Preparation method for large-size hard alloy
A cemented carbide, large-size technology, applied in the field of large-size cemented carbide preparation, can solve the problems of long mold making cycle, long product production cycle, long delivery cycle, etc., so as to reduce mold occupation time and shorten production cycle. , the effect of strengthening the degree of toughness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
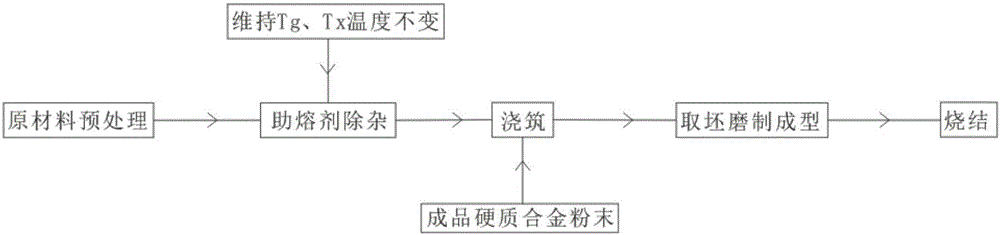
[0022] A preparation method of large-scale cemented carbide, comprising the following steps:
[0023] S1. Pretreatment of raw materials, cleaning the raw materials, removing the attached pollutants on the surface, and then using pickling to remove the oxides on the surface;
[0024] S2. Flux removes impurities, melts oxides composed of alloy components in a crucible, and then melts the raw materials that have been removed from the surface into oxides. During this process, the molten state temperature of oxides is maintained at Tg temperature, and stay the same;
[0025] S3. For pouring, after all the raw materials are dissolved, reduce the temperature of the oxide molten state to Tx temperature, the average cooling rate is 10°C / min, and stand for 2 hours, the temperature remains unchanged, remove the pure molten material in the lower layer, and melt Put the material into the water-cooled copper mold. During the pouring process, keep the temperature of the water-cooled copper ...
Embodiment 2
[0030] A preparation method of large-scale cemented carbide, comprising the following steps:
[0031] S1. Pretreatment of raw materials, cleaning the raw materials, removing the attached pollutants on the surface, and then using pickling to remove the oxides on the surface;
[0032] S2. Flux removes impurities, melts oxides composed of alloy components in a crucible, and then melts the raw materials that have been removed from the surface into oxides. During this process, the molten state temperature of oxides is maintained at Tg temperature, and stay the same;
[0033] S3, pouring, after all the raw materials are dissolved, reduce the temperature of the molten oxide to Tx temperature, the average cooling rate is 10°C / min, and let it stand for 2.5 hours, the temperature remains unchanged, remove the pure molten material in the lower layer, and melt Put the material into the water-cooled copper mold. During the pouring process, keep the temperature of the water-cooled copper m...
Embodiment 3
[0038] A preparation method of large-scale cemented carbide, comprising the following steps:
[0039] S1. Pretreatment of raw materials, cleaning the raw materials, removing the attached pollutants on the surface, and then using pickling to remove the oxides on the surface;
[0040] S2. Flux removes impurities, melts oxides composed of alloy components in a crucible, and then melts the raw materials that have been removed from the surface into oxides. During this process, the molten state temperature of oxides is maintained at Tg temperature, and stay the same;
[0041] S3, pouring, after all the raw materials are dissolved, reduce the temperature of the molten oxide to Tx temperature, the average cooling rate is 10°C / min, and let it stand for 3 hours, the temperature remains unchanged, remove the pure molten material of the lower layer, and melt Put the material into the water-cooled copper mold. During the pouring process, keep the temperature of the water-cooled copper mol...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com