Cyclic vinylogous amides as bromodomain inhibitors
A sustained release and formulation technology, applied in the direction of peptide/protein components, medical preparations with non-active ingredients, medical preparations containing active ingredients, etc., can solve the problems of unsuccessful deployment of therapeutic proteins, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0185] Example 1. Preparation of a reservoir formulation of a therapeutic protein. The weight / volume and ratios of polymer, solvent, aqueous phase, buffer, excipients, and co-solvents are as follows: 1.0 g of polymer was dissolved in 5.0 mL of dichloro in methane. Next, 0.5 mL of 20 mM phosphate-buffered saline (PBS; pH 6.0) containing 100 mg / mL ShK-186 (or ShK-192) was added. The primary emulsion was homogenized for 2 minutes at 20,000 rpm using a 10 x 195 mm probe. The primary emulsion was then added to an aqueous solution of 20 mM phosphate buffer (pH 6.0), 0.5% dioctyl sulfosuccinate (DDS) and 0.05% PVA; Qualify for 2 minutes. A stir bar was added to the secondary emulsion and the suspension was stirred overnight in a fume hood to evaporate volatile solvents. The next day, filter the suspension through a 325 mesh sieve. The filtered material was centrifuged (20,000 g, 5 minutes) and the supernatant layer was drawn off, and passed through an assay involving high perform...
example 2
[0187] Example 2. Measuring encapsulation, mass balance, and in vitro release of a therapeutic protein from a sustained release depot formulation. Typically immediately following a depot formulation, by following a separation method such as centrifugation and using the equation ( 1) Analyze the free protein content of the supernatant layer to measure the encapsulation percentage:
