Isolated nucleic acids encoding popdc1 mutants and uses thereof
A mutant and nucleic acid technology, which is applied in the field of biotechnology and can solve problems such as difficulty in statistics on the incidence of LGMD
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
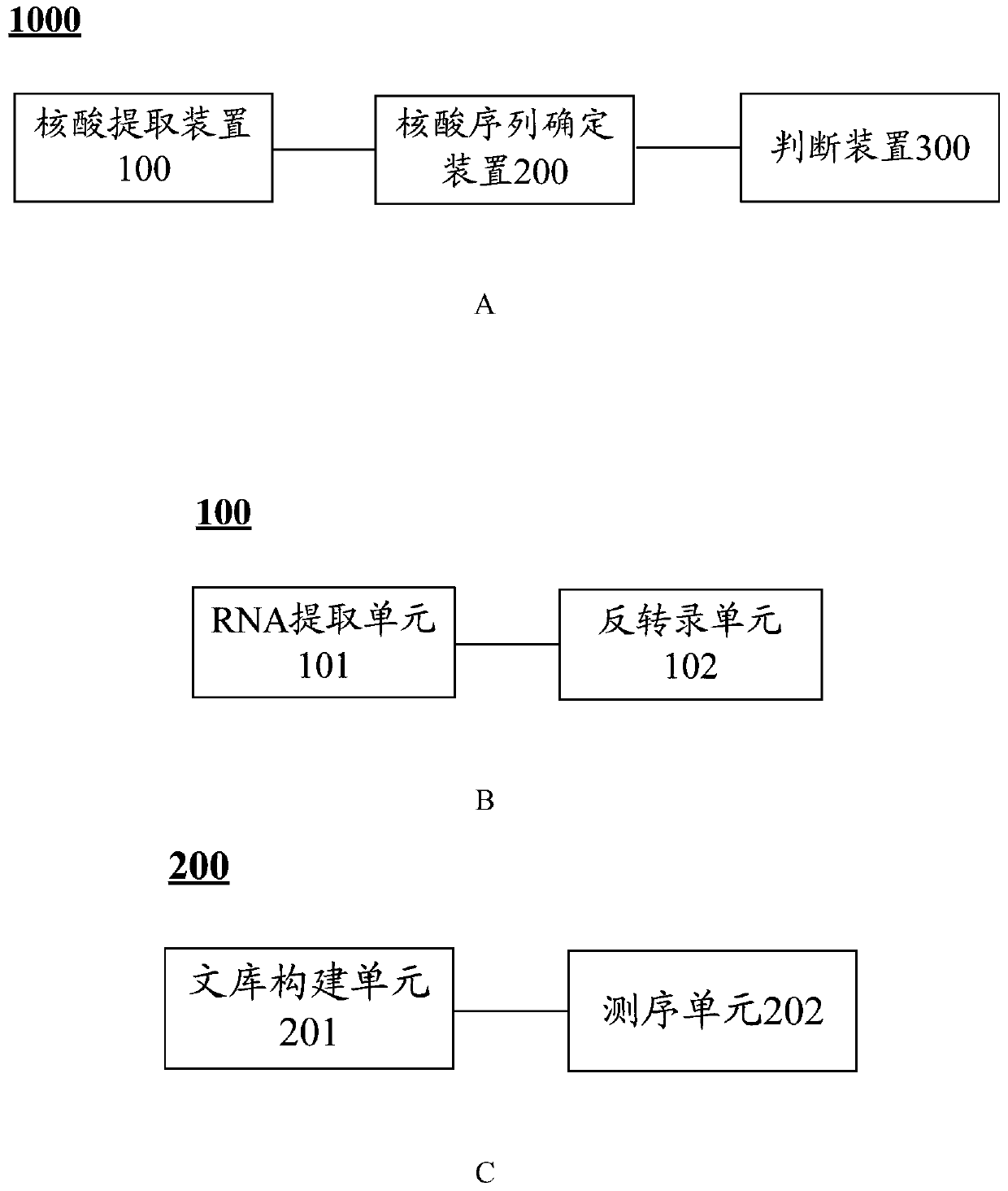
[0095] Methods for identifying mutated genes for limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, as follows:
[0096] 1. Sample collection
[0097] In this example, samples from 4 families in different regions were collected, and there were patients with limb-girdle muscular dystrophy in each family. Among them, the patient information in the family is as follows:
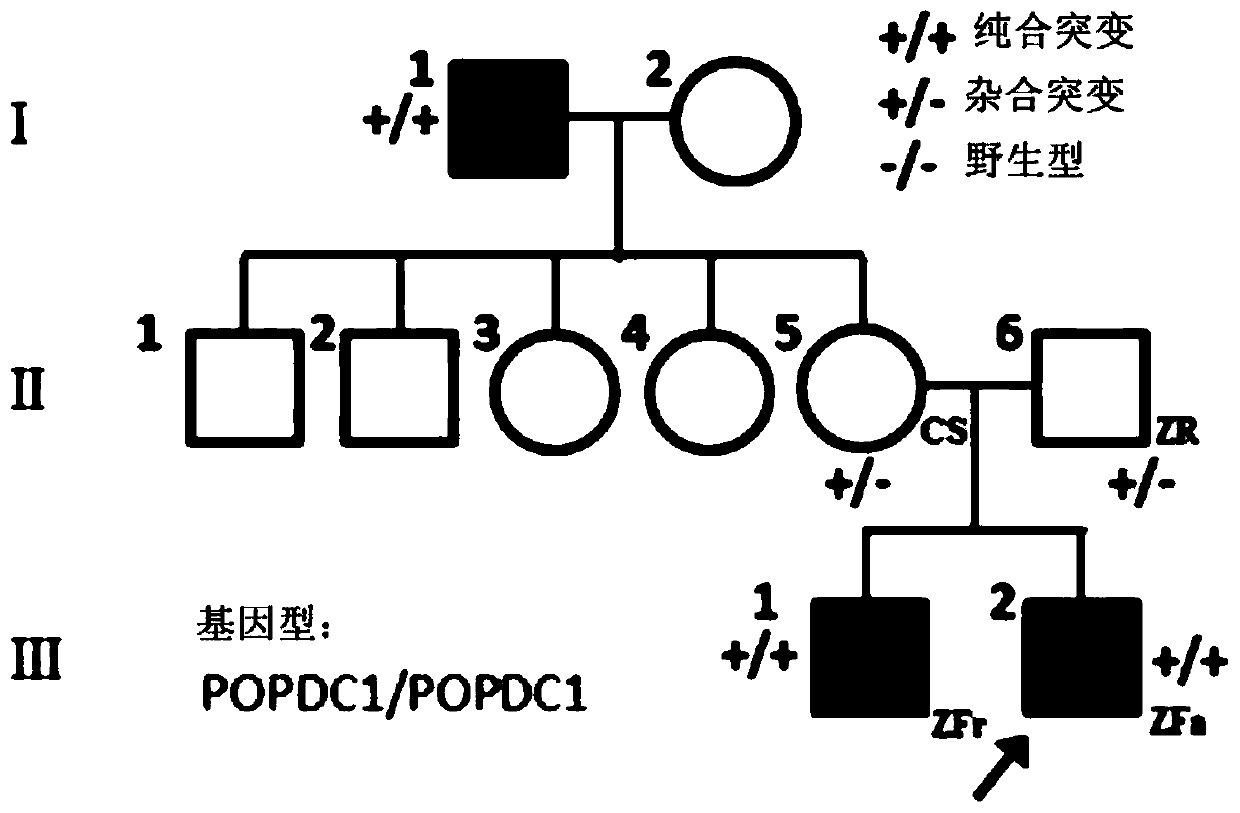
[0098] No. 1 family, the family picture is as follows Figure 2A As shown, the family is a family from the Calabria region in southern Italy, which shows pseudo-dominant inheritance, and the family originated from a small town in the Albanian enclave with a population of about 3000. The grandfather was a patient, and he had 2 brothers and 7 sisters with normal phenotypes; one of the sisters had two grandchildren with similar symptoms, and both parents believed that they were not consanguineous. Among them, the specific conditions of the patients are as follows
[0099] Patient Ⅰ1, whose grandfather suffered from limb-girdle mu...
Embodiment 2
[0123] Due to a certain degree of false positives in exome sequencing, this example uses the Sanger sequencing method to verify the mutation sites of the POPDC1 gene found in the 4 families in Example 1. The specific method is as follows:
[0124] Using the 4 families in Example 1, the Sanger method was used to verify the pathogenic mutation sites of limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, including designing primers for the No. 3 and No. 4 exons of the POPDC1 gene and the sequences around them, and amplifying The relevant sequence of the POPDC1 gene was obtained by means of amplification, product purification and sequencing, and the correlation between POPDC1 and the patient's clinical phenotype was verified according to whether the sequence determination result was mutant or wild type. Specific steps are as follows:
[0125] 1. DNA extraction
[0126] Peripheral venous blood was collected from two brothers of patients in family No. 1, their parents and grandfather, patient II 2 fro...
