Touch sensor substrate, touch panel, display device, and method for manufacturing touch sensor substrate
A touch sensor and touch panel technology, applied to instruments, conductive layers on insulating carriers, input/output processes of data processing, etc. The effect of visibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
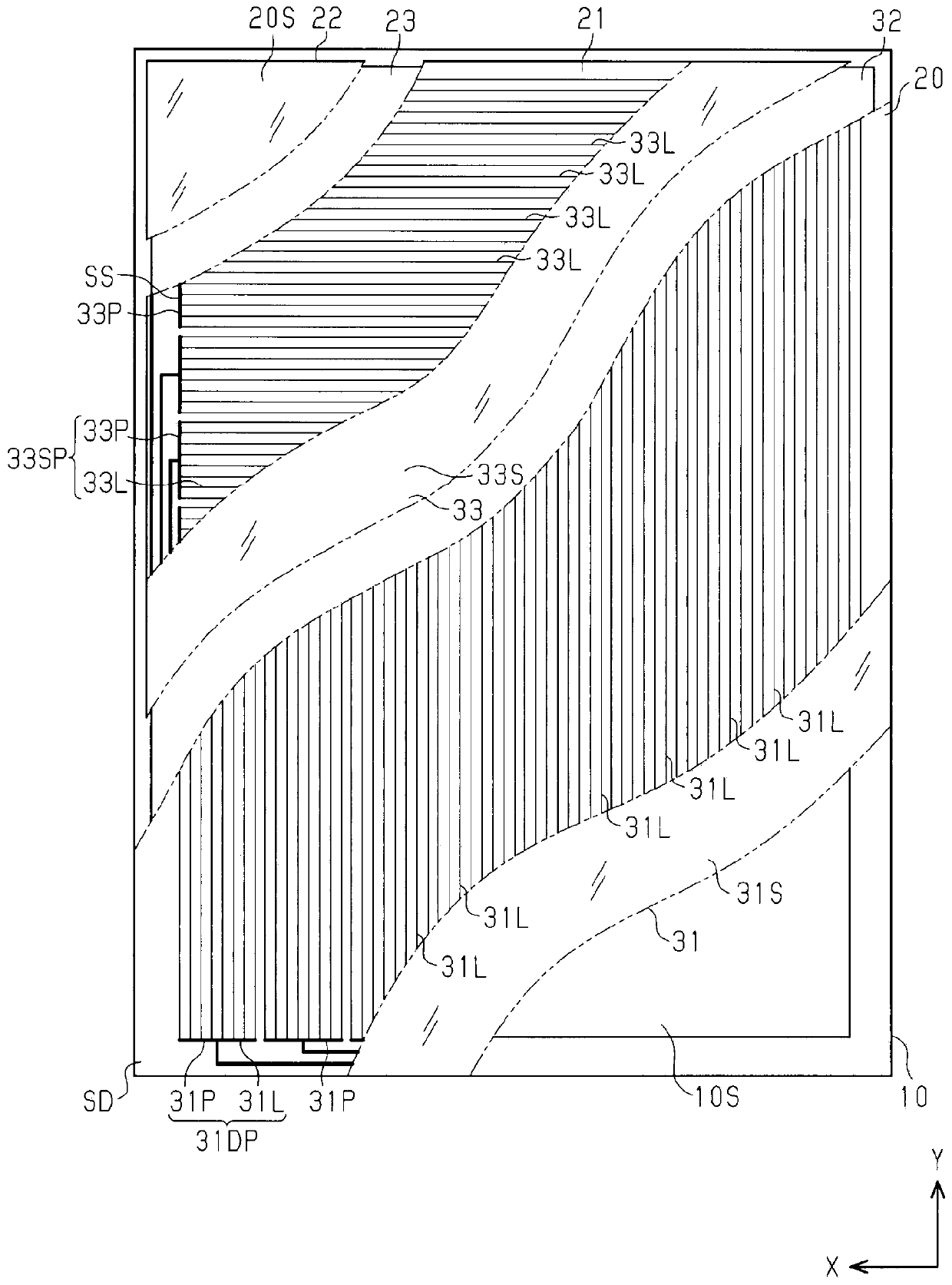
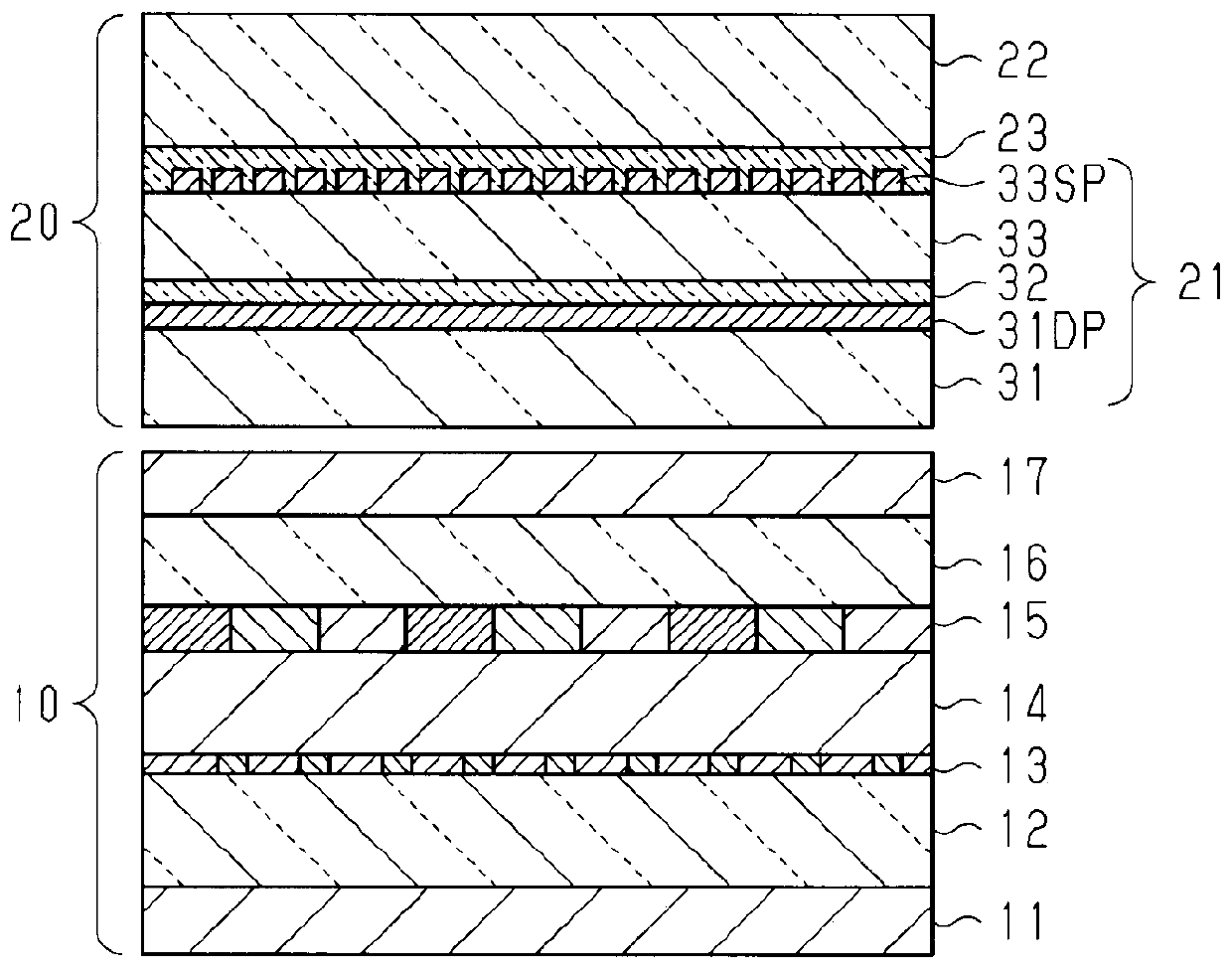
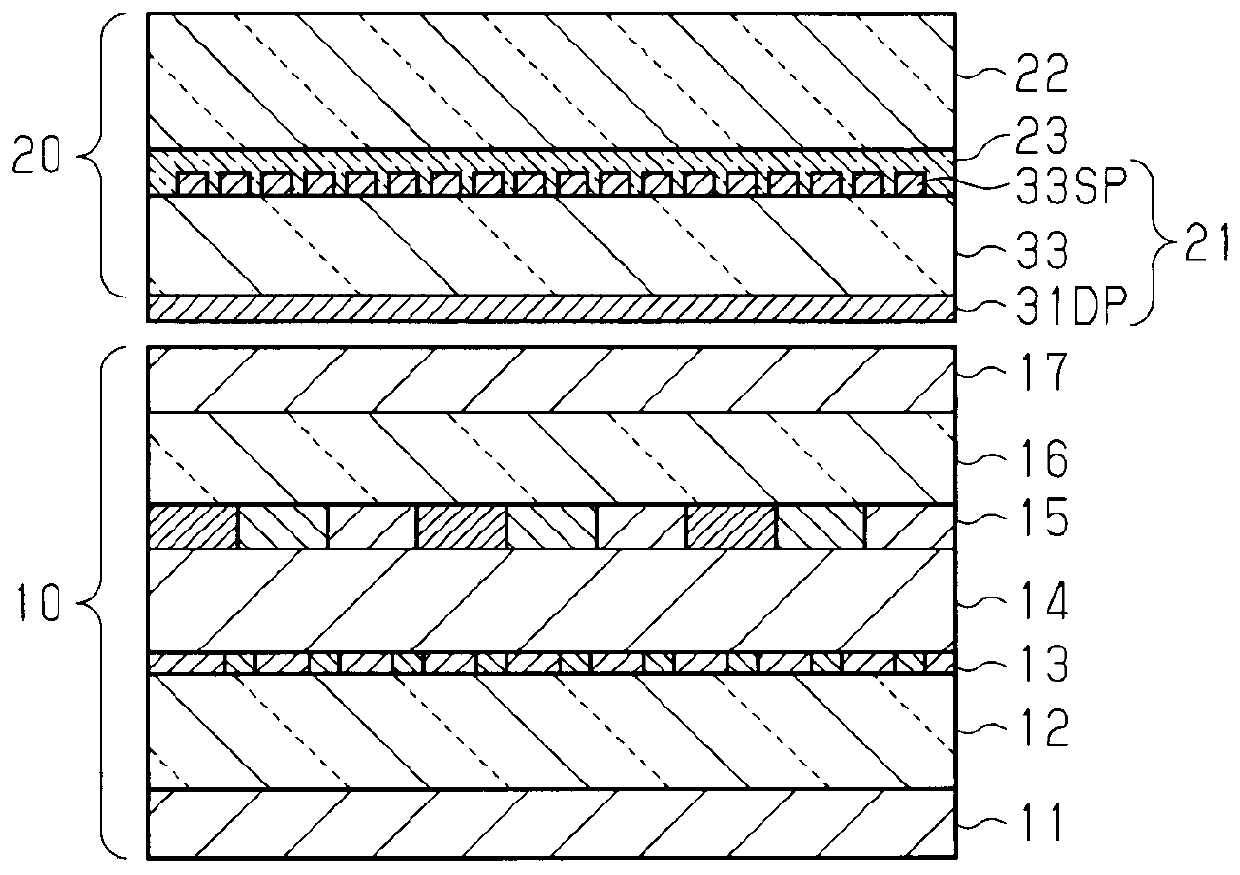
[0117] refer to Figure 12 (a) to (e) illustrate an embodiment of a method for manufacturing a touch sensor substrate. In addition, since the method of forming the first electrode 31DP is basically the same as the method of forming the second electrode 33SP, an example of obtaining a touch sensor substrate by forming the second electrode 33SP on the base material on which the second electrode 33SP is formed will be described below. in addition, Figure 12 In , an example of using PET with electrolytic copper foil bonded on one side and fabricating electrode groups