Single nucleotide polymorphism marker sites, primers, kits and applications for identifying peach fruit skin coloring traits
A kit and fruit technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve problems such as low accuracy, inability to guarantee SNPs, and target gene positioning distance, etc. The effect of accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Example 1 Obtaining of SNPs marker sites
[0027] In the present invention, 129 peach germplasms randomly obtained from the peach germplasm resource garden of Zhengzhou Institute of Pomology, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences were used as samples, and the sample DNA was extracted by conventional CTAB method, and the 129 peach germplasms were reconstructed by Illumina HiSeq 2000 sequencer. Sequencing obtained 121Gb data, covering an average of 89.28% of the peach genome, and the average sequencing depth was about 4.21×. According to the 50-150bp reads obtained by sequencing, compared with the peach reference genome v.1.0 (http: / / www.rosaceae.org / node / 355), 4,063,377 SNPs were identified, and these SNPs were used to analyze 129 germplasm Genome-wide association analysis was performed on the phenotypic traits, and the SNPs significantly associated with peach peel coloring were identified at the 3473250bp of chromosome 3.
Embodiment 2
[0028] Example 2 The method for identifying peach fruit epidermis coloring (red) traits using SNP markers
[0029] 1. DNA extraction
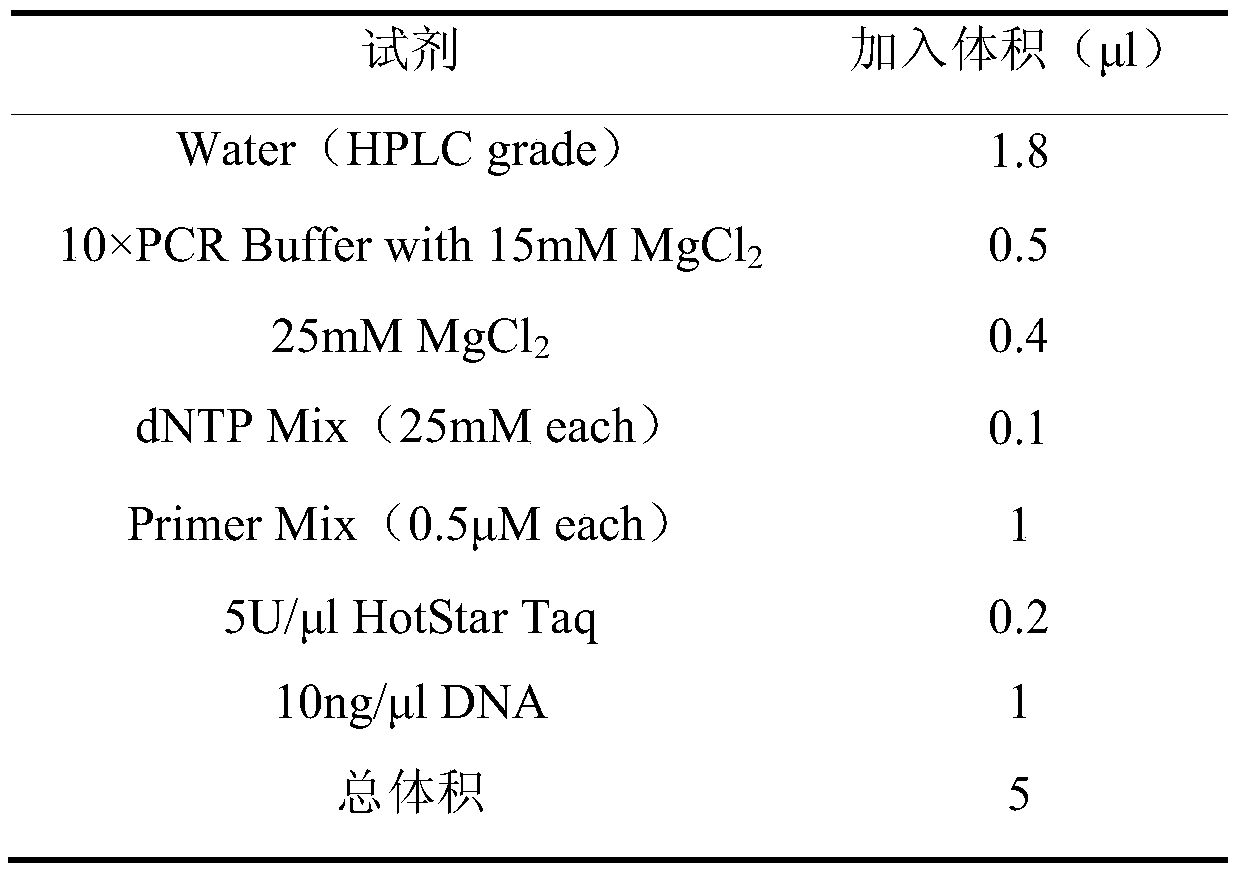
[0030] The DNA of the peach sample tissue to be tested was extracted by the conventional CTAB method, and the RNA was removed. The total volume of the DNA sample was not less than 15 μl. Measure the OD value of the DNA sample at 260nm and 280nm with a UV photometer, and calculate the DNA content and OD 260 / 280 ratio. DNA sample purity OD 260 / 280 The value should be between 1.8-2.0 and the concentration should be diluted to 10ng / μl.
