A production method of anhydrous iron phosphate and its special molding tool
A production method and technology of ferric phosphate dihydrate, applied in chemical instruments and methods, phosphorus compounds, inorganic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of heat transfer attenuation, slow heat transfer, large specific surface area of powder, etc. The effect of improving production efficiency and small specific surface area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
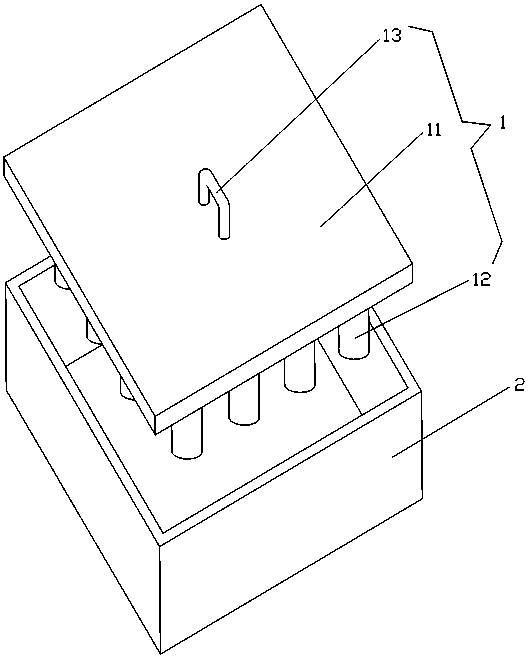
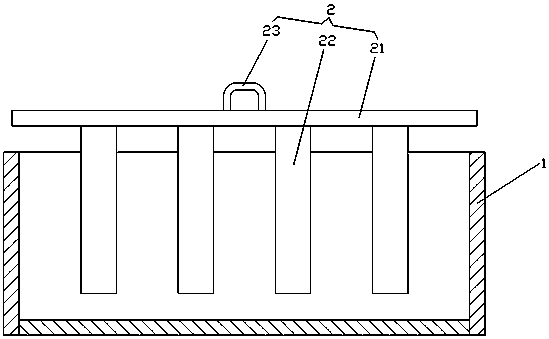
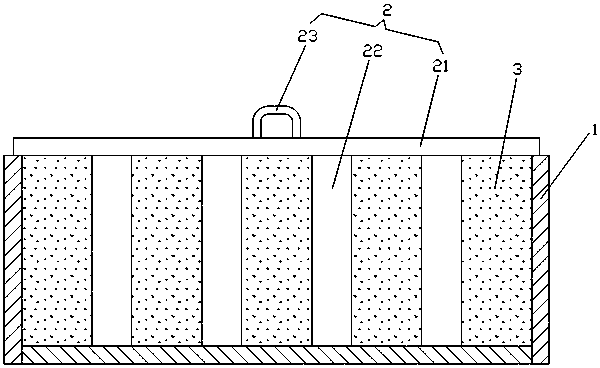
[0024] Using the sagger in the prior art, put the iron phosphate dihydrate powder into the sagger, and use a molding tool to evenly arrange 9 elliptical heat conduction vent holes in the powder. The vent holes extend from the opening end of the gate body to the gate. The bottom of the body extends until the bottom of the gate body; then roasting and dehydration are carried out at a temperature of 580°C. After the powder is roasted and dehydrated, the specific surface area is 7.3-10m 2 / g of anhydrous iron phosphate with a small specific surface area.
Embodiment 2
[0026] Using the sagger in the prior art, the iron phosphate dihydrate powder is put into the sagger, and 16 circular heat-conducting air holes are evenly arranged in the powder by using a molding tool. The air holes extend from the opening end of the gate body to The bottom of the lock body extends until the bottom of the lock body; then roasting and dehydration are carried out at a temperature of 600°C. After the powder is roasted and dehydrated, the specific surface area is 4-7.3m 2 / g of anhydrous iron phosphate with a small specific surface area.
Embodiment 3
[0028] Using a larger sagger than the prior art, put iron phosphate dihydrate powder into the sagger, and use modeling tools to evenly arrange 25 prismatic heat-conducting vent holes in the powder. The open end extends to the bottom of the gate body until the bottom of the gate body; then roasting and dehydration are carried out at a temperature of 630°C. After the powder is roasted and dehydrated, the specific surface area is 5-7.5m 2 / g of anhydrous iron phosphate with a small specific surface area.
[0029] The following is an orthogonal experiment with 9 circular heat conduction vents as an example, using three methods of no heat conduction ventilation, mesh ventilation and heat conduction hole ventilation, and conducting orthogonal experiments under different temperature conditions. The specific experimental data statistics are as follows: Among them, Table 1 shows four groups of experimental schemes, and Table 2 shows the statistical results of orthogonal experimental d...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com