Cylindrical layered luneberg lens
A columnar and lens technology, which is applied in the field of electromagnetic lenses, can solve the problems of impossibility, difficult control of dielectric constant, and degradation of lens performance, and achieve the effects of stabilizing electromagnetic scattering characteristics, avoiding reflection, and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
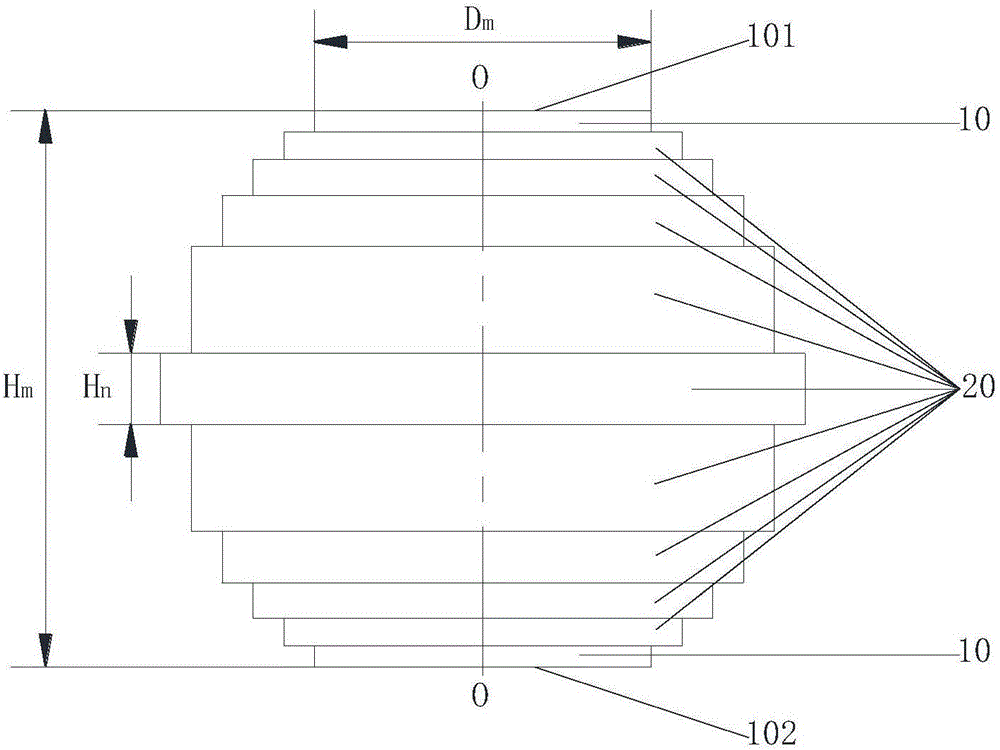
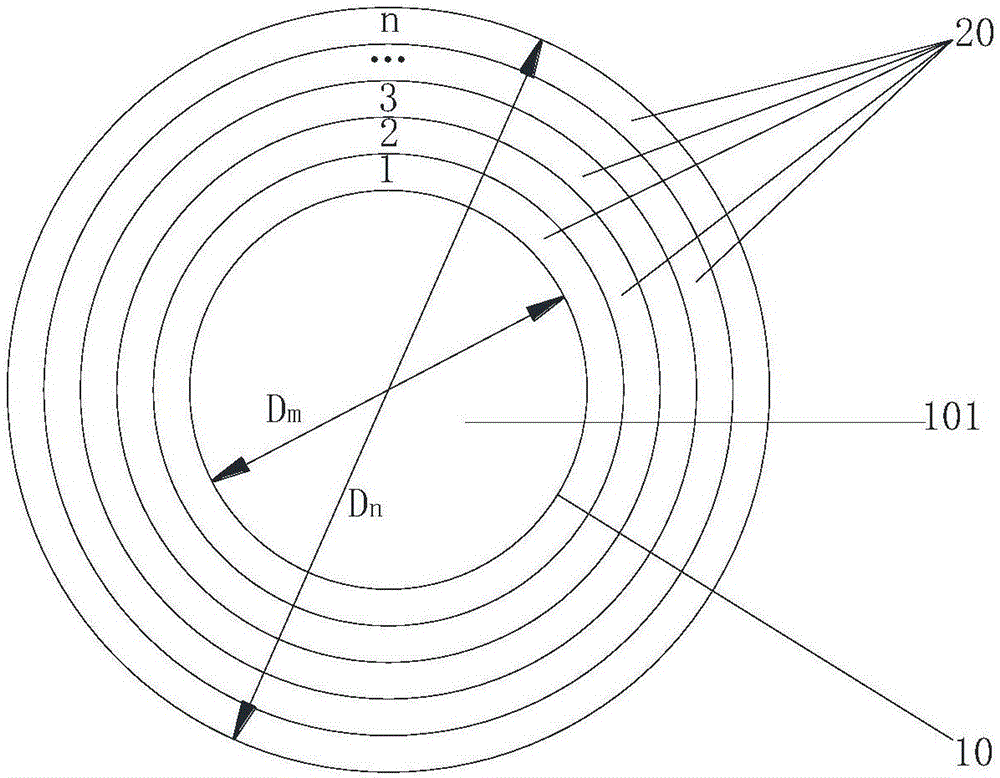
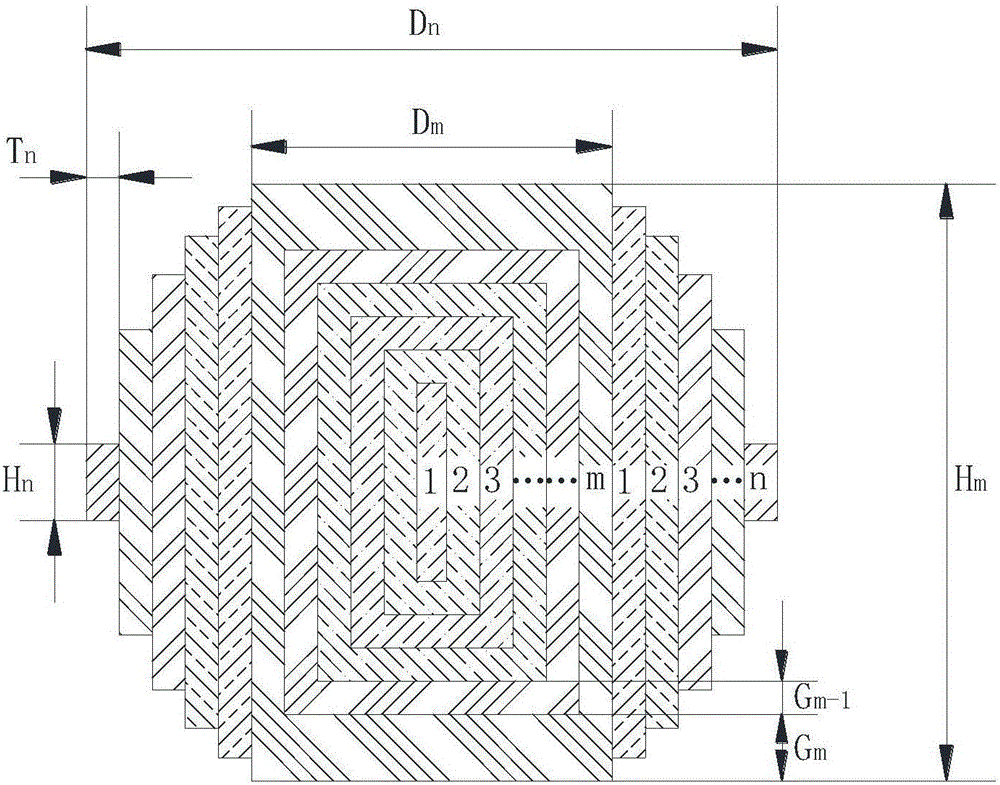
[0031] In this example, the columnar layered Lunberg lens includes two parts: the core and the cylinder, such as Figure 4 As shown, the column core in this example is composed of 7 nested cylinders, that is, the column core has a 7-layer structure, corresponding to m=7. The cylinder of this example includes 5 layers of cylinders sleeved in the middle of the column core, namely n=5. Depend on Figure 4 It can be seen that the lens in this example has a total of 12 layers from the innermost cylinder to the outermost cylinder. The radius of the innermost cylinder of the column core is 5mm (diameter is 10mm), and the radius of the subsequent outer cylinder is gradually increased to the outermost cylinder radius of 60mm (that is, Dn=120mm) according to the rule of increasing 5mm each time. In this example, both the thickness of the cylinder and the cylinder Ti are 5mm, and the maximum diameter of the lens is 120mm. In the column core of this example, the height of the innermost...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com