Method for preparing CdS/MIL-53(Fe) visible-light-induced photocatalyst
A catalyst, visible light technology, applied in the field of photocatalytic material preparation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
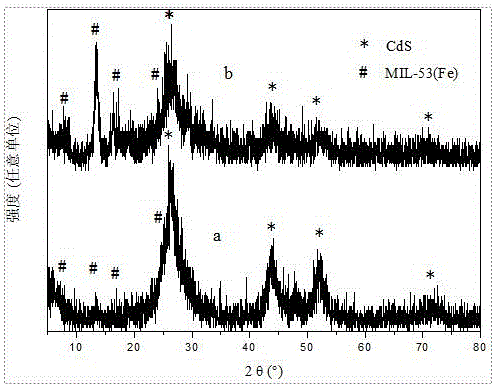
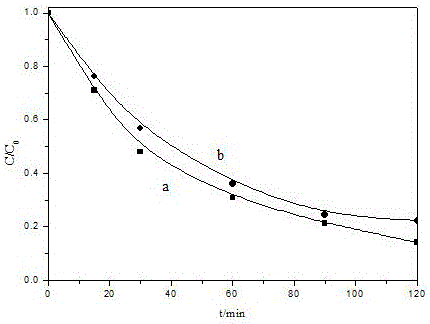
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] The concrete steps of this embodiment are as follows:
[0035] In this embodiment, the preparation method of CdS / MIL-53(Fe) visible light catalyst is to use ferric chloride, terephthalic acid and N,N-dimethylformamide as raw materials, and adopt the solvothermal method Preparation of MIL-53 (Fe) material; then using the obtained MIL-53 (Fe) and cadmium acetate, thioacetamide, polyvinylpyrrolidone and ethylene glycol as raw materials, the solvothermal method was used to prepare CdS / MIL-53 (Fe ) composite material. Its technological process is: weigh the FeCl of 10 mmol 3 ·6H 2 O and 10 mmol of terephthalic acid were dissolved in 50 mL of N,N-dimethylformamide reagent, and stirred continuously at room temperature to fully dissolve ferric chloride and terephthalic acid; the resulting mixture was Move it into a 100 mL reaction kettle, put the reaction kettle in an oven at 150°C, and react for 12 hours; after cooling to room temperature, centrifuge, wash with double disti...
Embodiment 2
[0039] The concrete steps of this embodiment are as follows:
[0040] In this embodiment, the preparation method of CdS / MIL-53(Fe) visible light catalyst is to use ferric chloride, terephthalic acid and N,N-dimethylformamide as raw materials, and adopt the solvothermal method Preparation of MIL-53 (Fe) material; then using the obtained MIL-53 (Fe) and cadmium acetate, thioacetamide, polyvinylpyrrolidone and ethylene glycol as raw materials, the solvothermal method was used to prepare CdS / MIL-53 (Fe ) composite material. Its technological process is: weigh the FeCl of 10 mmol 3 ·6H 2 O and 10 mmol of terephthalic acid were dissolved in 50 mL of N,N-dimethylformamide reagent, and stirred continuously at room temperature to fully dissolve ferric chloride and terephthalic acid; the resulting mixture was Move it into a 100 mL reaction kettle, put the reaction kettle in an oven at 150°C, and react for 12 hours; after cooling to room temperature, centrifuge, wash with double disti...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com