Novel electronic tag production process
A technology of electronic tags and production technology, which is applied in the direction of recording carriers used in machines, instruments, computer parts, etc., can solve the problems of RFID technology application range limitation, label chip and antenna disconnection, epoxy resin damage, etc., to meet the requirements of large The effect of mass production, remarkable effect, and ingenious design ideas
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
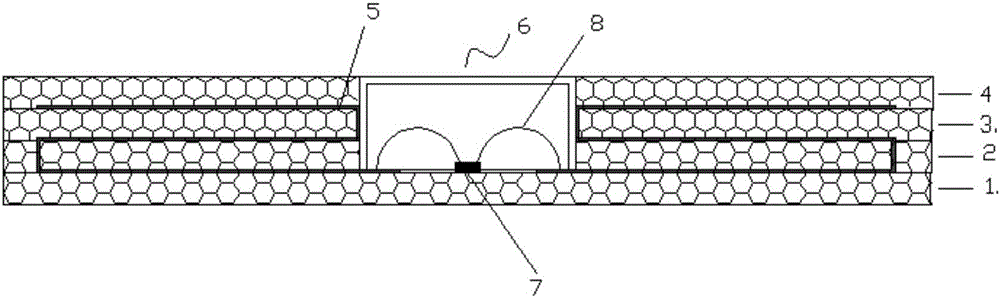
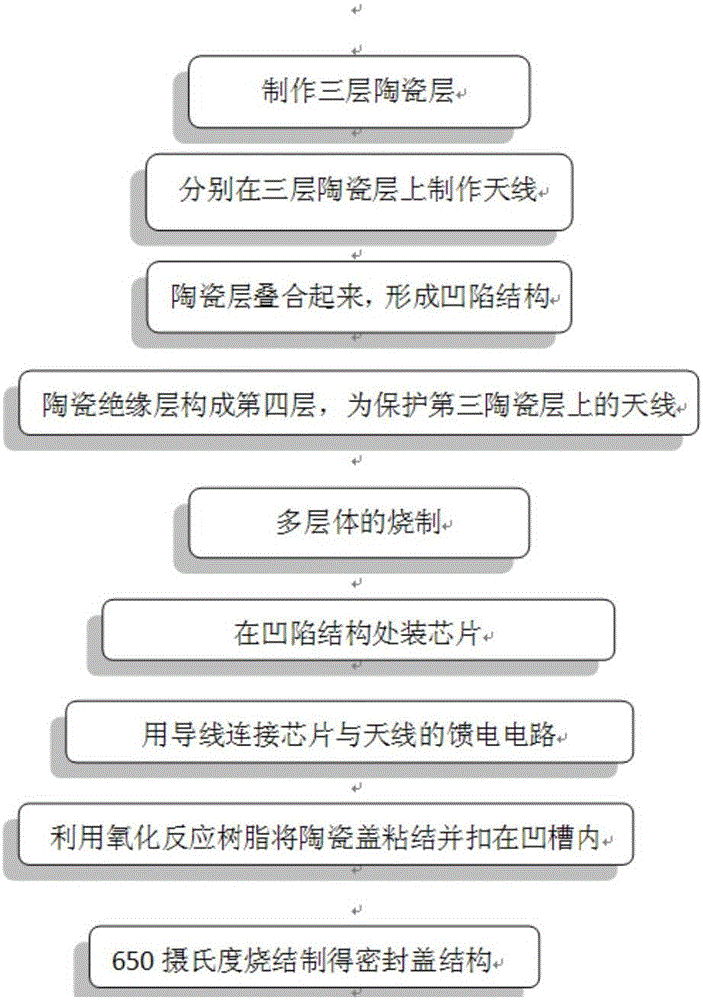
[0024] Such as figure 1 , image 3 As shown, the specific production process of ceramic RFID is as follows:
[0025] 1) Make three ceramic layers
[0026] 2) Make the antenna on the ceramic layer respectively
[0027] 3) The multilayer body with groove structure composed of three layers of ceramic layer, antenna and ceramic insulating layer is fired into the antenna substrate
[0028] 4) Put the IC chip into the groove structure of the antenna substrate, and use conventional prior art methods to bind the IC chip to the feed antenna circuit of the antenna in the groove
[0029] 5) Buckle the cover of the ceramic material on the groove structure of the substrate, and the contact part is pre-coated with oxidation reaction glue
[0030] 6) High temperature firing into RFID
Embodiment 2
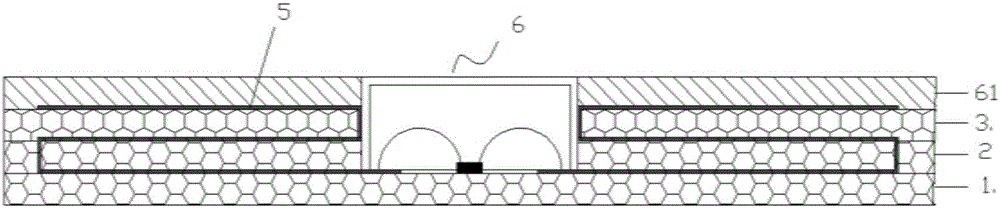
[0032] This embodiment 2 is an alternative to embodiment 1, and the final product is as figure 2 shown. refer to image 3 The flow shown in this embodiment is adjusted to:
[0033] The specific production process of ceramic RFID is as follows:
[0034] 1) Make three ceramic layers
[0035] 2) Make the antenna on the ceramic layer respectively
[0036] 3) The multilayer body with groove structure composed of ceramic layer and antenna is fired into the antenna substrate
[0037] 4) Put the IC chip into the groove structure of the antenna substrate, and use conventional prior art methods to bind the IC chip to the feed antenna circuit of the antenna in the groove
[0038] 5) Buckle the cover 6 of ceramic material on the groove structure of the substrate, the outer part of the cover 6 has a ceramic edge structure, and the contact with the substrate is pre-coated with oxidation reaction glue
[0039] 6) Firing into RFID at high temperature to obtain the whole integrated cera...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com