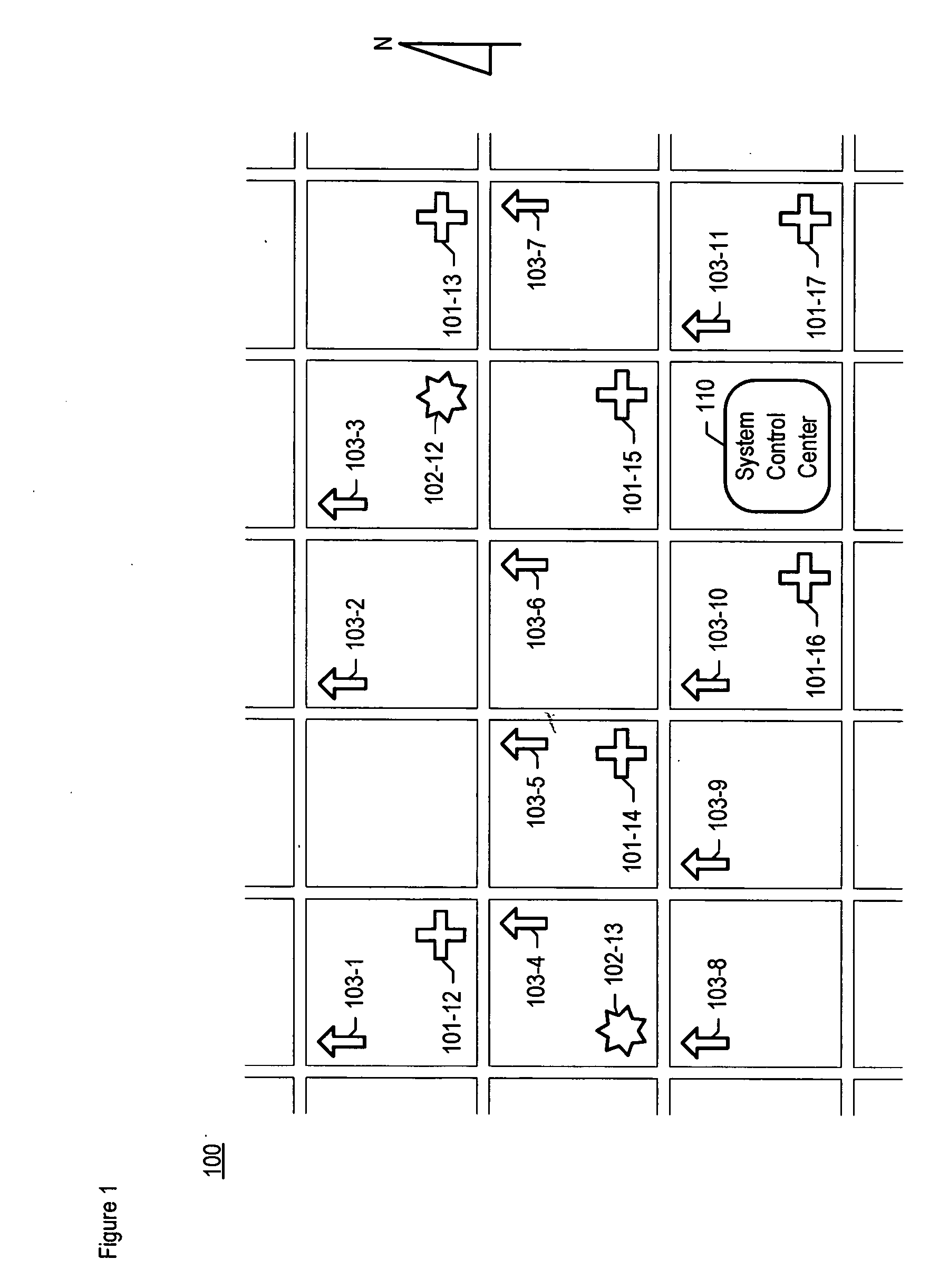
Chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear weapon detection system comprising array of spatially-disparate sensors
ActiveUS20060187018A1Quickly and accurately informingConfidenceBiological testingSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringNuclear weapon
A chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear weapons detection system is disclosed that comprises an array of spatially-disparate hazardous material sensors that all feed into a centralized system control center. This enables the embodiment to receive and coordinate in one place all of the hazardous material sensors spread over a wide area, and, therefore, enables an alarm to be quickly issued in the event of a real attack. The illustrative embodiment also incorporates a mechanism to reduce the probability that a false alarm will be issued. In particular, the illustrative embodiment requires that at least 2 stations report an alarm for the same hazardous material within an interval of time. This prevents a false alarm from one hazardous material detection station from issuing a false system-wide alarm. This is based on the assumption that a real attack is more likely to be detected by stations that are near each other than by stations that have no proximity.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
System and method for suppressing electromagnetic pulse-induced electrical system surges
ActiveUS10530151B2Testing dielectric strengthArrangements responsive to excess currentOvervoltageShunt Device
Owner:CARTY TIMOTHY A +1
Chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear weapon detection system with alarm thresholds based on environmental factors
ActiveUS7088230B2Quickly and accurately informingConfidenceEpidemiological alert systemsAnalogue computers for chemical processesEfficacyEngineering
A chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear weapon detection system is disclosed that incorporates a mechanism to reduce the probability that a false alarm will be issued. In particular, the mechanism causes an alarm to be triggered when the amount of a hazardous material reaches a threshold, but changes the threshold based, at least in part, on environmental (e.g., meteorological, etc.) characteristics (e.g., whether is it precipitating or not, whether it is sunny or not, etc) that effect the efficacy of a chemical, biological, radiological, or nuclear weapon. Given that there are environmental factors that make an attack less effective, and given that terrorists are aware of this, the illustrative embodiment is less likely to issue an alarm when the environmental factors suggest that an attack is less effective, and, therefore, less likely. The illustrative embodiment accomplishes this by changing the threshold needed to issue an alarm based on one or more the environmental factors.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear weapon detection system comprising array of spatially-disparate sensors
ActiveUS7084753B1Quickly and accurately informingConfidenceBiological testingSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringNuclear weapon
A chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear weapons detection system is disclosed that comprises an array of spatially-disparate hazardous material sensors that all feed into a centralized system control center. This enables the embodiment to receive and coordinate in one place all of the hazardous material sensors spread over a wide area, and, therefore, enables an alarm to be quickly issued in the event of a real attack. The illustrative embodiment also incorporates a mechanism to reduce the probability that a false alarm will be issued. In particular, the illustrative embodiment