Smart grid sensing device
A technology of sensing device and smart grid, applied in the direction of measuring device, measuring electricity, fault location, etc., can solve the problems of low efficiency of troubleshooting and positioning, single method of line selection device, insulation breakdown, etc., to solve single-phase grounding faults Effects of line selection and positioning problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0040] The present invention will be described in more detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and preferred embodiments.
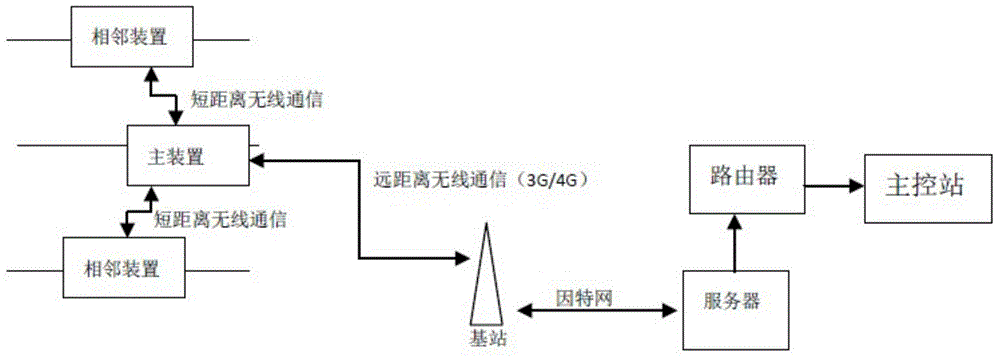
[0041] like figure 1 Shown is a schematic diagram of this embodiment applied to a distribution network. The device of this embodiment is installed on each busbar and branch line of the distribution network of 35KV and below, and 3 devices (phase A, phase B and phase C corresponding to the power line) will be installed at each place, and the global positioning system ( GPS) to realize the precise synchronization of the internal sampling data of each point device, and then collect them on a main device through a short-distance wireless communicator, and then the main device finally forwards it to the Background master control station. The background master control station adopts various fault judgment algorithms and manual decision-making systems to realize the comprehensive line selection and location of faults.
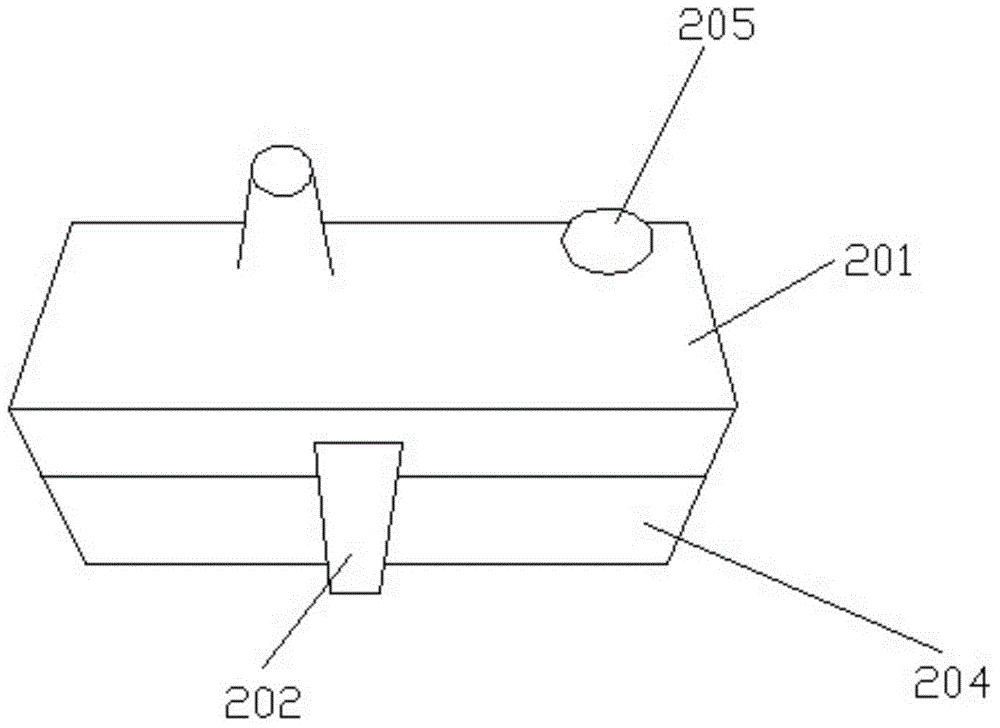
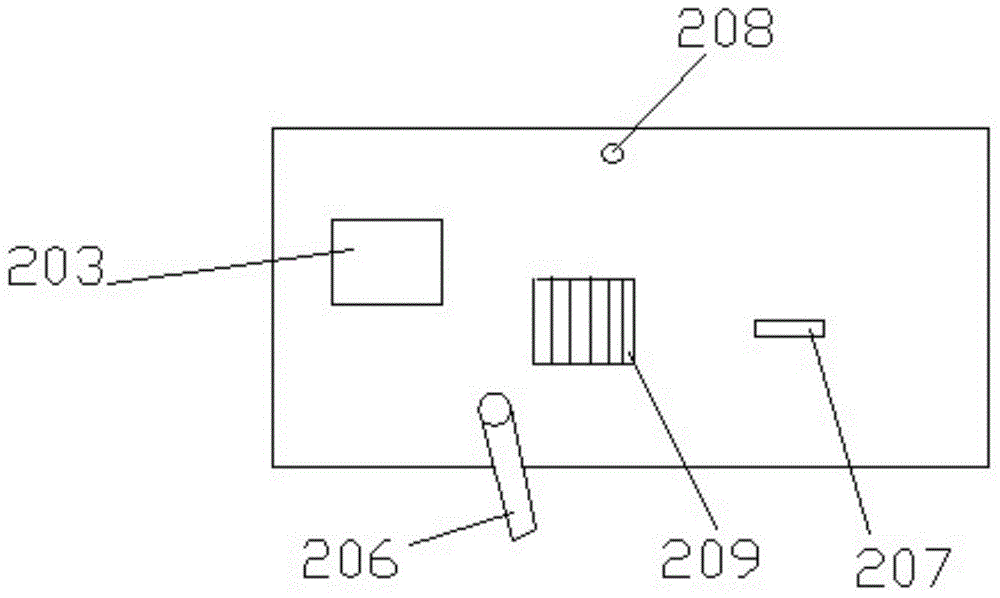
[0042] figure 2 an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com