Method for high-efficiency extraction of extracellular DNA in sediments
A sediment and high-efficiency technology, applied in the fields of environmental science and bioengineering, to achieve the effect of strong practicability and high degree of reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Embodiment 1: the extraction of extracellular DNA in the sediment sample;
[0027] Step 1: Construction of extracellular DNA internal standard gene;
[0028] Section 1.1: Construction of extracellular DNA internal standard gene cloning vector;
[0029] The CESA9 gene in Arabidopsis thaliana was amplified by PCR and recovered by gel cutting. Take 0.5-4 μl PCR and 1 μlpEASY-T1 cloning vector and mix gently, and react at room temperature for 5 minutes. After the reaction, place the centrifuge tube on ice;
[0030] Section 1.2: Amplification of extracellular DNA internal standard gene
[0031] Add the ligation product to 50 μl of competent E.coli DH5α cells, heat shock in a water bath at 42°C for 30 seconds, and immediately place on ice for 2 minutes; add 250 μl of LB medium equilibrated to room temperature, and incubate at 200 rpm at 37°C for 1 hour; take 8 μl 500mM IPTG and 40μl 20mg / ml X-gal were mixed, evenly spread on the prepared plate, and placed in a 37°C incubato...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Embodiment 2: the extraction efficiency of microbial extracellular DNA in the PCR test sediment;
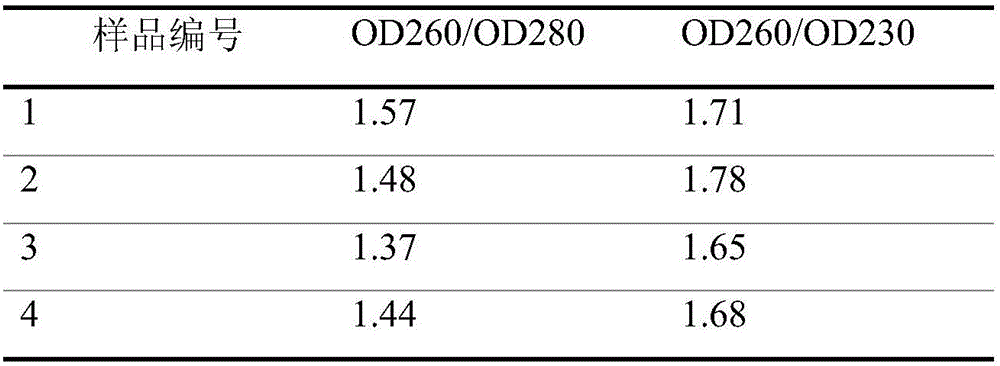
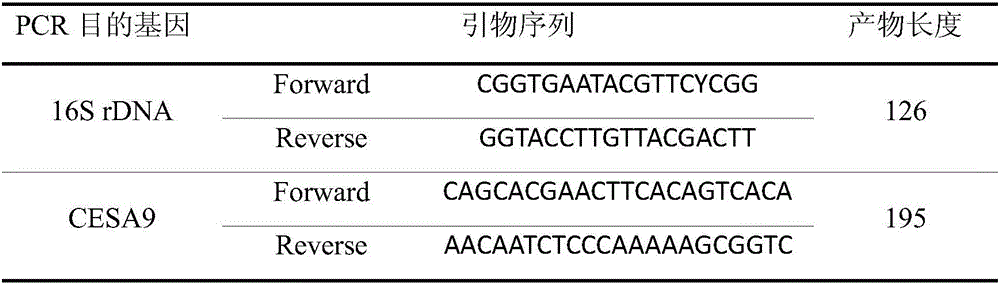
[0047] (1) Target gene primer sequence
[0048]
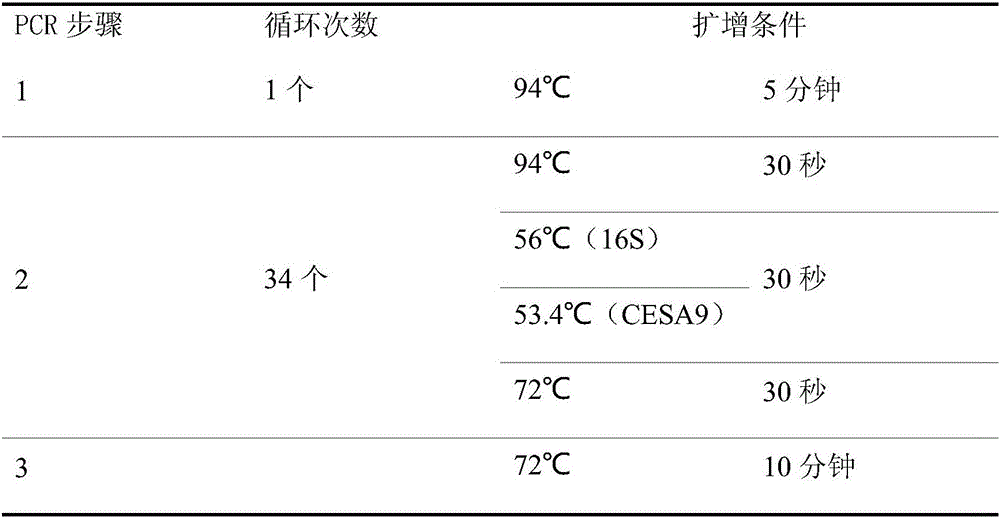
[0049] (2) Qualitative PCR reaction program
[0050]
[0051] (3) Fluorescence real-time quantitative PCR reaction
[0052]
[0053] (4) Qualitative PCR reaction system
[0054]
[0055] (5) Quantitative PCR reaction system
[0056]
[0057] Table 2: Detection of extraction efficiency of microbial extracellular DNA in sediment samples
[0058]
[0059] Using the method described in Example 2, it can be detected that the extraction efficiencies of microbial extracellular DNA in sediment samples are all higher than 44%, and the highest can reach 57%. Therefore, the present invention is suitable for extracting microbial extracellular DNA in sediment samples. In addition, the scope of application of the present invention not only includes sediments, but also the quality and extraction efficiency of DNA ex...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com