A method for infrared degradation of marine sulfated polysaccharides
A sulfated polysaccharide and marine technology, applied in the field of biological preparations, achieves the effects of simple equipment, reduced purification process, and low production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
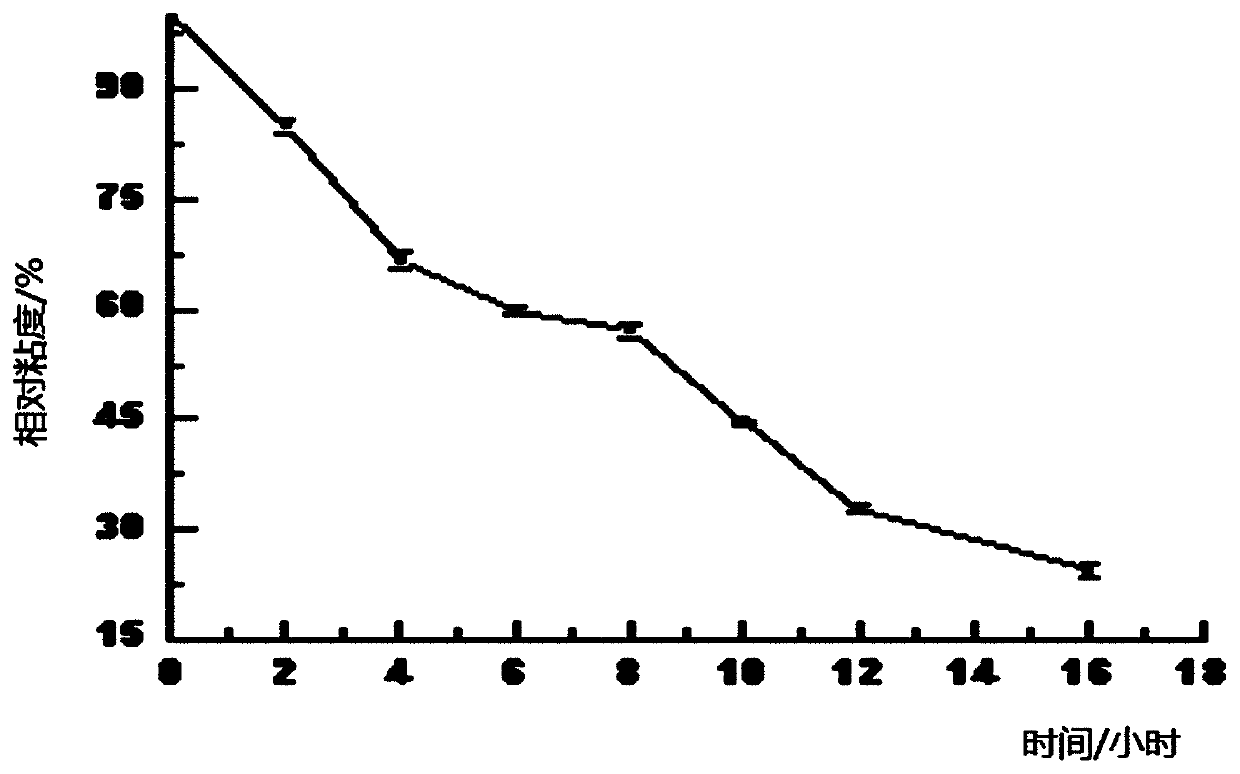
[0019] Spread 100g of kelp fucoidan dry powder on a clean stainless steel tray with a thickness of 0.1cm, and then put it into a drying box equipped with a 2200w infrared lamp. The height of the infrared lamp from the kelp fucoidan powder is 10cm. Turn on the switch of the infrared drying oven and heat for 2h, 4h, 6h, 8h, 10h, 12h, 14h, 16h, and the relative viscosity values are 84.3%, 65.2%, 61.3%, 57.6%, 44.8%, 36.2%, 21.4% Low molecular weight kelp fucoidan dry powder. Such as figure 1 shown.
Embodiment 2
[0021] Spread 100g of sea cucumber fucoidan dry powder on a clean stainless steel tray with a thickness of 0.15cm, and then put it into a drying box equipped with a 2200w infrared lamp. The height of the infrared lamp from the sea cucumber fucoidan powder is 20cm. Turn on the switch of the infrared drying oven and heat for 2h, 4h, 6h, 8h, 10h, 12h, 14h, 16h, and the relative viscosity values are 81.7%, 59.2%, 55.3%, 50.2%, 42.1%, 33.5%, 18.2% Low molecular weight sea cucumber fucoidan dry powder.
Embodiment 3
[0023] Spread 100g of shark chondroitin sulfate dry powder on a clean stainless steel tray with a thickness of 0.2cm, and then put it into a drying box equipped with a 2200w infrared lamp. The height of the infrared lamp from the shark chondroitin sulfate powder is 30cm. Turn on the infrared Drying box switch, heating 2h, 4h, 6h, 8h, 10h, 12h, 14h, 16h, that is, the relative viscosity values are 85.6%, 70.1%, 65.2%, 60.4%, 46.3%, 39.9%, 26.4% low Molecular shark chondroitin sulfate dry powder.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com