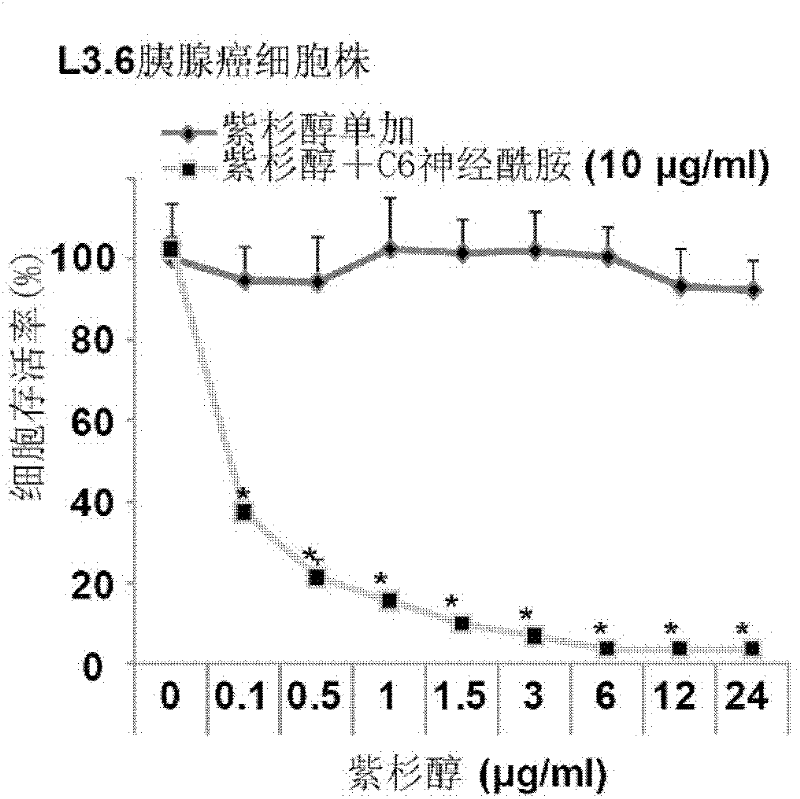
Drug-eluting stent carrying short-chain ceramide
A ceramide, short-chain technology, applied in the field of medical devices, can solve the problems of tumor cell apoptosis, large toxic and side effects, and low blood drug concentration in cancer tissue, and achieves the promotion of tumor cell apoptosis, good histocompatibility, and reduced The effect of restenosis rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] The short-chain ceramide is in the form of an implant, and the carrier used is a caprolactide / lactide copolymer, and the short-chain ceramide is directly carried on the bracket by using a rapidly degradable material such as polycaproic acid The propyl ester is made into small capsules and pasted on the stent body 1, and the cavity of the small capsules is loaded with a therapeutically effective dose of short-chain ceramides.
Embodiment 2
[0044] The short-chain ceramide is in the form of an implant, and the carrier used is polylactic acid, which is adhered to the biodegradable coating through polylactic acid pressure-sensitive adhesive. If necessary, in order to prevent the explosive release of the drug in the initial stage and control the release rate more effectively, a dense controlled release layer is arranged outside the drug coating. This coating consists of the non-degradable material polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE).
Embodiment 3
[0046] Thoroughly mix short-chain ceramide, polymer material polycaprolactone, and solvent chloroform to prepare a drug polymer solution, wherein the mass volume concentration of short-chain ceramide and polymer material polycaprolactone in the solvent is 0.1 μg respectively / ml and 0.5 μg / ml; the drug polymer solution is coated on the surface of the stent body 1 by spraying and dipping methods, and then the stent body 1 is placed in a vacuum oven at 30°C, and vacuum-dried for 24 hours. In order to prevent the explosive release of the drug at the initial stage, a slow-release layer with a thickness of 0.1 μm is formed on the surface of the drug film layer by vapor phase deposition, and dried at 20-90°C for 1-5 days to prepare A stent with drug sustained-release properties is formed, and the composition of the sustained-release layer is a derivative of parylene.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com