requires that at least 2 stations report an alarm for the same hazardous material within an interval of time. This prevents a false alarm from one hazardous material detection station from issuing a false system-wide alarm. This is based on the assumption that a real attack is more likely to be detected by stations that are near each other than by stations that have no proximity.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear weapon detection system comprising array of spatially-disparate sensors and environmental acuity
InactiveUS20120326879A1Quickly and accurately informingConfidenceBiological testingAlarmsEngineeringNuclear weapon
A chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear weapons detection system is disclosed that comprises an array of spatially-disparate hazardous material sensors that all feed into a centralized system control center. This enables the embodiment to receive and coordinate in one place all of the hazardous material sensors spread over a wide area, and, therefore, enables an alarm to be quickly issued in the event of a real attack. To accurately reduce false alarms, the illustrative embodiment requires that at least N of M neighboring stations report an alarm for the same hazardous material within an interval of time, and that the values of at least one of N and M change and are based on at least one environmental factor.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
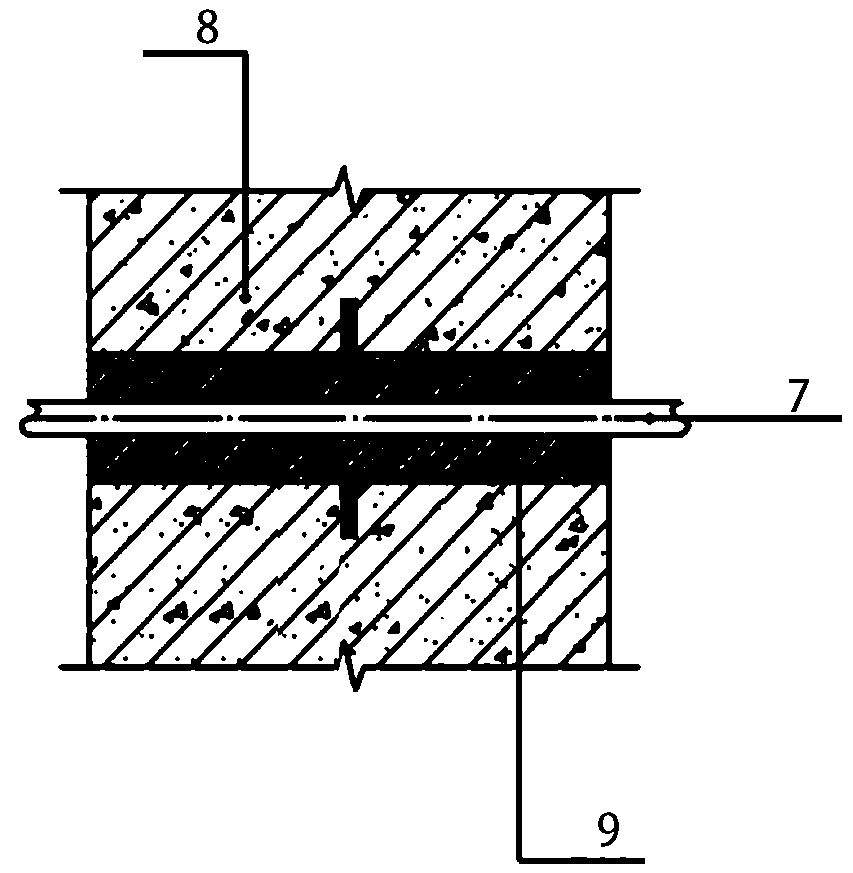
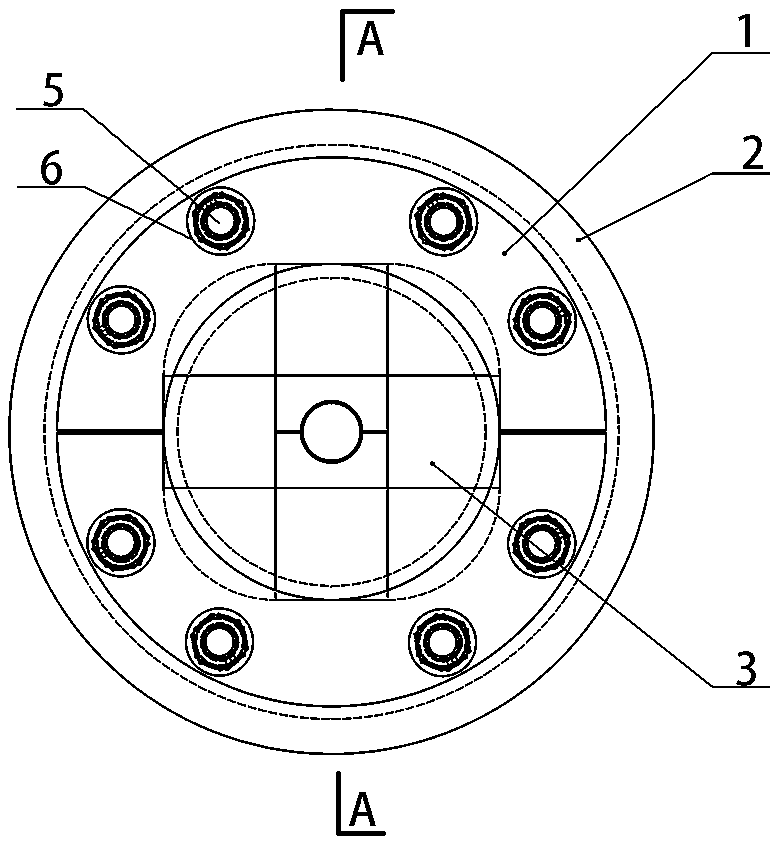
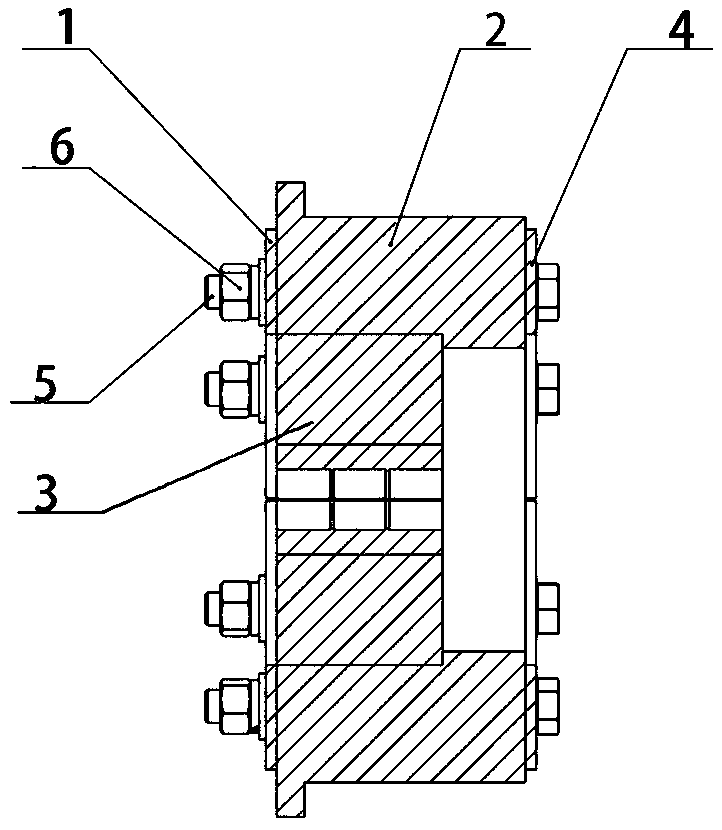
Modular pipe hole sealing device for civil air defense projects and use method thereof
PendingCN109099221ATo achieve the effect of airtightImprove work efficiencyPipesNuclear weaponEnvironmentally friendly
