Implanted completely bioresorbable blood vessel polymer support
A polymer and implantable technology, applied in the field of medical devices, can solve problems such as insufficient segmental support and stability, inability to perfectly unify technical indicators, and affect the risk of thrombosis in the stent, achieving strong passing ability and operability, Reduction of restenosis rate and good effect of endothelialization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0058] Embodiment 1 An implantable fully bioabsorbable vascular polymer stent
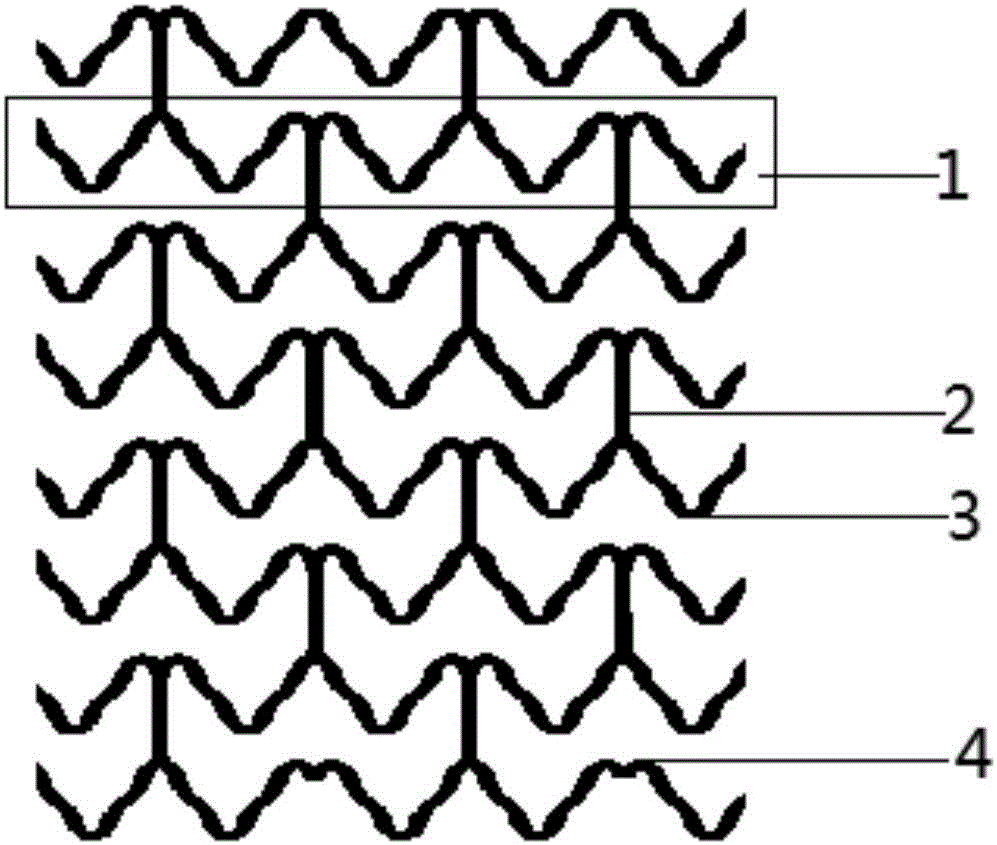
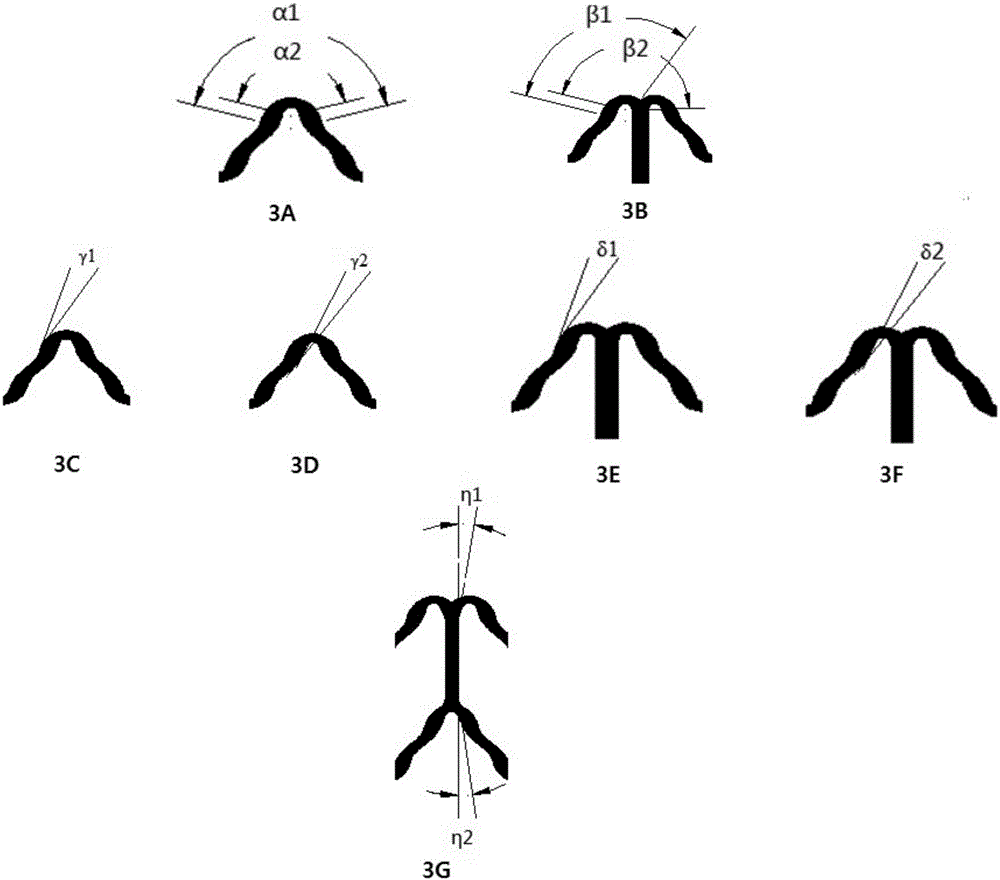
[0059] See attached figure 1 , 2 As shown in 3A-3G, an implantable fully bioabsorbable vascular polymer stent, made of polylactic acid, includes more than five ring-shaped corrugated support rods 1, and connecting rods 2 connected to the support rod 1 at intervals, The support rod 1 of the bracket is formed by alternately connecting "Ω"-shaped waves 3 and "m"-shaped waves 4, and the connection between two adjacent support rods is formed by connecting rods 2 in the "Ω"-shaped wave The top is connected with the "m"-like wave bottom.
