Base improvement and ecological rehabilitation method for windward side embankment
A technology for ecological restoration and windward side, which is applied in the fields of basement improvement and ecological restoration of banks with windward side, basement improvement and ecological restoration of windward side embankments, which can solve the problems of embankment stability and plant restoration, and achieve excellent drainage and water permeability The effects of performance, biodiversity index improvement, and physical and chemical performance improvement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
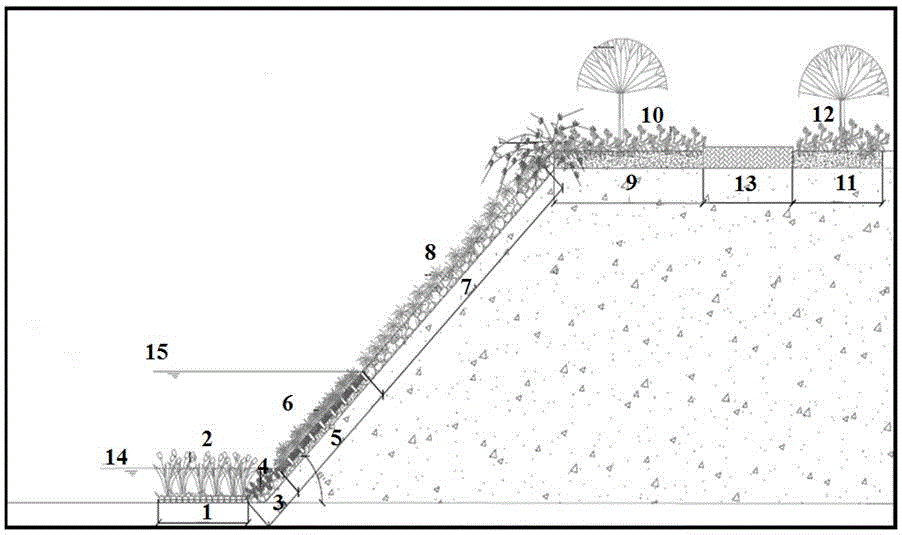
[0031] Attached below figure 1 The present invention is further described in detail.
[0032] A base improvement and ecological restoration method for a windward embankment, the steps of which are:
[0033] 1. Regional selection. The embankment (lake, reservoir, river, etc.) with strong wind and waves or strong erosion should be selected in the project implementation area, and the project implementation conditions are available near the embankment: the slope of the embankment is 15 or 20 or 25 or 30 or 35 or 40 or 45 or 50 or 55 Between degrees, there are construction vehicles (mixer trucks, transport vehicles, etc.) working sites and roads;
[0034] 2. The broken surface is leveled and compacted. Repair the slope of the embankment to achieve the purpose of leveling, and at the same time compact and reinforce the soil of the embankment to ensure the stability of the broken surface of the embankment. The slope of the embankment is preferably 1:2-1:1;
[0035] 3. Ecological ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com