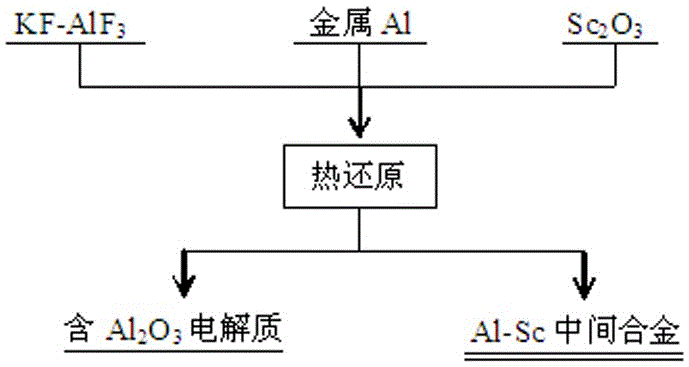
Method for preparing aluminum-scandium intermediate alloy by thermally reducing aluminum in elpasolite fused salt
A technology of master alloy and potassium cryolite, applied in the field of materials, can solve the problems of low solubility, high alloy cost, serious alloy segregation, etc., and achieve the effects of simple process, reduced production cost, and shortened preparation process.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] anhydrous KF and anhydrous AlF 3 Mixed to make molten salt, in which KF and AlF 3 The molar ratio is 1.5;
[0032] Will Sc 2 o 3 Add to molten salt and mix well to make mixed salt, Sc 2 o 3 The addition amount is KF and AlF 3 3% of the total mass;
[0033] Place the mixed salt in a corundum crucible and heat it up to 720°C, keep it warm for 60 minutes to completely melt the material and form a molten mixed salt;
[0034] Add the reducing agent metal aluminum to the molten mixed salt, the dosage is according to the metal aluminum and Sc 2 o 3 The molar ratio is 40:1, and then thermal reduction is carried out at 720°C for 3 hours. After the reduction, the alloy part and the electrolyte part are separated, and the alloy part is condensed to form an aluminum-scandium master alloy; the mass of scandium in the aluminum-scandium master alloy The percentage is 2.1%; the components of the electrolyte part include KF, AlF 3 , AlO produced by the reaction 3 and unreacte...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Method is with embodiment 1, and difference is:
[0037] (1) KF and AlF 3 The molar ratio is 1.8;
[0038] (2) Sc 2 o 3 The addition amount is KF and AlF 3 9% of the total mass;
[0039] (3) Heat the mixed salt to 1020°C and keep it warm for 30 minutes;
[0040] (4) Add the amount of metal aluminum according to metal aluminum and Sc 2 o 3 The molar ratio is 35:1, thermal reduction is carried out at 1020°C, and the reduction time is 0.5h; the mass percentage of scandium in the aluminum-scandium master alloy is 2.33%.
Embodiment 3
[0042] Method is with embodiment 1, and difference is:
[0043] (1) KF and AlF 3 The molar ratio is 2.0;
[0044] (2) Sc 2 o 3 The addition amount is KF and AlF 3 4% of the total mass;
[0045] (3) Heat the mixed salt to 800°C and keep it warm for 50 minutes;
[0046] (4) Add the amount of metal aluminum according to metal aluminum and Sc 2 o 3 The molar ratio is 30:1, thermal reduction is carried out at 800°C, and the reduction time is 2.5h; the mass percentage of scandium in the aluminum-scandium master alloy is 2.47%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com