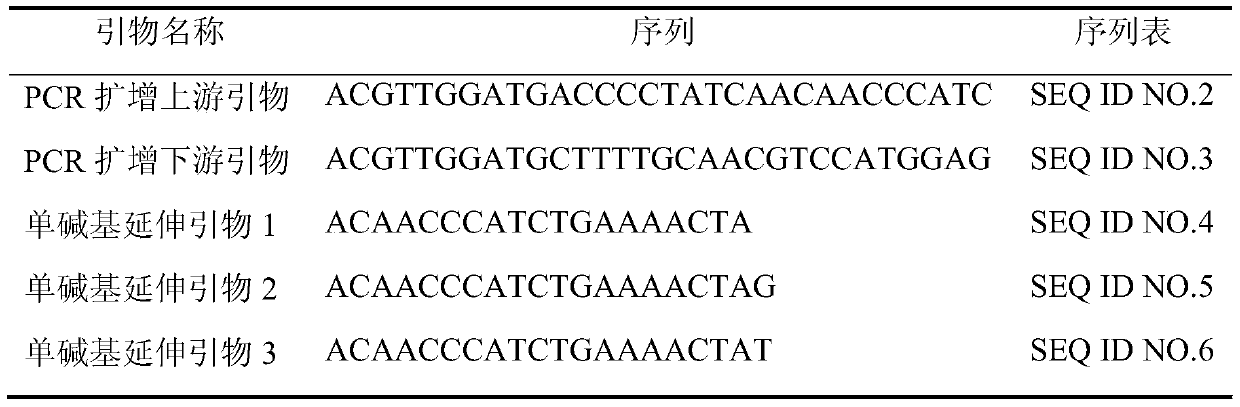
[0031] 2. Design primers
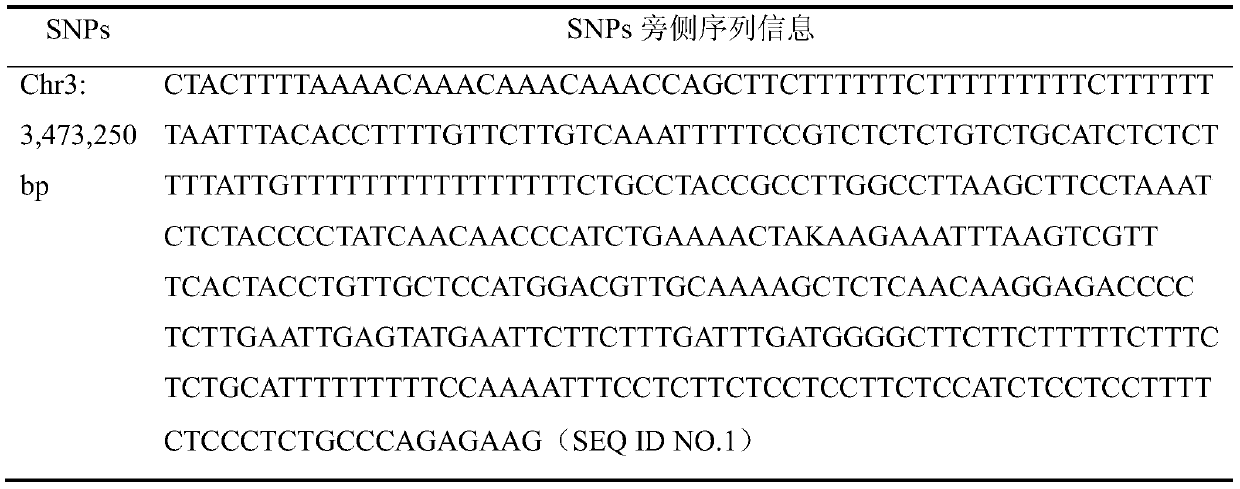
[0032] Primers were designed according to the 200 bp sequences at the left and right positions at position 3473250 of the third chromosome of the peach genome (see Table 1 for the specific nucleotide sequence).
[0033] Table 1 SNPs flanking sequence information
[0034]
[0035] Among them, K represents T or G.
[0036]After the primers were synthesized by the biotechnology com...
Embodiment 3
[0062] Example 3 Blind test verification of phenotypic traits in 15 hybrid populations using pericarp coloring-associated SNP markers
[0063] 1. Selection of experimental materials
[0064] Taking the conventional peach varieties planted in the resource garden of Zhengzhou Pomology Research Institute as experimental materials, 15 hybrid populations with investigated phenotypic traits were selected from which a total of 221 individual plants were selected. See Table 6 for details.
[0065] Table 6 The name and population size information of the tested hybrid population
[0066]
[0067]
[0068] 2. Identification method using pericarp coloring-associated SNP markers
[0069] Using the 3473250th position of the third chromosome of the peach genome of the present invention as a nucleotide polymorphism marker site, a total of 221 peach single plant peel colorings from 15 hybrid populations were blindly tested and identified. For the specific identification method, refer to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com