The invention discloses a modular pipe hole sealing device for civil air defense projects and a use method thereof, and mainly relates to the technical field of civil air defense project pipelines andthrough-wall hole protective closing devices for the pipelines. The modular pipe hole sealing device structurally comprises a front pressing plate, a rubber pipe, sealing modules, a rear pressing plate, bolts and nuts. The front pressing plate and the rear pressing plate are respectively connected to two sides of the rubber pipe; the front pressing plate, the rubber pipe and the rear pressing plate are connected and fixed through multiple bolts; a rectangular fillet sealing space is formed inside the rubber pipe; multiple sealing modules are arranged inside the sealing space; and the sealingmodules comprise a plurality of solid unit rubber blocks having fan-shaped, square or rectangular-pore cross sections. The modular pipe hole sealing device disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that the sealing modules can be combined in various specifications, so that the modular pipe hole sealing device is wide in application range, convenient for construction, economical and environmentally friendly; a gap between the pipeline and the sealing space is effectively blocked to fulfill the aims of resisting striking of water, poisons, fire, nuclear weapons and conventional weapons; and the sealing effect is outstanding.
Owner:CHINA INST OF BUILDING STANDARD DESIGN & RES
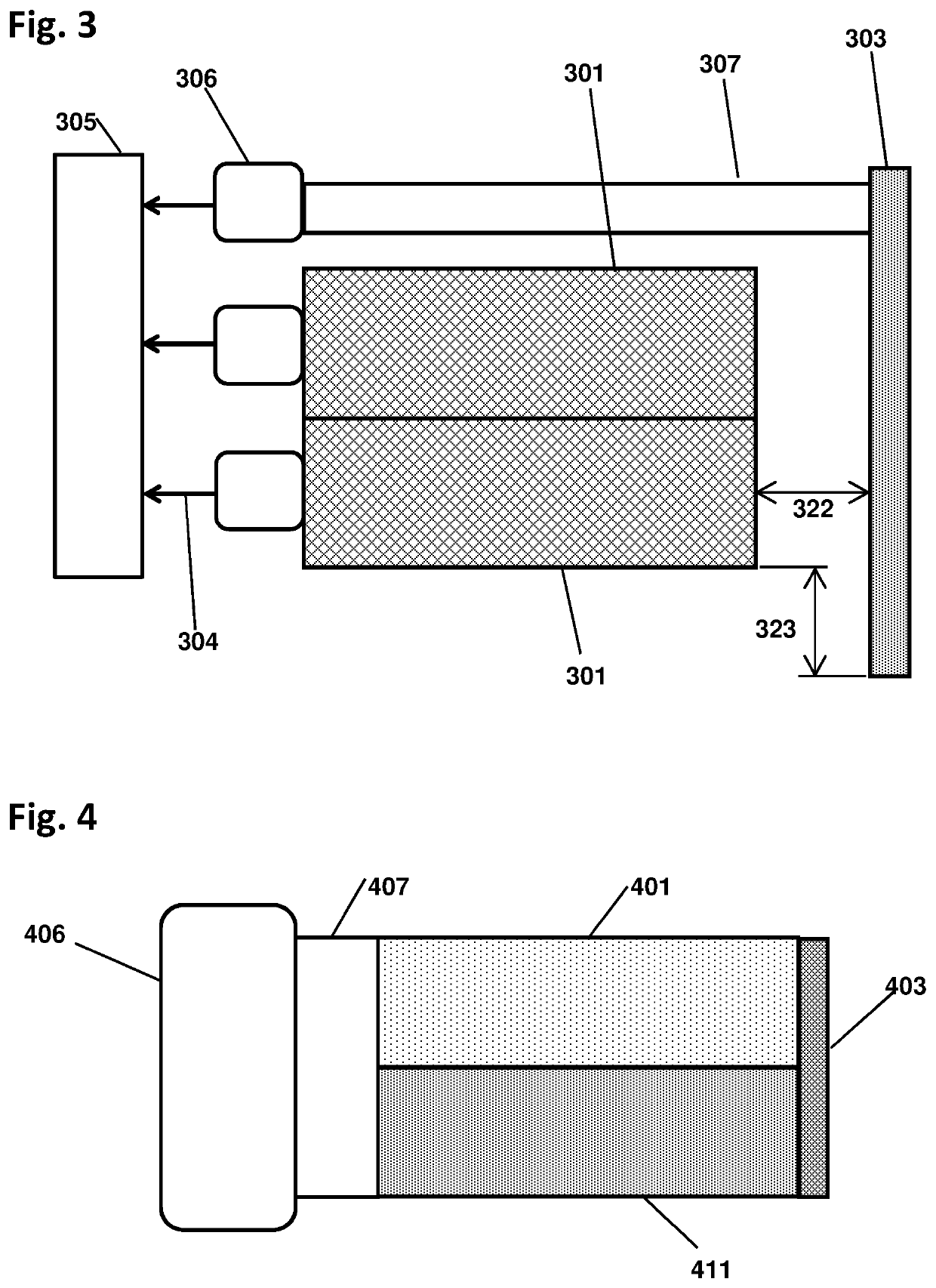
One-Dimensional Directional Shieldless Particle Detector
ActiveUS20200142081A1Measurement with scintillation detectorsRadiation intensity measurementEngineeringRadiological weapon
A device for determining the location of a source of radiation, based on data acquired at a single orientation of the device without iteration or rotations. Embodiments may comprise two side detector panels positioned closely parallel to each other and adjacent to each other, plus a front detector