Method for quickly smelting low-nitrogen stainless steel through vacuum induction furnace
A low-nitrogen stainless steel, vacuum induction furnace technology, applied in the field of iron and steel metallurgy, can solve the problems of unstable nitrogen yield, high production cost, slow production rhythm, etc., to achieve stable and controllable reaction process, short and accurate smelting cycle The effect of smelting
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Example 1: 316L nitrogen-containing stainless steel was smelted in a 50kg vacuum induction furnace.
[0029] (1) Add 21.77kg of pure iron, 1.57kg of ferromolybdenum, 4.31kg of nickel plate, and 6.71kg of metal chromium into the crucible of the vacuum induction furnace.
[0030] (2) First evacuate to 4Pa, and then heat it with electricity until the charge is melted.
[0031] (3) Measure the temperature after melting, and carry out refining for 3 minutes under the condition of vacuum degree <1Pa.
[0032] (4) Fill the furnace with nitrogen to 50000Pa.
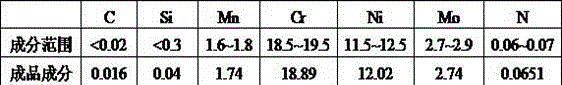
[0033] (5) Add 0.63kg of metal manganese and 0.01kg of carbon powder for alloying and sampling, and pour when the nitrogen atmosphere is maintained for 8 minutes. See Table 1 for product composition requirements and finished product composition.
[0034] Table 1 316L stainless steel composition requirements and smelted finished product composition (wt%)
[0035]
Embodiment 2
[0036] Example 2: A 500kg vacuum induction furnace was used to smelt 0Cr16Ni5Mo nitrogen-containing stainless steel.
[0037] (1) Add 386.4kg of pure iron, 2.2kg of ferromolybdenum, 27.58kg of nickel plate, and 80.73kg of metal chromium into the crucible of the vacuum induction furnace.
[0038] (2) First evacuate to 5Pa, and then heat it with electricity until the charge is melted.
[0039] (3) Measure the temperature after melting, and refine for 2.5 minutes under the condition of vacuum degree <1Pa.
[0040] (4) Fill the furnace with nitrogen to 50000Pa.
[0041] (5) Add 3.08kg of metal manganese for alloying and sampling, and pour when the nitrogen atmosphere is maintained for 9.5 minutes. See Table 2 for product composition requirements and finished product composition.
[0042] Table 2 0Cr16Ni5Mo stainless steel composition requirements and smelting finished composition (wt%)
[0043]
Embodiment 3
[0044] Example 3: Smelting X12CrMoWVNbN nitrogen-containing steel in a 50kg vacuum induction furnace.
[0045] (1) Add 38.2kg of pure iron, 0.78kg of ferromolybdenum, 0.324kg of nickel plate, 4.5kg of metal chromium, and 0.565kg of ferrotungsten into the crucible of the vacuum induction furnace.
[0046] (2) First evacuate to 5Pa, and then heat it with electricity until the charge is melted.
[0047] (3) Measure the temperature after melting, and carry out refining for 2 minutes under the condition of vacuum degree <1Pa.
[0048] (4) Fill the furnace with nitrogen to 40000Pa.
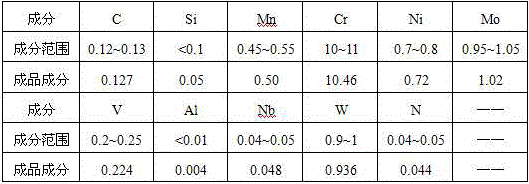
[0049] (5) Add 0.21kg of electrolytic manganese, 0.03kg of ferroniobium, and 0.17kg of ferrovanadium for alloying and sampling, and pour when the nitrogen atmosphere is kept for 5min20s. See Table 3 for product composition requirements and finished product composition.
[0050] Table 3 X12CrMoWVNbN nitrogen-containing steel composition requirements and smelted product composition (wt%)
[0051]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com