Embodiment 3
[0141] Carry out gene interaction analysis on the mutation gene detection results of No. 2, No. 3 and No. 4 families detected in Example 1. The specific analysis content is as follows:
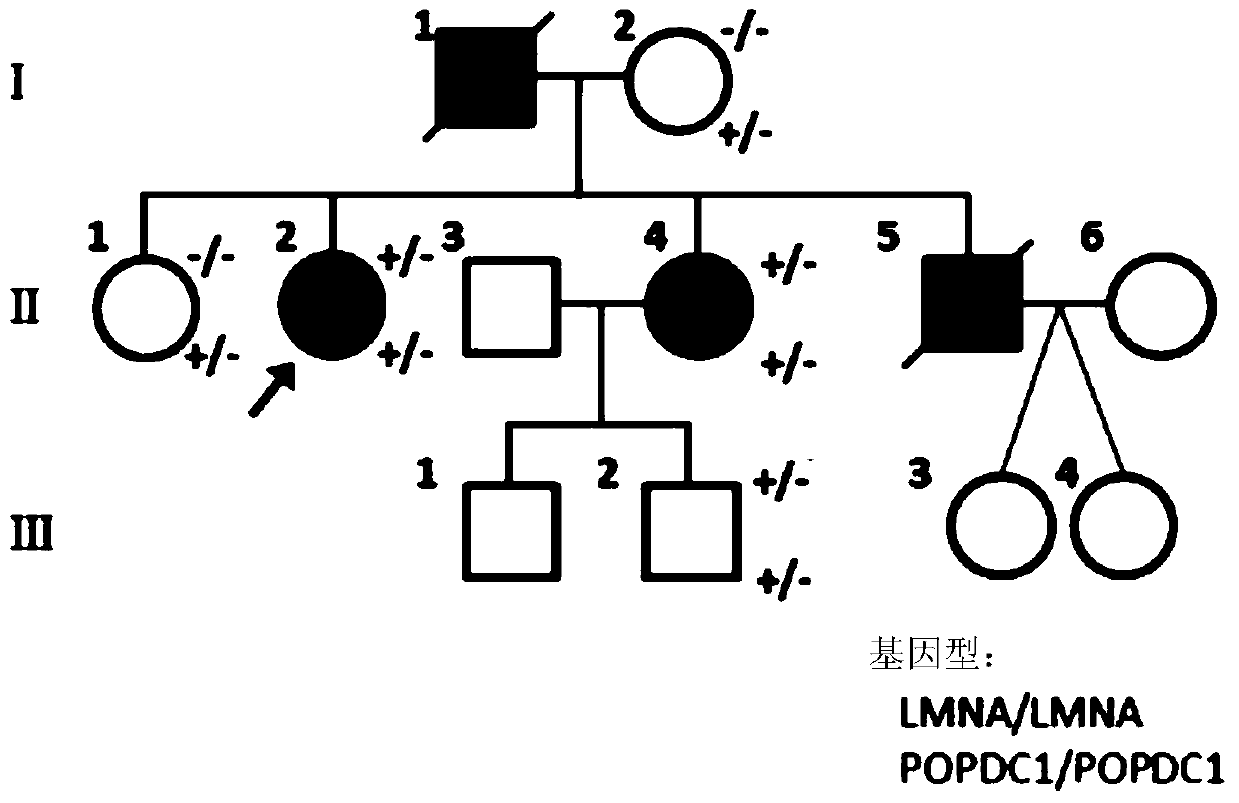
[0142] In the analysis of the No. 2 family, the inventor detected the missense mutation of the LMNA gene (c.1070A>C, p.D357A) in the form of heterozygosity in patient Ⅱ2 and its diseased patients by using clinical exome analysis. sister and a healthy son, while LMNA mutations and another subtype were found to be associated with DCM (dilated cardiomyopathy) in similar cases.
[0143] In family No. 3, the inventors used clinical exome analysis to detect 4 heterozygous missense mutations in the following four genes: SDHA (R465Q), DSP (I1216V), and TTN (G33394D and S35939T), a total of Segregation analysis showed that these mutations were inherited from mother I2. In family No. 4 from Italy, the SDHA mutation was predicted to be a deleterious mutation according to the Polyphen software, and the fr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com