Synthetic promoters for CHO cells, and methods of producing synthetic promoters using transcription factor binding site modules
A technology of transcription factor regulation and promoter, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, animal cells, vertebrate cells, etc., can solve problems such as limited and discontinuous expression levels
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0328] Example 1: Identification of active transcription factor regulatory elements in CHO-S cells
[0329] In silico analysis of transcription factor regulatory elements
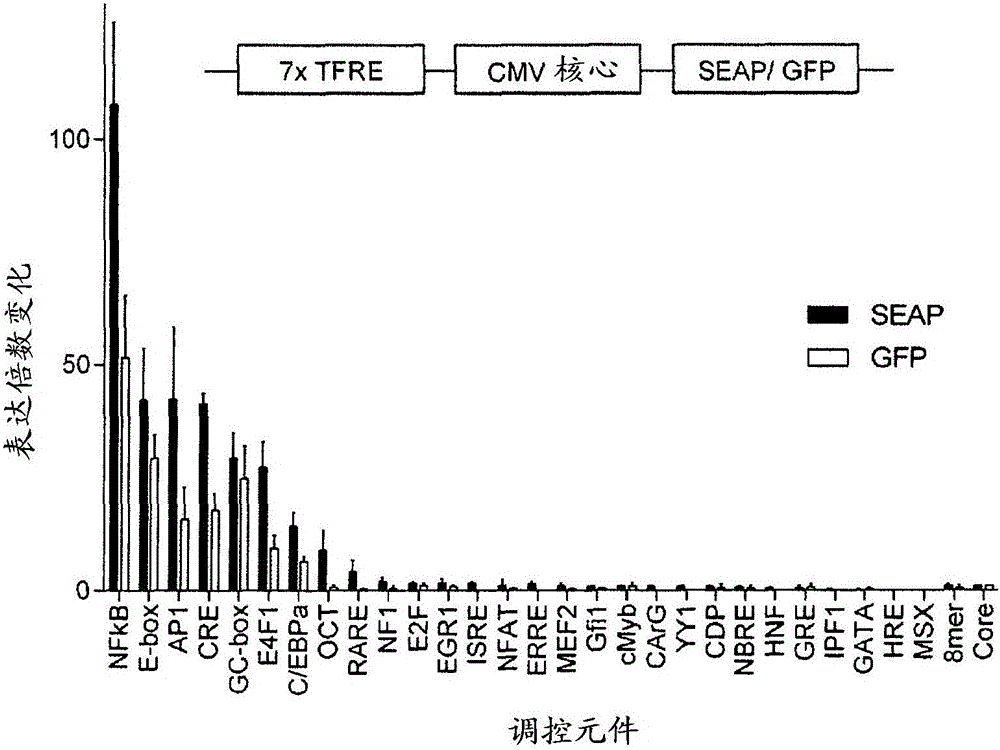
[0330] To identify discrete TFREs (transcription factor binding sites) capable of transactivating recombinant genes in CHO-S cells, the inventors surveyed putative TFREs in 10 viral promoters generally known to be active in CHO cells .
[0331] The following promoter sequences were retrieved from the GenBank database: hCMV-IE1 (accession number M60321.1), mouse CMV-IE1 (M11788), rat CMV-IE1 (U62396), guinea pig CMV-IE1 (CS419275), small Murine CMV-IE2 (L06816.1), Simian virus 40 early promoter and enhancer (NC_001669.1), Adenovirus major late promoter (KF268310), Myeloproliferative sarcoma virus long terminal repeat (LTR) (K01683.1) , Rous sarcoma virus LTR (J02025.1) and human immunodeficiency virus LTR (K03455.1).
[0332] Using the Transcriptional Element Search System (TESS: http: / / www.cbil.upenn...
Embodiment 2
[0348] Example 2: Construction and analysis of the 1st generation promoter
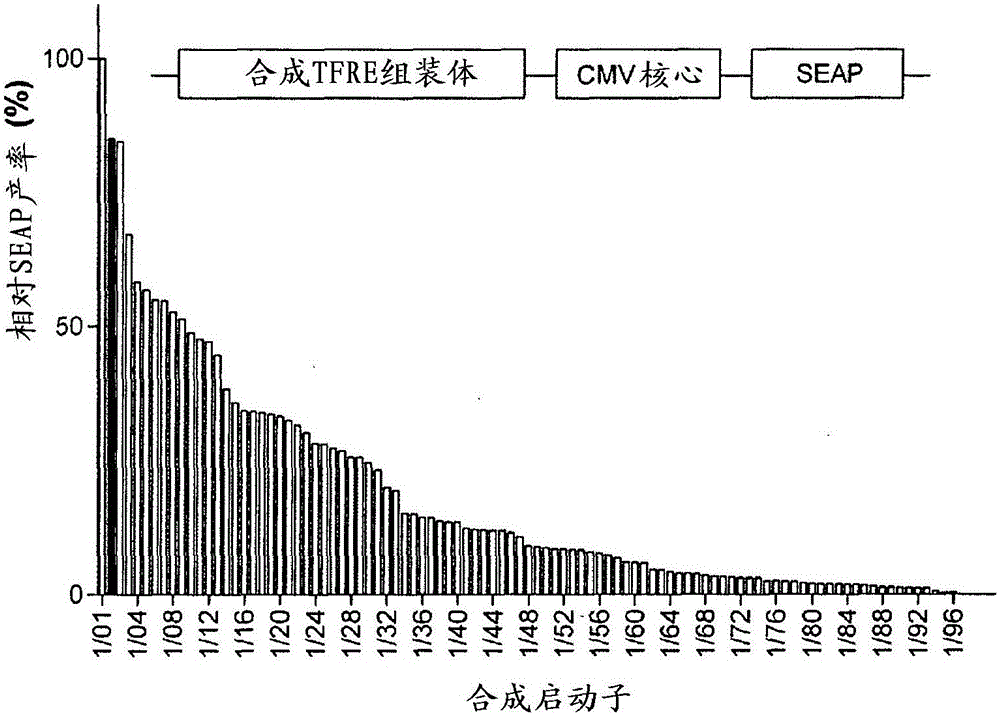
[0349] Synthetic promoter library construction
[0350] Synthetic promoter TFRE was constructed from complementary single-stranded 5' phosphorylated oligonucleotides (Sigma, Poole, UK) by heating at 95 °C for 5 minutes, followed by slow cooling to 25 °C over 2 hours, in STE buffer (100 mM NaCl , 50mM Tris-HCl, 1mM EDTA, pH7.8, Sigma) annealed. Oligonucleotides were designed such that the resulting double-stranded blocks contained specific TFREs (Table 1), and 4 bp TCGA single-stranded overhangs at each 5' end. For example, the sequence for the NFkB-RE block is as follows (RE site underlined): 5'-TCGAT GGGACTTTCC A - 3' SEQ ID NO: 171 and 5'-TCGAT GGAAAGTCCC A-3' SEQ ID NO: 172.