[0188] Encapsulation %=(total ShK-serum layer ShK) / total ShK
[0189] Typical packaging efficiencies are in the range of 60 to 90%.
[0190]Pressurize the system to release the ShK protein almost completely by heating above the glass transition temperature of the polymer, adding a surfactant substance (such as concentrated SDDS), mechanical agitation, sonication, alkaline or acid hydrolysis, or a combination of these accelerated release methods combination to achieve mass balance. A typical in vitro release profile can be obtained by sampling the serum layer at multiple times and under different c...
example 3
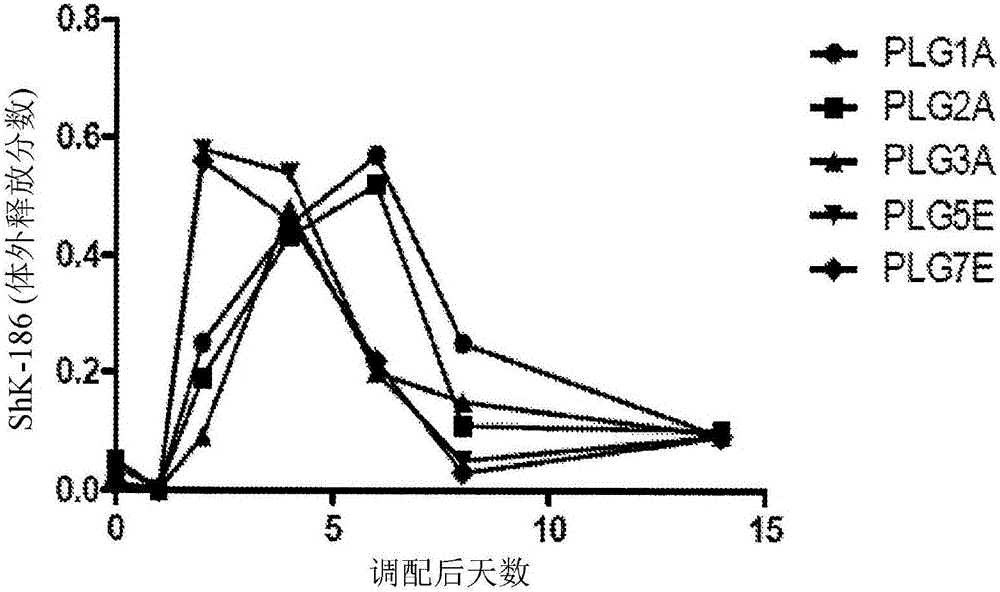
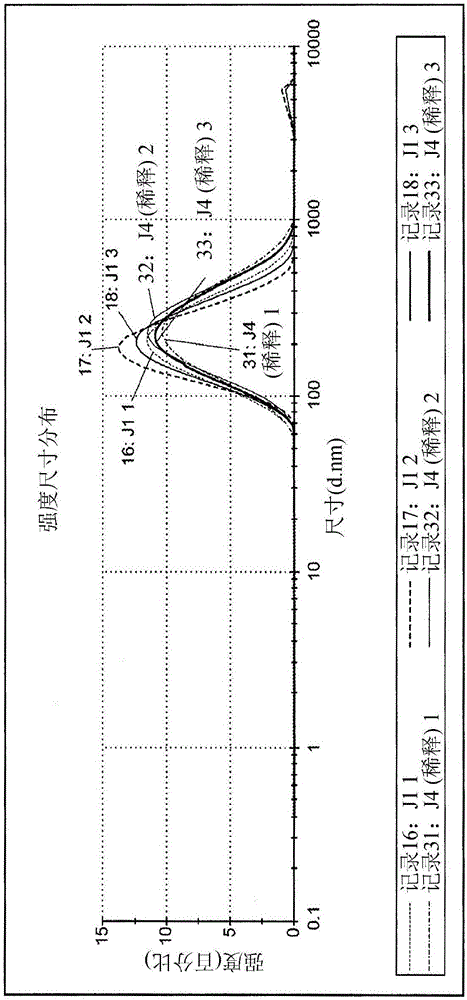
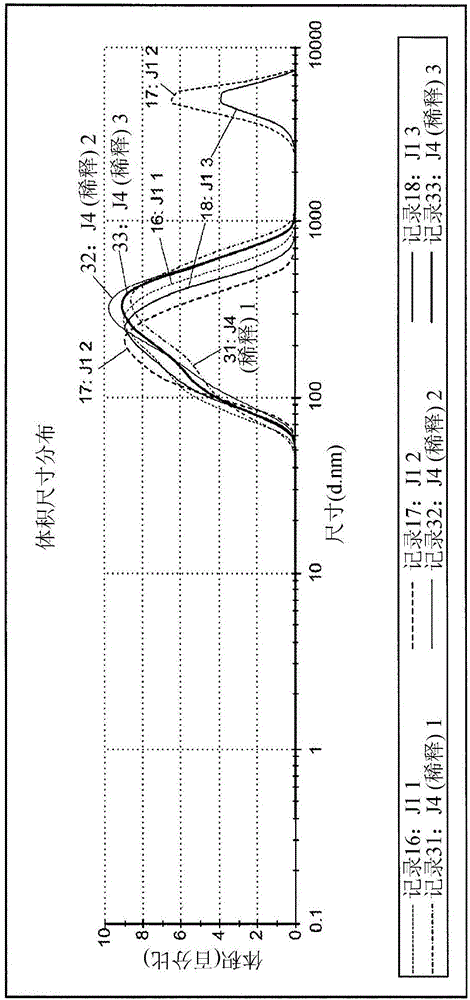
[0194] Example 3. Characterization of Physical Properties of Depot Formulations. Standard analytical characterization methods were employed to analyze the physical and chemical properties of depot formulations of ShK-186 disclosed herein and formed according to the method of Example 1 using PLG2A polymer. . Size and electrophoretic mobility were measured by light scattering using a Malvern nanosizer. Morphology / homogeneity was measured by light microscopy. The results are shown in Figures 2-4.
[0195] Figure 2A and 2B Dispersion sizes are shown for three independent batches of tank formulations as measured by dynamic light scattering. Figure 2A and 2B Shown by the intensity of the formulation suspension as measured by dynamic light scattering ( Figure 2A ) and by volume ( Figure 2B ) plotted the size distribution of the reservoir formulation.
[0196] image 3 is a measure of the zeta potential (particle surface charge as measured by electrophoretic mobility) of ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com