Primers for cloning SPFMV (sweet potato feathery mottle virus) O strain and full length genome sequence of SPVC (sweet potato virus C) and cloning method
A feathery mottled virus and genome sequence technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems that it is difficult to obtain the full-length genome sequence of the virus, the full-length genome sequence of the isolate has not been seen, and the content is low
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
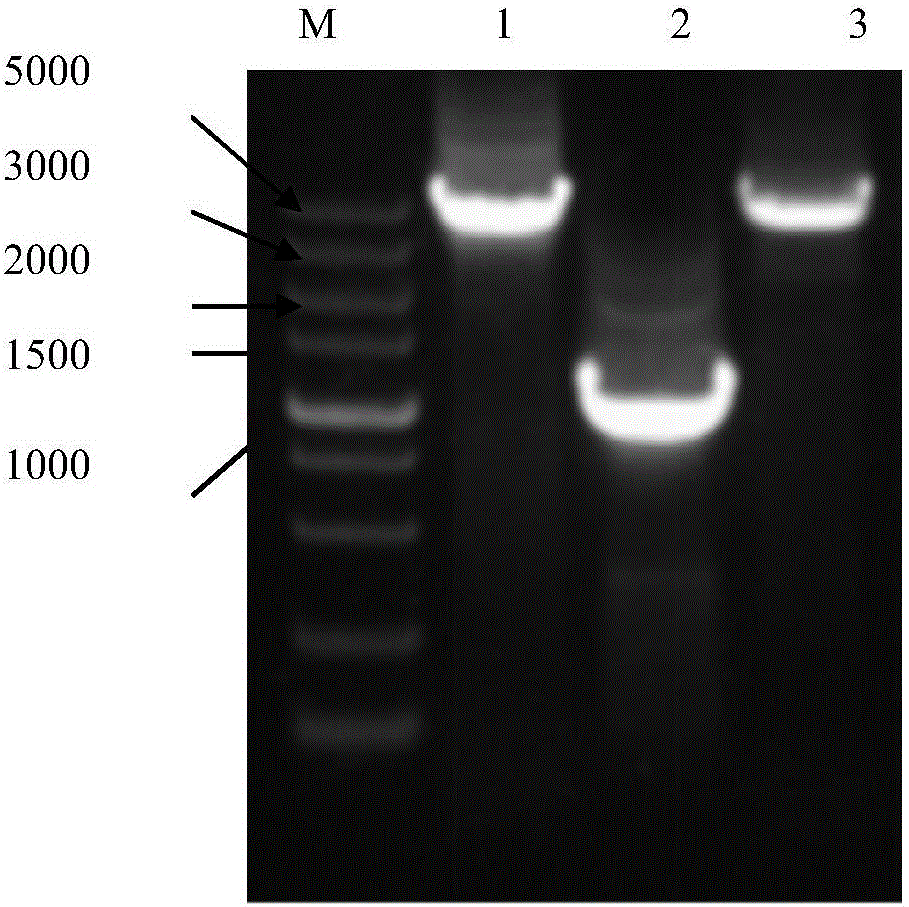
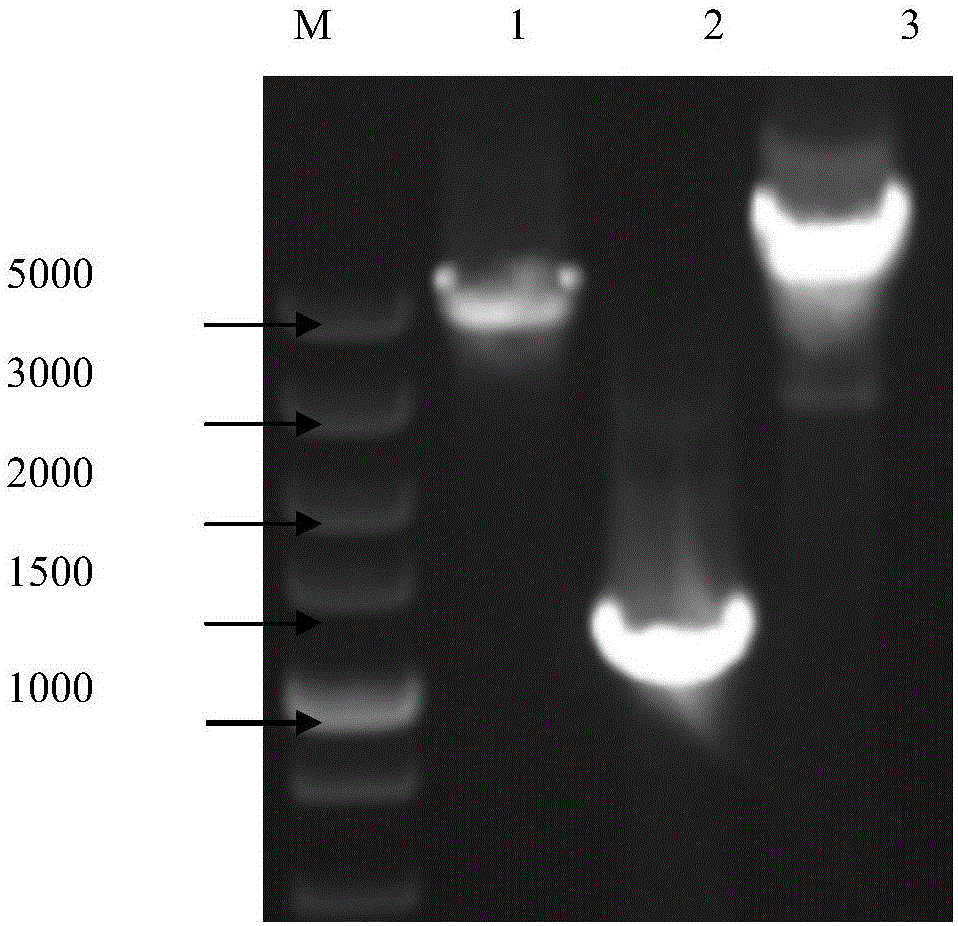
[0065] Embodiment 1 A kind of method of cloning SPFMV-O strain full-length genome sequence
[0066] 1. Materials and methods
[0067] (1) Tested virus material: the leaves of sweet potato plants infected with SPFMV, SPVC and SPCSV were used as materials. The symptoms were as follows: the plants were short, the leaves were shrunken, yellowed, and the veins were distorted. The total RNA was extracted for subsequent experiments.
[0068] (2) Reagents and kits: UNIQ-10 Column Total RNA Extraction Kit was produced by Shanghai Sangon Bioengineering Company; DNA Gel Recovery Kit was purchased from Axygen Biotechnology (Hangzhou) Co., Ltd.; RNase inhibitor, AMV Reverse transcriptase, LATaq DNA polymerase, and pMD19-T vector were purchased from TaKaRa Company, and other commonly used reagents were of domestic analytical grade.
[0069] (3) Primer design: According to the nucleotide sequence of the full-length genome of SPFMV-O registered in GenBank (accession numbers are AB509454, AB4...
Embodiment 2
[0088] Embodiment 2 A kind of method for cloning sweet potato virus C full-length genome sequence
[0089] 1. Materials and methods