[0351] For construction of the first generation synthetic promoter library, all seven TFREs identified as transcriptionally active in CHO-S cells were used. Oligonucleotide building blocks containing a single copy ...
Embodiment 3
[0367] Example 3: Construction and analysis of the second generation synthetic promoter
[0368] Based on the above analysis of the 1st generation synthetic promoters, the present inventors sought to further improve Synthetic promoter activity.
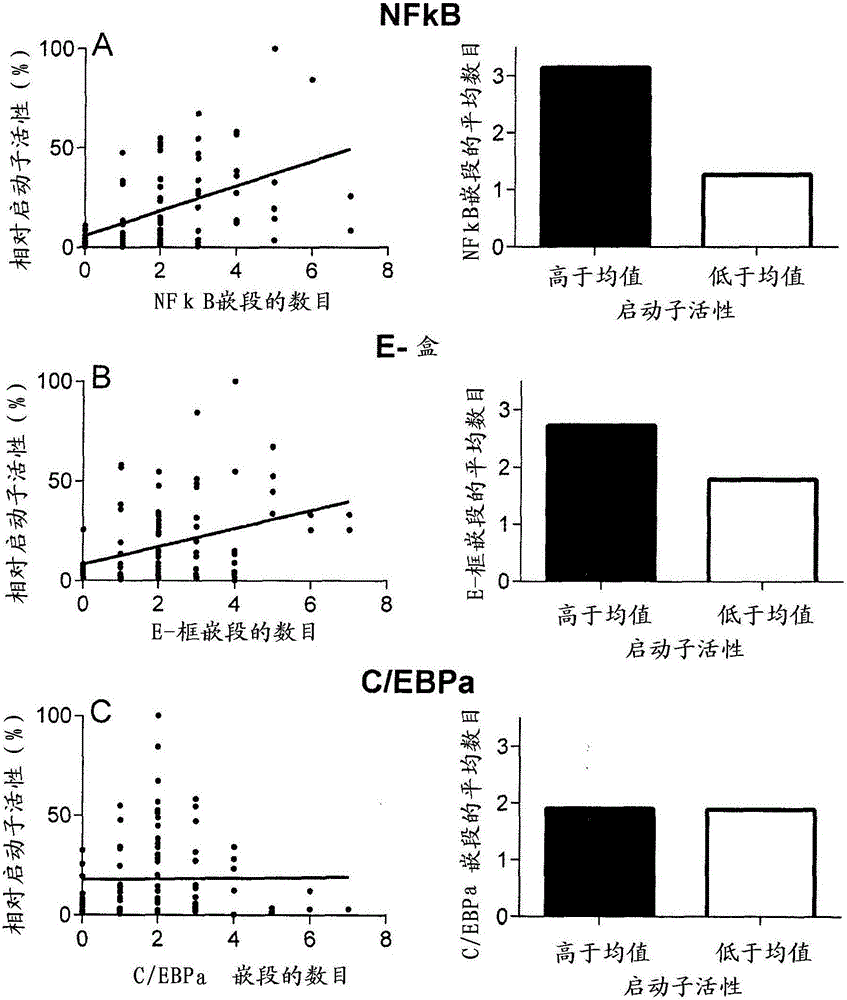
[0369] Using the initial seven identified TFREs (see figure 1 ) were used to construct a library of 2nd generation synthetic promoters with a stoichiometry derived quantitatively from their relative representation among the active synthetic promoters in the 1st generation synthetic promoter constructs. The stoichiometric ratio used was 5:3:1:1 (NFkB-RE:E-box:C / EBPa-RE:GC-box).
[0370] Specifically, of the original seven TFREs, negative TFREs, E4F1 and CRE (see Figure 3) had been omitted (i.e. promoters containing greater numbers of these TFREs were associated with lower expression levels of reporter genes), Whereas the neutral TFRE, C / EBPa and GC-boxes were included on the assumption that increased complexity might be advantageo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com