[0060] The class "m" shaped wave 4, such as image 3 As shown in A, and "Ω" shaped wave 3, such as image 3 As shown in B, it is composed of two groups of positive "s" and inverted "s" connections, respectively as figure 2 shown.
[0061] The connecting rods between the two adjacent supporting rods are all straight rods.
[0062] This implantable fully bioabsorb...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Embodiment 2 An implantable fully bioabsorbable vascular polymer stent
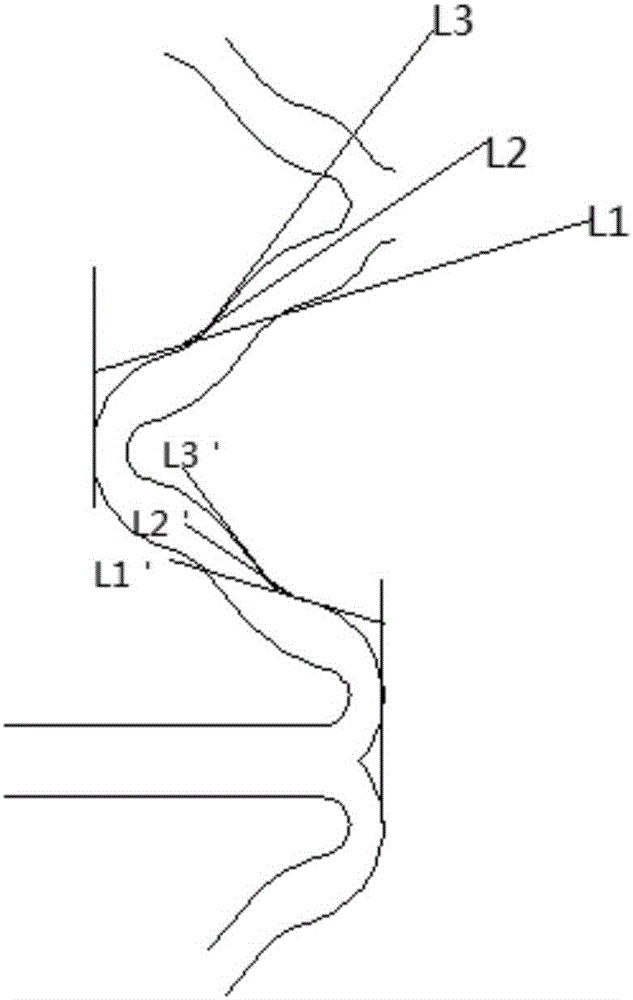
[0064] See attached figure 1 , 2As shown in 3A-3G, an implantable fully bioabsorbable vascular polymer stent includes five or more ring-shaped corrugated support rods 1, and connecting rods 2 connected to the support rod 1 at intervals, and the embodiment 1 The difference is that in this specific embodiment, the widths of the support rods and the connecting rods are different, the width of the support rods at both ends of the bracket is the thickest, and the width of the connecting rods at the two ends of the bracket is next, Then to the width of the remaining support rods, the width of the remaining connecting rods is the thinnest. Among them, the angle between the positive "s" and inverted "s" connecting segments is 5-10 degrees.
Embodiment 3
[0065] Example 3 An implantable fully bioabsorbable vascular polymer stent
[0066] See attached figure 1 , 2 As shown in 3A-3G, an implantable fully bioabsorbable vascular polymer stent includes five or more ring-shaped corrugated support rods 1, and connecting rods 2 connected to the support rod 1 at intervals, and the embodiment 1 The difference is that in this specific embodiment, the widths of the support rods and the connecting rods are different, the width of the support rods at both ends of the bracket is the thickest, and the width of the connecting rods at the two ends of the bracket is next, Then to the width of the remaining support rods, the width of the remaining connecting rods is the thinnest. Among them, the angle between the positive "s" and inverted "s" connecting segments is 40-45 degrees.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com