Preparation method of low-cost heat-resistant food grade polylactic acid material
A polylactic acid material, low-cost technology, applied in the field of polymer materials, can solve the problems of PLA application limitation, slow PLA crystallization rate, poor heat resistance of PLA, etc. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
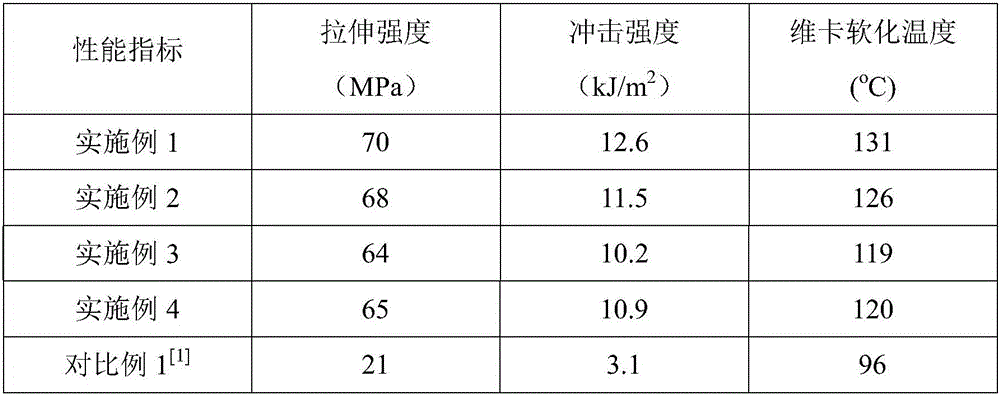
Embodiment 1
[0022] Clean the experimental equipment, weigh the experimental drugs (500g of dehydrated D-lactic acid, 3g of stannous octoate, 3g of toluene-4-sulfonic acid), and build the experimental device; 2 , to condense water, start the reaction, gradually increase the temperature to polymerize, and raise the temperature to 120°C for 2 hours, to 150°C for 2 hours, and to 170°C for 1 hour. Will N 2 The device was disassembled, the reaction flask was sealed, and the condenser section was connected to a vacuum pump, and the vacuum was pumped at a low power until no more water droplets dripped. Remove the condensing device, connect the vacuum pump directly to the flask, pump the vacuum with high power, and react for 8 hours. After the reaction, the product was poured out and cooled.
[0023] Pour the cooled sample into a 1000mL beaker, dissolve it with dichloromethane, seal it and let it stand until the sample is completely dissolved, add absolute ethanol to the beaker, white precipitat...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Clean the experimental equipment, weigh the experimental drugs (300g of dehydrated D-lactic acid, 1.8g of stannous octoate, 1.8g of toluene-4-sulfonic acid), and build the experimental device; 2 , to condense water, start the reaction, gradually increase the temperature to polymerize, and raise the temperature to 120°C for 2 hours, to 150°C for 2 hours, and to 170°C for 1 hour. Will N 2 The device was disassembled, the reaction flask was sealed, and the condenser section was connected to a vacuum pump, and the vacuum was pumped at a low power until no more water droplets dripped. Remove the condensing device, connect the vacuum pump directly to the flask, pump the vacuum with high power, and react for 12 hours. After the reaction, the product was poured out and cooled.
[0027] Pour the cooled sample into a 1000mL beaker, dissolve it with dichloromethane, seal it and let it stand until the sample is completely dissolved, add absolute ethanol to the beaker, white preci...
Embodiment 3
[0030] Clean the experimental equipment, weigh the experimental drugs (200g of dehydrated D-lactic acid, 1.2g of stannous octoate, 1.2g of toluene-4-sulfonic acid), and build the experimental device; 2 , to condense water, start the reaction, gradually increase the temperature to polymerize, and raise the temperature to 120°C for 2 hours, to 150°C for 2 hours, and to 170°C for 1 hour. Will N 2 The device was disassembled, the reaction flask was sealed, and the condenser section was connected to a vacuum pump, and the vacuum was pumped at a low power until no more water droplets dripped. Remove the condensing device, connect the vacuum pump directly to the flask, pump the vacuum with high power, and react for 16 hours. After the reaction, the product was poured out and cooled.
[0031] Pour the cooled sample into a 1000mL beaker, dissolve it with dichloromethane, seal it and let it stand until the sample is completely dissolved, add absolute ethanol to the beaker, white preci...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com