[0090] (1) Tested virus material: the leaves of sweet potato plants infected with SPFMV, SPVC and SPCSV were used as materials. The symptoms were as follows: the plants were short, the leaves were shrunken, yellowed, and the veins were distorted. The total RNA was extracted for subsequent experiments.
[0091] (2) Reagents and kits: UNIQ-10 Column Total RNA Extraction Kit was produced by Shanghai Sangon Bioengineering Company; DNA Gel Recovery Kit was purchased from Axygen Biotechnology (Hangzhou) Co., Ltd.; RNase inhibitor, AMV Reverse transcriptase, LATaq DNA polymerase, and pMD19-T vector were purchased from TaKaRa Company, and other commonly used reagents were of domestic analytical grade.
[0092] (3) Primer design: According to the nucleotide sequence of the full-length genome of SPVC registered in GenBank (accession numbers are JX489166,...
Embodiment 3
[0107] Example 3 A method for simultaneous cloning of sweet potato feather mottle virus O strain and sweet potato virus C full-length genome sequence
[0108] 1. Materials and methods
[0109] (1) Tested virus material: the leaves of sweet potato plants infected with SPFMV, SPVC and SPCSV were used as materials. The symptoms were as follows: the plants were short, the leaves were shrunken, yellowed, and the veins were distorted. The total RNA was extracted for subsequent experiments.
[0110] (2) Reagents and kits: UNIQ-10 Column Total RNA Extraction Kit was produced by Shanghai Sangon Bioengineering Company; DNA Gel Recovery Kit was purchased from Axygen Biotechnology (Hangzhou) Co., Ltd.; RNase inhibitor, AMV Reverse transcriptase, LATaq DNA polymerase, and pMD19-T vector were purchased from TaKaRa Company, and other commonly used reagents were of domestic analytical grade.
[0111] (3) Primer design: according to the nucleotide sequences of the full-length genomes of SPFMV...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com