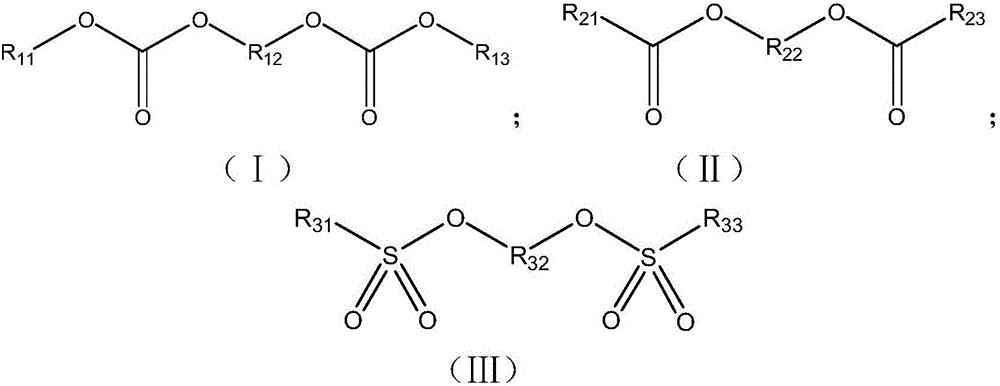
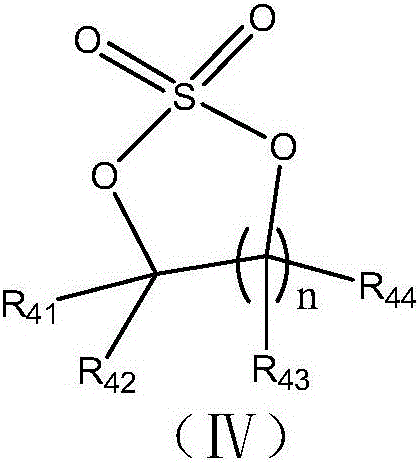
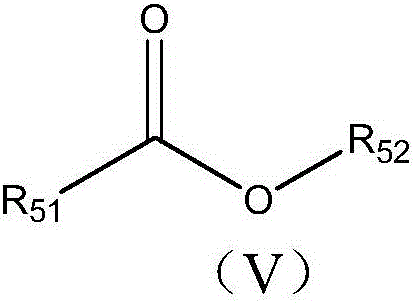
Electrolyte and lithium-ion battery comprising same
An electrolyte and lithium salt technology, applied in secondary batteries, organic electrolytes, non-aqueous electrolytes, etc., can solve problems such as low oxidation potential, deterioration of lithium-ion battery cycle performance, and intensified electrochemical reactions, so as to inhibit oxidation reactions, Improve the effect of high-rate charging performance, high-temperature storage and cycle performance improvement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0115] The preparation of embodiment 1 lithium ion battery
[0116] In Comparative Examples 1# to 11# and Examples 1 to 32, lithium-ion batteries (hereinafter referred to as batteries) were prepared according to the following method:
[0117] (1) Preparation of electrolyte
[0118] In an argon atmosphere glove box with water content <10ppm, mix the organic solvent that has been rectified, dehydrated and purified evenly, dissolve the fully dried lithium salt in the above mixed organic solvent, then add additives to the organic solvent, and mix evenly , to obtain the electrolyte. Wherein, the concentration of the lithium salt is 1 mol / L.
[0119] (2) Preparation of positive pole piece
[0120] Lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO 2 ) positive electrode active material, binder (PVDF), and conductive agent (acetylene black) are mixed according to the mass ratio of 98:1:1, N-methylpyrrolidone (NMP) solvent is added until the system becomes uniform and transparent, and the vacuum mixer i...
Embodiment 2
[0157] The electrolyte is prepared according to the method in Example 1, the difference is that the formula of the electrolyte is as shown in Table 4, wherein the organic solvent contains EC, PC, DEC and the compound shown in Formula V, and the compound shown in Formula V is shown in Table 4 As shown, the lithium salt is 1M LiPF 6 ;
[0158] Wherein, the content of the additive is the weight percentage calculated based on the total weight of the electrolyte.
[0159] Table 4:
[0160]
[0161]
[0162] Wherein, in the electrolyte solution 33-35, EC:PC:DEC:Formula V=20:20:30:30;
[0163] In the electrolyte solution 36-38, EC:PC:DEC:Formula V=20:20:20:40;
[0164] In the electrolyte solution 39-41, EC:PC:DEC:Formula V=20:15:15:50;
[0165] In electrolyte solutions 42-44, EC:PC:DEC:Formula V=20:10:10:60.
[0166] The lithium-ion battery was prepared by using the electrolyte in Table 4, and the properties of the prepared lithium-ion battery were similar to those of Exam...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com