positioned orthogonally in front of the side detectors, without collimators or shields. The various detectors have contrasting angular sensitivities, so that a predetermined angular correlation function can determine the sign and magnitude of the source angle according to the detection rates of the front and side detectors. Embodiments enable rapid detection and localization of nuclear and radiological weapon materials for greatly improved inspection of cargo containers and personnel. Advanced detectors such as those disclosed herein will be needed in the coming decades to protect against clandestine weapon transport.
Owner:NEWMAN DAVID EDWARD
Gamma ray detector with two-dimensional directionality
InactiveUS10401510B2High angular accuracyReduce weightMeasurement with scintillation detectorsMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationCounting rateRadiological weapon
The invention is a gamma ray detector that locates a source, both horizontally and vertically. The detector comprises a tubular shield surrounded by scintillator panels. Gammas incident from one side can fully strike the scintillator facing the source, but are blocked from reaching the scintillators on the opposite side of the shield. The scintillator counting rates thus indicate the lateral direction of the source. By iteratively rotating toward the highest-counting scintillator, the detector converges to the source. An additional, central detector can be mounted within the tubular shield. When analyzed with the outer scintillators, the central detector determines the overall angular separation between the source and the detector axis, thereby locating the source in two dimensions automatically. The invention enables rapid detection and precise localization of clandestine nuclear and radiological weapons, despite shielding and clutter obfuscation, while quickly passing clean loads.
