Composting method capable of regulating microbial community structure of unculturable microorganisms
A technology of microbial flora and composting method, which is applied to the treatment of biological organic parts, organic fertilizers, fertilization devices, etc. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0020] Specific embodiment one: the composting method of this embodiment difficult to cultivate microbial flora structure regulation is carried out according to the following steps:
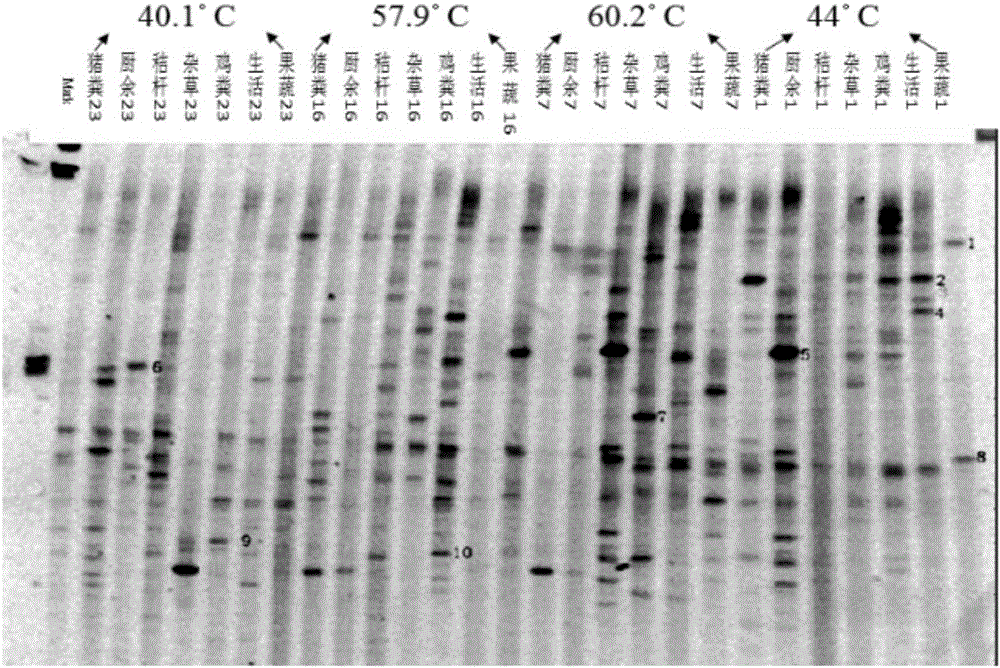
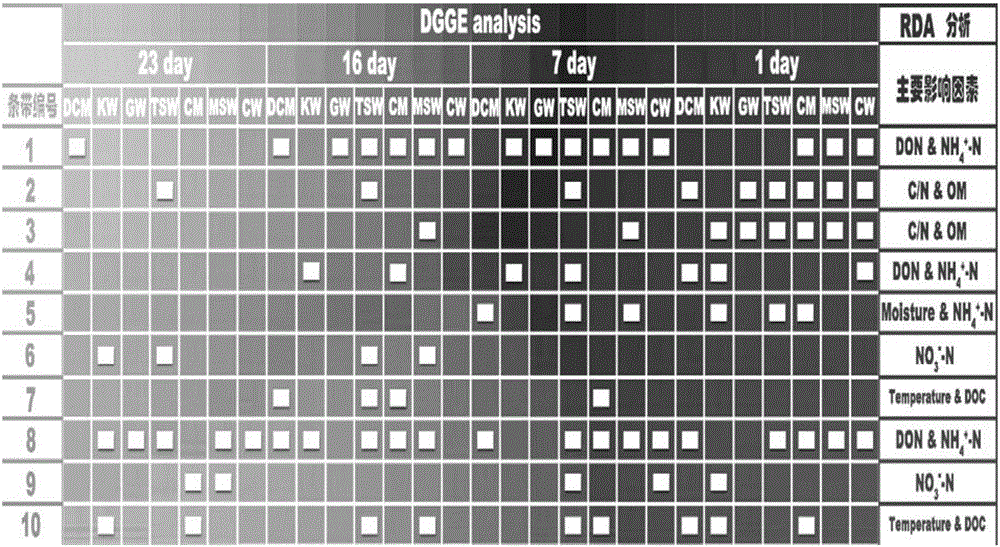
[0021] 1. Take a small amount of compost raw materials for composting, and then collect samples from the four stages of compost heating period, high temperature period, cooling period and decomposing period, and perform PCR-DGGE identification on the samples in these four stages, and then analyze the conditions of the dominant bacteria in the samples. The bands were sequenced, and the physicochemical properties of samples in different periods were obtained;
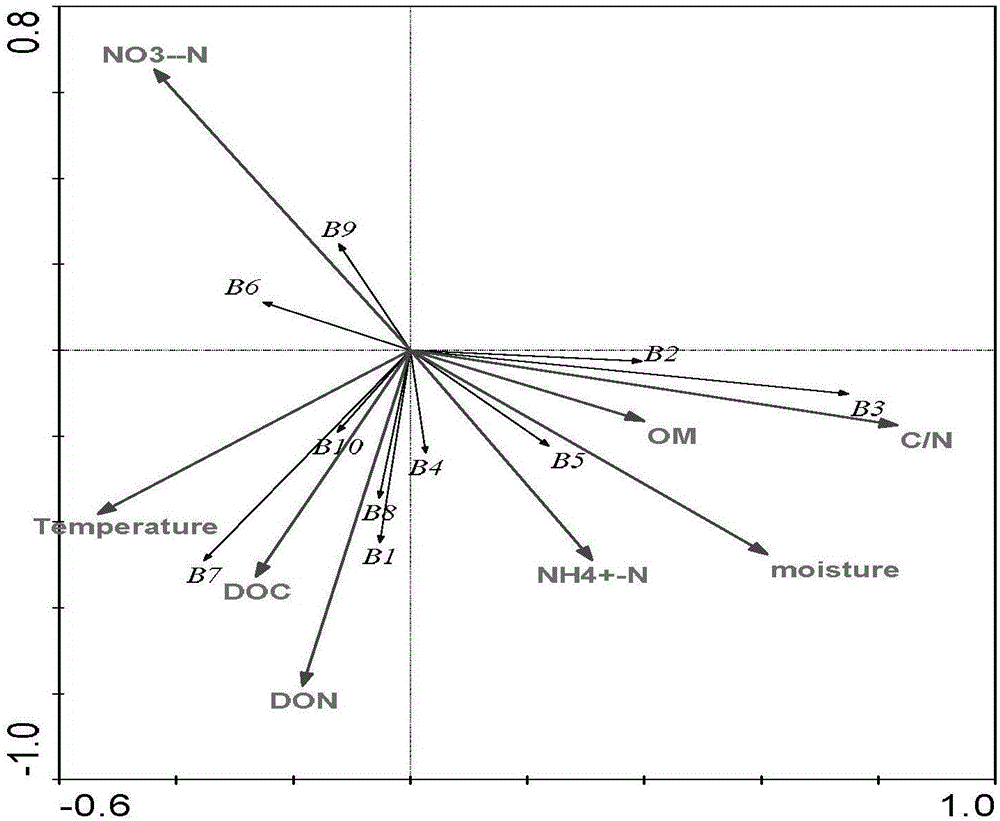
[0022] 2. Use RDA to analyze the key control factors of different bacterial flora structures, and determine the control range of key factors for different microorganisms;
[0023] 3. According to the target requirements of composting, determine the target functional strains of composting, then compost and adjust the composting parameters acc...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0026] Specific embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is that the physical and chemical properties obtained in step 1 include the carbon-to-nitrogen ratio, moisture, temperature, pH, germination index, water-soluble organic carbon, and water-soluble organic nitrogen of the sample. , ammonia nitrogen, nitrate nitrogen and organic matter content. Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0027] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or 2 is that in step 3, the carbon metabolism, nitrogen metabolism, phosphorus metabolism and humification process of the composting target functional strain are controlled by regulating the composting parameters. Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com