arranged in stripes on PET by applying photolithography is described. However, the film formation method of the electrode pattern constituting the electrode group is not limited to foil paste.
[0118] like Figure 12 As shown in (a), a PET sheet with a thickness of 50 μm was used as the substrate.
[0119] like Figure 12 As shown in (b), an electrolytic copper foil 33R having a thickness of 3 μm was laminated ...
Embodiment 2
[0126] The blackening process of Example 1 was replaced with a substitution blackening process, and the conditions other than that were the same as Example 1, and the electrode which has the blackening layer BL of Example 2 was obtained. Specifically, copper on the surface of the copper electrode is substituted with palladium (Pd) to allow adhesion. At this time, the PET sheet on which the electrode pattern was formed was dipped in a hydrochloric acid solution containing Pd in a range of 100 ppm to 500 ppm. Furthermore, when the color tone of the electrode pattern is changed to blue, the reflectance is less than 20% in the visible region (400nm to 780nm), and the surface resistivity is suppressed to 1Ω / □ or less. At this time, the thickness of the blackened layer BL is also about 0.2 μm. From this result, it can also be seen that from the viewpoint of reducing the increase in the resistance value of the electrode, the treatment time for performing the sulfurization treatmen...
Embodiment 3
[0133] The blackening treatment in Example 1 was changed to metal plating (Ni, Cr) treatment, and the conditions other than that were the same as in Example 1, and an electrode having a blackened layer BL in Example 3 was obtained. According to the electrode obtained by metal plating (Ni, Cr) treatment, compared with the electrode without blackening treatment, the reflectance in the visible region (400nm or more and 780nm or less) can be suppressed. As in Example 2, both the reflectance of less than 20% and the surface resistivity of 1Ω / □ or less are satisfied.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com