Core spun yarn taking collagenous fibers as main material and as leather layer and processing method of core spun yarn
A collagen fiber and processing method technology, applied in the field of yarn, can solve the problems of insufficient tensile strength, failure to process, and inability to give full play to the excellent properties of collagen fibers, and achieve the effect of high quality and performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
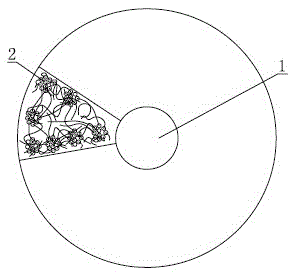
[0037] Such as figure 2 As shown, the core-spun yarn with collagen fibers as the main skin layer includes a core yarn 1 which is covered with a skin layer, and the skin layer contains only collagen fiber bundles 2.
[0038] The core yarn 1 is a single or multiple synthetic fiber or chemical fiber filament or spun spun yarn.
[0039] The collagen fiber bundle 2 and its branches and the adjacent collagen fiber bundle and its branches form a three-dimensional network structure that is intertwined and twisted into an axial arrangement.
[0040] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the collagen fiber bundle 2 is a structure in which a band 21 is formed after being combed, and the band has gradual branches 22.
[0041] The processing method of core-spun yarn with collagen fiber as the main skin layer is:
[0042] (1) Extract collagen fibers.
[0043] (2) Split and comb the collagen fibers to split the collagen fibers and produce branches to form collagen fiber bundles arranged in a straight axis.
[00...
Embodiment 2
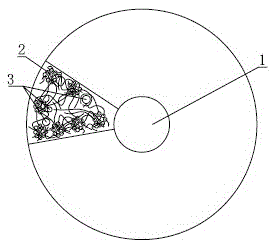
[0052] Such as image 3 As shown, the core-spun yarn with collagen fibers as the main skin layer includes a core yarn 1, which is covered with a skin layer, and the skin layer contains 60% collagen fiber bundles 2 and 40% other textile fibers 3.
[0053] The core yarn 1 is a single or multiple synthetic fiber or chemical fiber filament or spun spun yarn.
[0054] Other textile fibers are at least one of natural fibers, chemical staple fibers, and synthetic staple fibers.
[0055] The collagen fiber bundle 2 and its branches and the adjacent collagen fiber bundle and its branches form a three-dimensional network structure that is intertwined and twisted into an axial arrangement. At the same time, the collagen fiber bundles and their branches and other adjacent textile fibers form a three-dimensional network structure that is interlaced and twisted into an axial arrangement.
[0056] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the collagen fiber bundle 2 is a structure in which a band 21 is formed aft...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Such as image 3 As shown, the core-spun yarn with collagen fibers as the main skin layer includes the core yarn 1, the core yarn 1 is covered with a skin layer, and the skin layer contains 20% collagen fiber bundles 2 and 80% other textile fibers 3.
[0069] The core yarn 1 is a single or multiple synthetic fiber or chemical fiber filament or spun spun yarn.
[0070] Other textile fibers are at least one of natural fibers, chemical staple fibers, and synthetic staple fibers.
[0071] The collagen fiber bundle 2 and its branches and the adjacent collagen fiber bundle and its branches form a three-dimensional network structure that is intertwined and twisted into an axial arrangement. At the same time, the collagen fiber bundles and their branches and other adjacent textile fibers form a three-dimensional network structure that is interlaced and twisted into an axial arrangement.
[0072] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the collagen fiber bundle 2 is a structure in which a band 21 i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com