Owner:NEWMAN DAVID EDWARD
Alpha aerosol-proof air suit adhesion technique
ActiveCN100543881CImprove sealingHigh mechanical strengthShieldingChloroprene adhesivesBonding processEngineering
The invention belongs to a manufacturing process of radiation protective clothing, in particular to a bonding process of an anti-alpha aerosol gas suit. This process first cleans the surface of the seams of the air clothing, selects the appropriate adhesive according to the material, and glues the seams. After the adhesive reaches the highest strength, selects a high-strength thread in the middle of the overlapping seams. Sewing, and then choose a 2 cm wide, long strip of the same material, press and glue the sewing line at the seam, and the adhesive can be used when it reaches the highest strength. The present invention adopts the method of sticking first, then sewing, and then sticking, which improves the mechanical strength of the seams of the anti-α aerosol gas clothing, strengthens the sealing performance of the gas clothing, and enables the anti-α aerosol gas clothing to better adapt to the nuclear environment. Complex work sites such as factory decommissioning, nuclear accident emergency response, and weapon equipment accident handling.
Owner:CHINA INST FOR RADIATION PROTECTION
Nuclear reactor (variants), fuel assembly consisting of driver-breeding modules for nuclear reactor (variants) and fuel cell for fuel assembly
The invention relates to a structural design for light-water-moderated nuclear reactors using a thorium fuel, in particular to the structural design for caseless fuel assemblies constituting the cores of water moderated power-producing reactors, such as a WWER-1000 reactor. A thorium fuel in a breeding module together with a conventional reactor fuel containing unshaped enriched uranium or power producing plutonium in a driver module are burned in the core of a nuclear reactor which comprises a fuel assembly consisting of a driver and breeding modules. The driver module comprises a bundle of three leaf-shaped fuel cells forming screw spacer ribs. The driver and breeding modules can be coupled to each other by means of a spigot joint or be free of a rigid mechanical coupling. The inventive structural design of the fuel assembly provides the total compatibility thereof with existing fuel assemblies used in the WWER-1000 reactors. The fact that the two-section fuel assembly can be disassembled makes it possible to individually reload the driver module.
Owner:THORIUM POWER
Guided missile system being prevented from being identified by satellite radar before launching
InactiveCN107192297ASmall shipping targetLow costCamouflage devicesProtective buildings/sheltersRadarNuclear power
A missile system to avoid being recognized by satellite radar before launch, relates to a missile system; in wartime, the components of liquid or colloidal propellant missiles are transported from overpasses in a smaller size in a carrier vehicle in the shape of a civilian car The elevators are transformed into assembled missile equipment, and the elevator shafts are transformed into launching silos; satellite radar cannot distinguish carrier vehicles from civilian vehicles, nor can it Distinguishing the high-rise civilian buildings converted into silos increases the human and public opinion pressure when the enemy country preemptively uses precision, non-nuclear weapons to destroy the missile system before launch, reduces the possibility of the missile system being completely destroyed before launch, and deters the The determination of an enemy nation to pre-emptively destroy our nuclear forces.
Owner:王建刚
Multifunctional interceptor missile
The invention provides a multifunctional interceptor missile which can deal with the enemy military attacks and belongs to the technical field of guided missile, plane, tank, nuclear weapon and photo-electricity weapon. A double rotating inner and outer magnetic suspension is provided, so the multifunctional interceptor missile can fight according to instructions. The technical scheme of the invention is that a duality function is designed in a missile centre pipeline. In atmosphere, Tokamak device technique is adopted and a central swing ring is arranged in the missile centre pipeline. The high temperature of thousands DEG C copes with the atmosphere by the air flowing from an exterior regulating rotating ring and then the air is directionally jetted. In outer space, the function of simulating solar core of the missile centre pipeline is performed and the computer energy level is regulated so as to acquire universal natural high speed effect. The multifunctional interceptor missile is mainly used for thoroughly wipe out the enemy weapon and fighters, can realize all-dimensionally fighting by using air thermo-magnetic technique and gives no chance to enemy to strike back.
Owner:李兵
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com